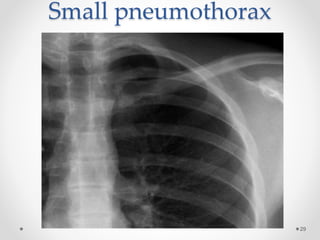
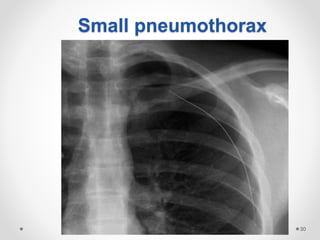
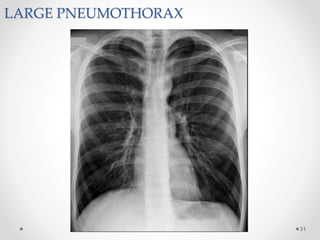
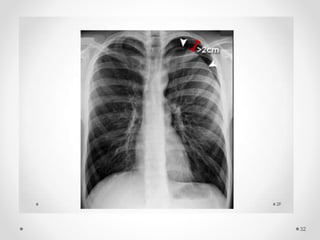
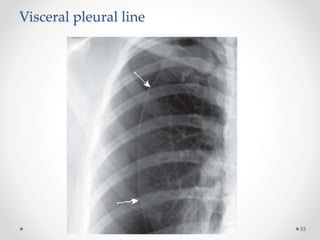
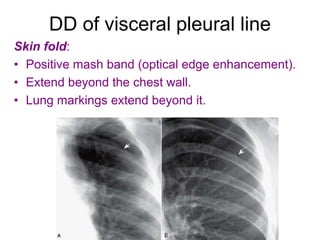
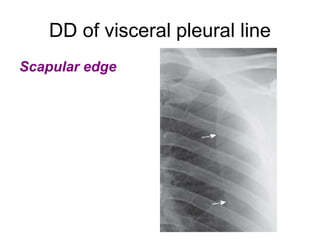
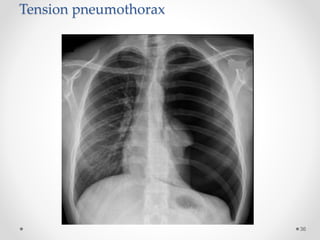
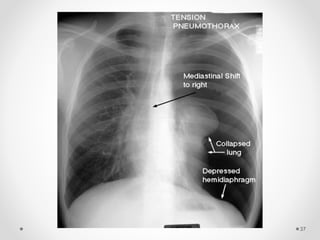
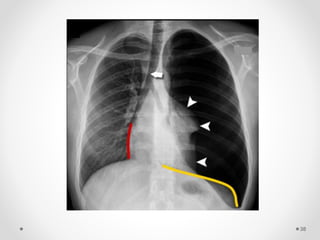
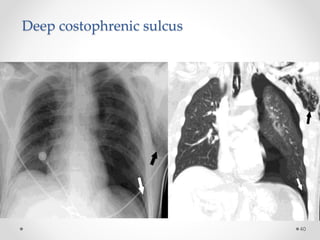
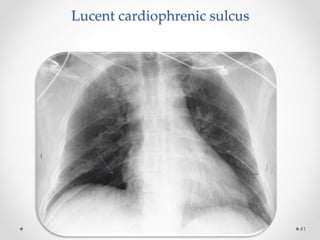
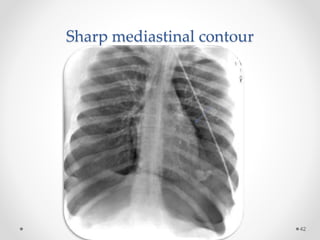
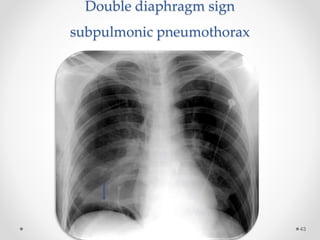
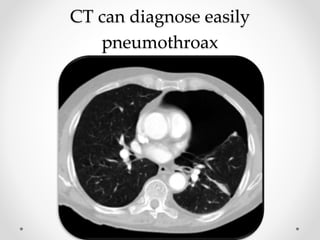
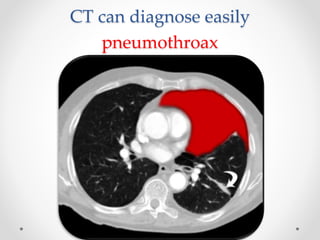
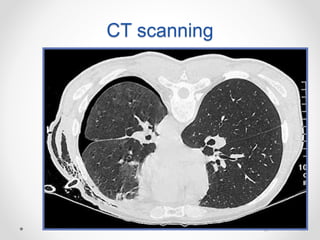
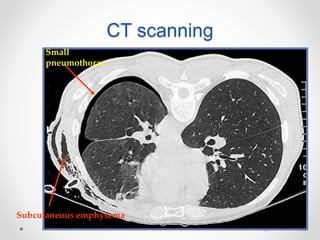
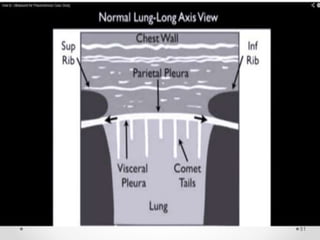
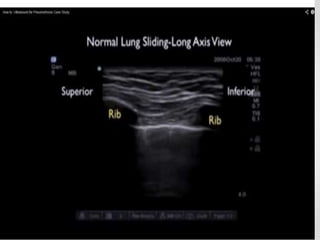
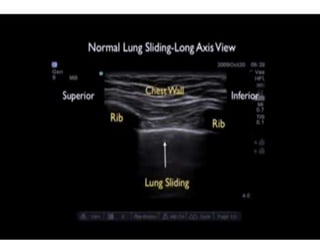
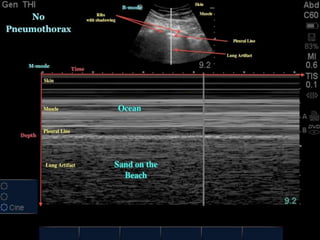
