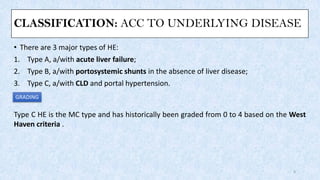
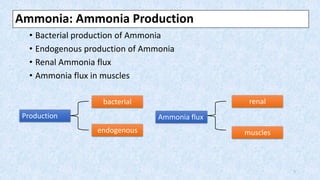
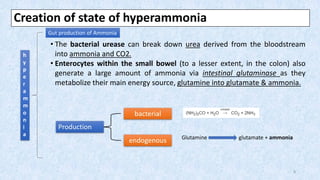
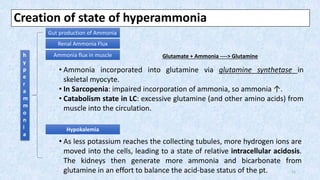
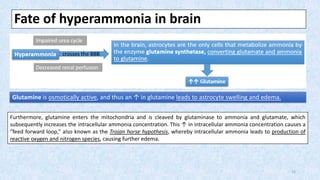
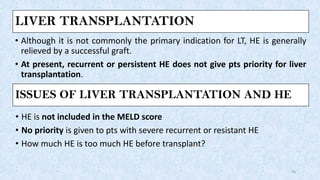
Hepatic encephalopathy is a brain dysfunction caused by liver failure or portal-systemic shunting. It ranges from mild subclinical alterations to coma. Type C hepatic encephalopathy, associated with chronic liver disease and portal hypertension, is the most common type. Management involves identifying and treating precipitating factors like infections, along with therapies to reduce ammonia like non-absorbable disaccharides (lactulose, lactitol), antibiotics (rifaximin), probiotics, and dietary changes. Resistant cases may require more invasive procedures like TIPS or liver transplantation.