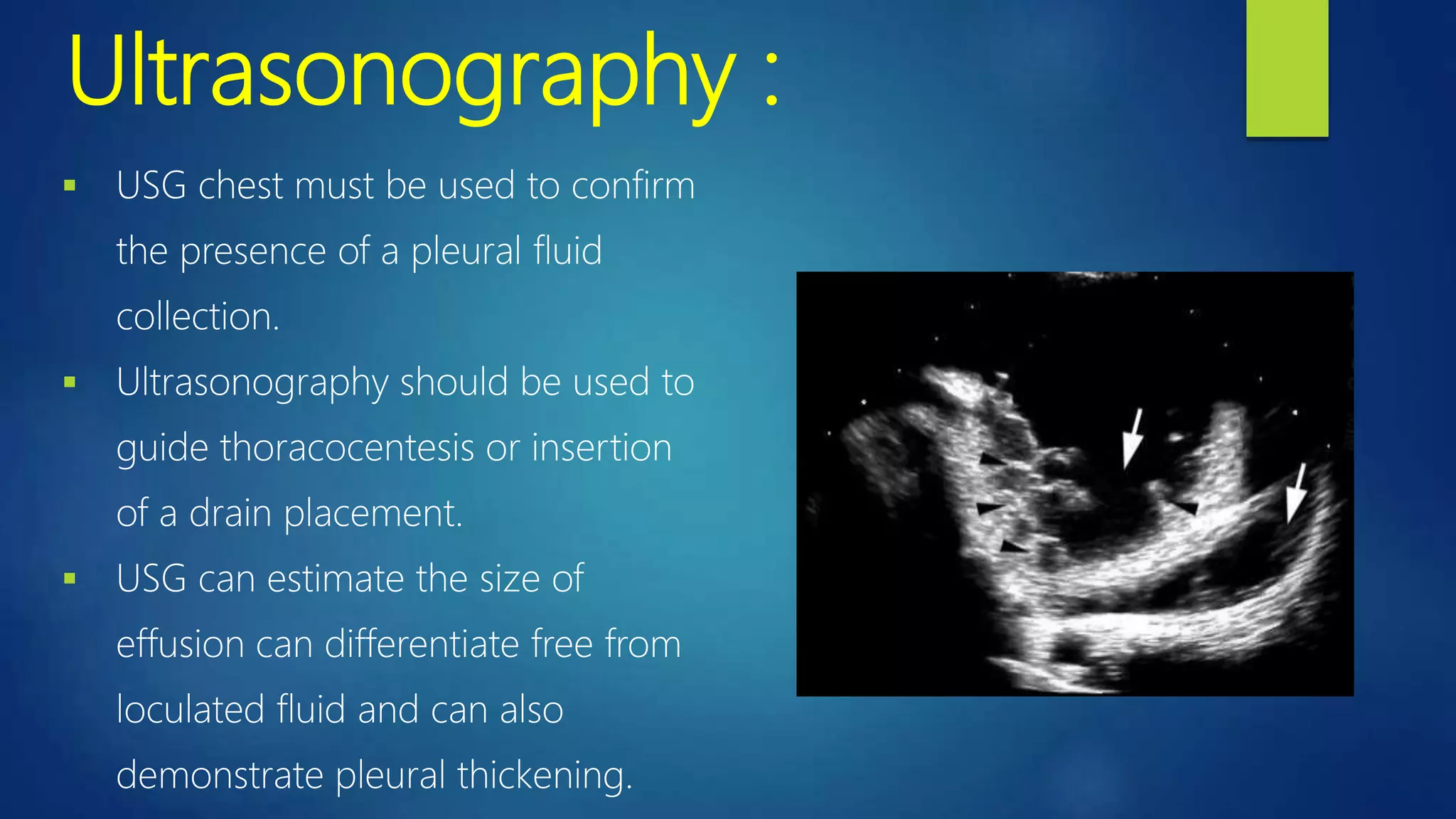
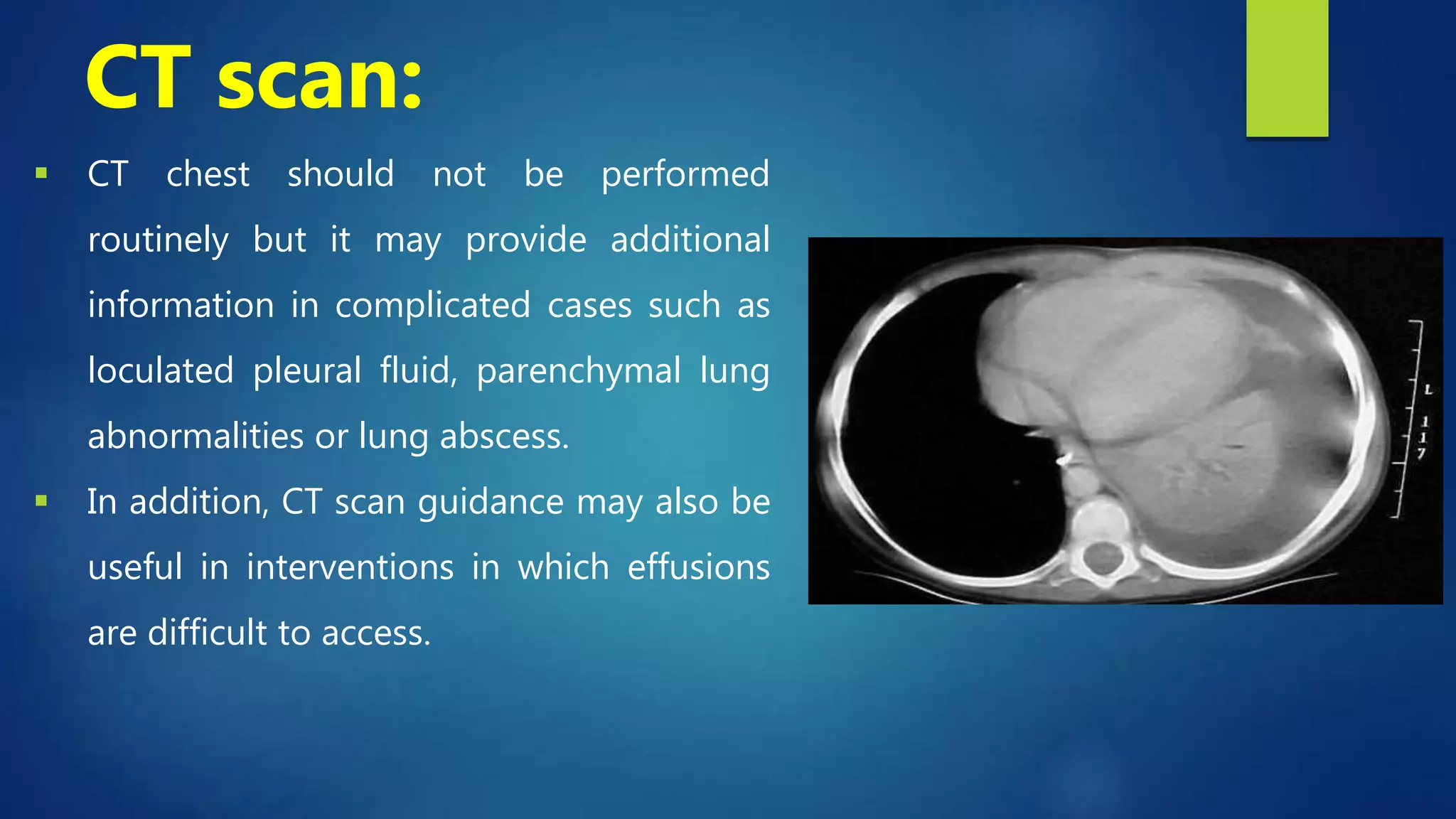
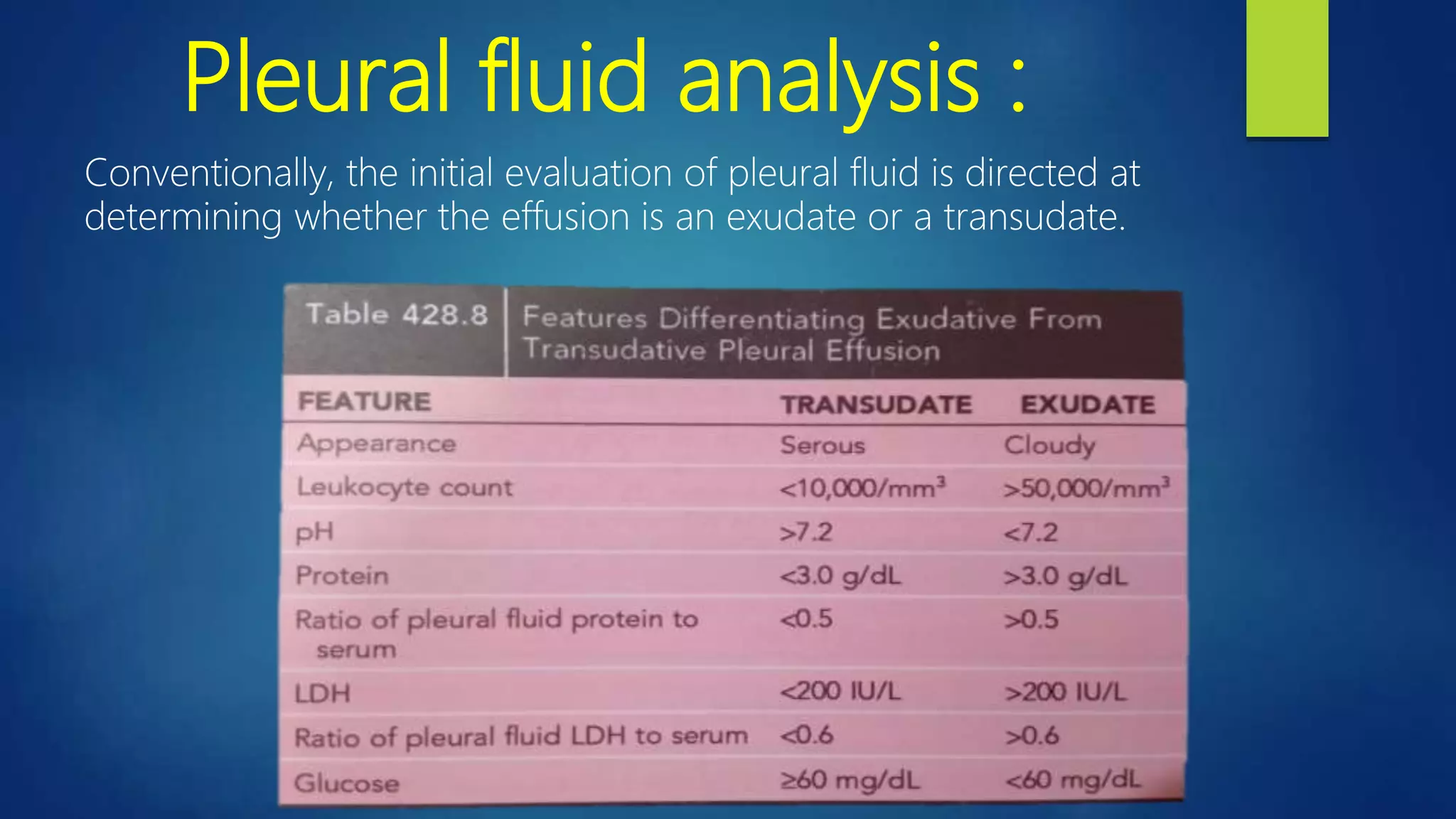
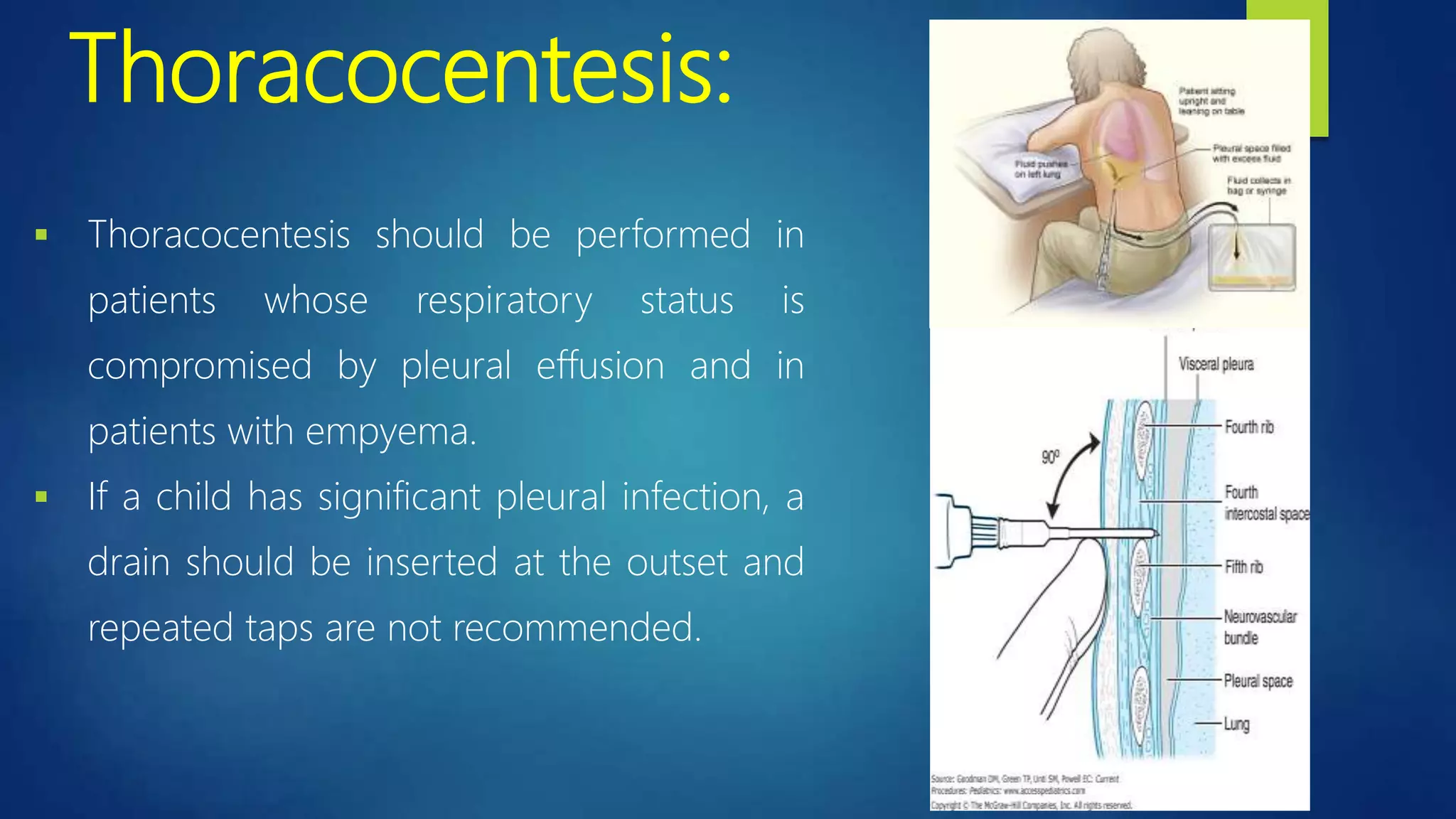