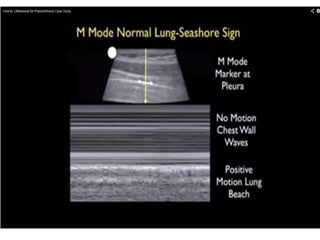
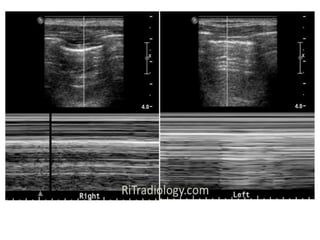
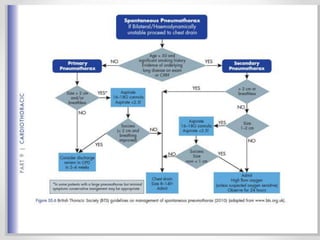
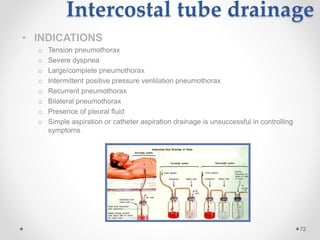
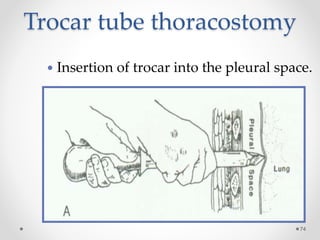
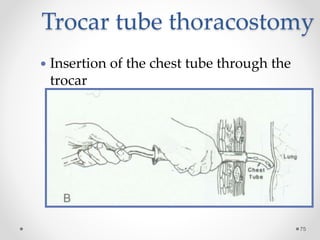
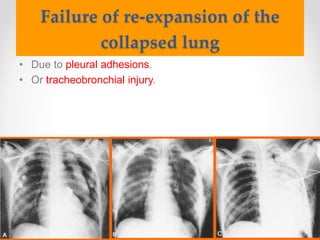
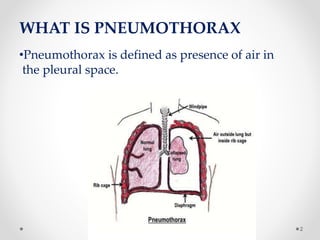
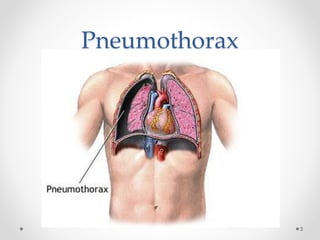
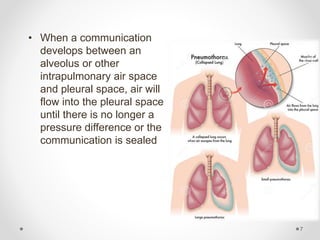
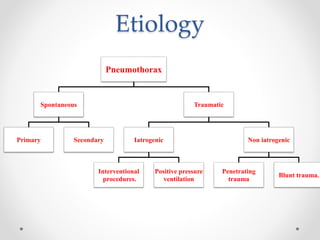
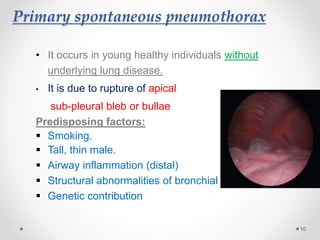
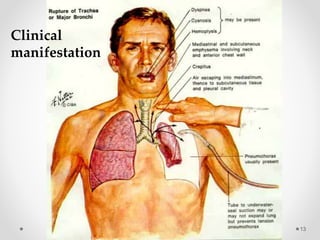
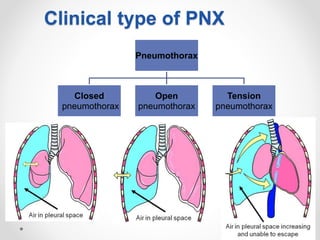
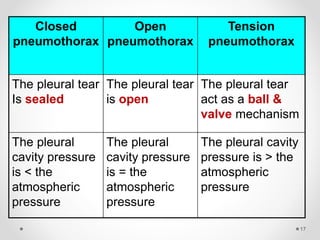
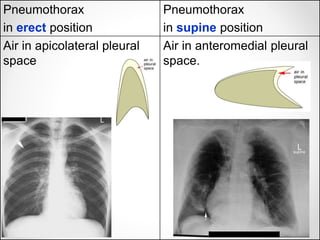
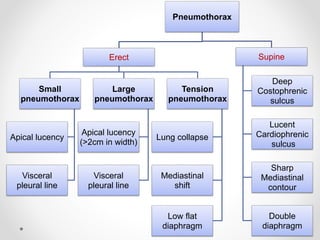
The document discusses pneumothorax, including its definition, pathophysiology, etiology, clinical manifestations, investigations, and management. Pneumothorax is defined as the presence of air in the pleural space. It can occur spontaneously due to ruptured blebs or bullae, or due to trauma. Clinical manifestations include dyspnea, chest pain, and decreased breath sounds on examination. Chest x-ray and CT scan are used to diagnose and characterize pneumothorax. Management involves oxygen therapy, needle aspiration, chest tube drainage, and chemical pleurodesis to promote lung re-expansion and prevent recurrence.













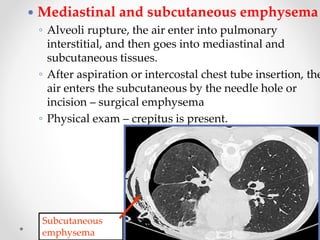
![26
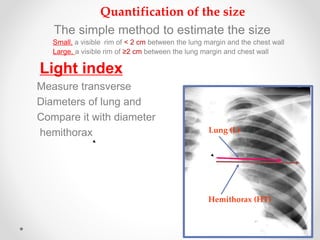
Estimation of pneumothorax volume
Light equation
pneumothorax%=(1-
L3/HT3) 100
Kircher equation
pneumothorax%
Thorax area-lung area
Thorax area
Collins equation
4.2+[4.7(A+B+C)]
100
Hemithorax (HT)
Lung (L)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pneumothorax-ramdhancomlete-170629184045/85/Pneumothorax-26-320.jpg)