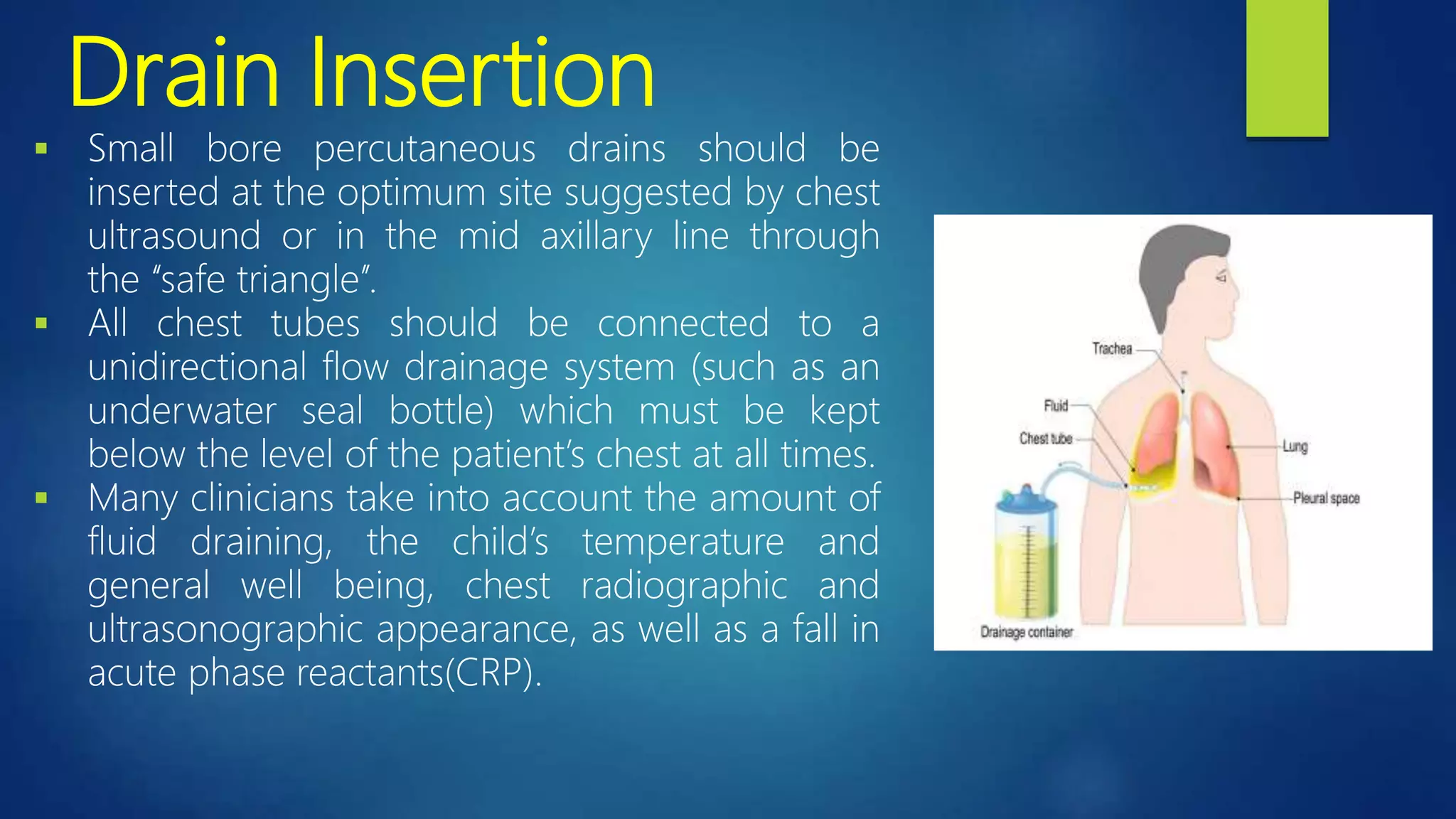
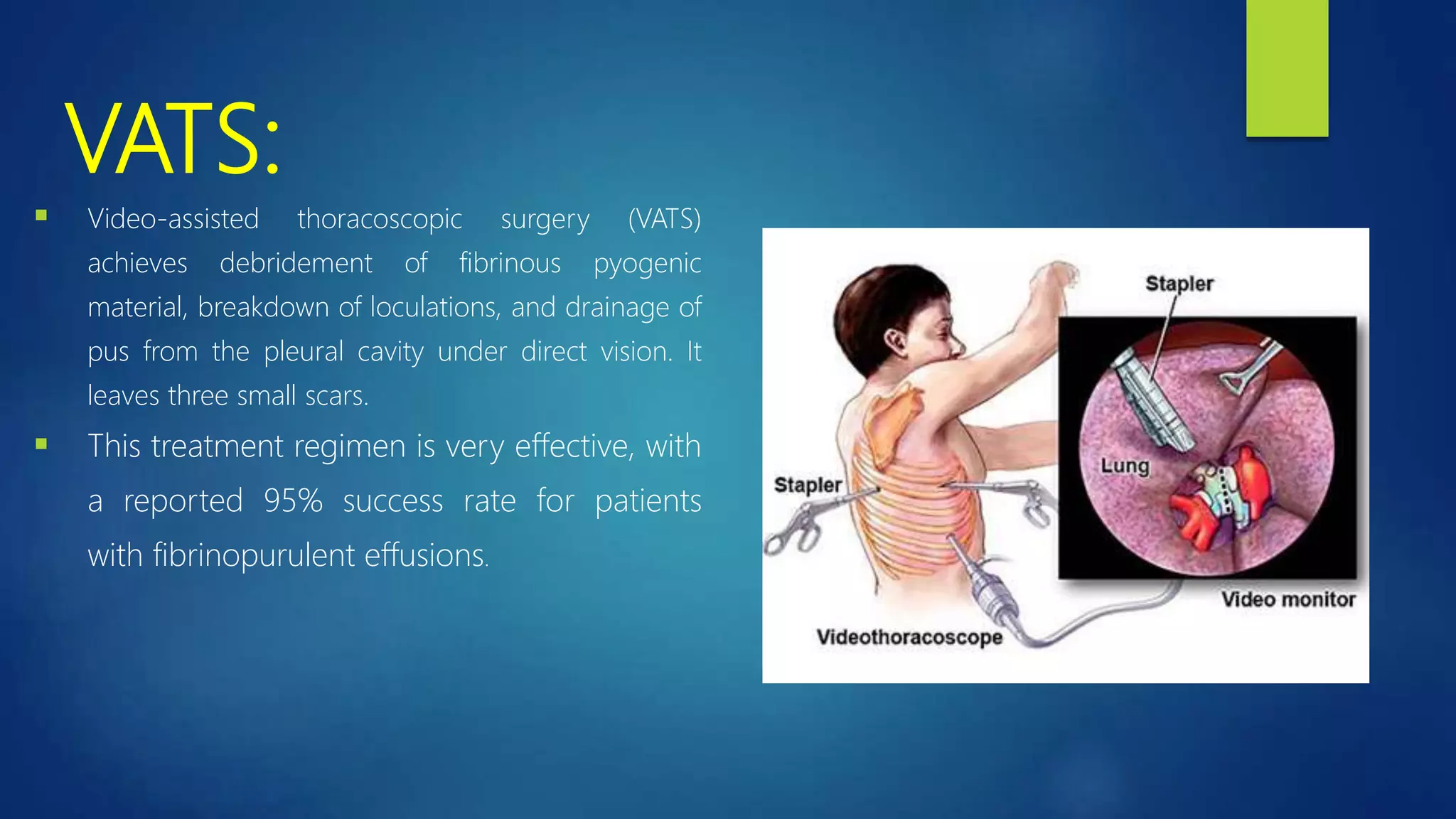
This document provides information on empyema, which is pus accumulation in the pleural space. It discusses the definition, epidemiology, etiology, stages, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, investigations, and treatment options. Empyema is usually secondary to acute bacterial pneumonia and progresses through exudative, fibrinopurulent, and organizing stages. Diagnosis involves imaging, pleural fluid analysis, and blood tests. Treatment includes antibiotics, thoracocentesis or drain insertion, intrapleural fibrinolytics, and potentially surgery like VATS. Prognosis is generally excellent with adequate treatment.