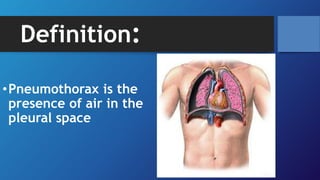
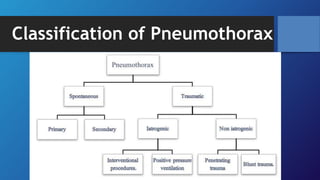
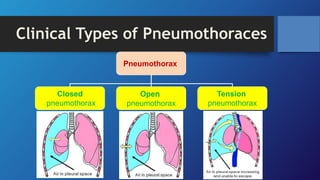
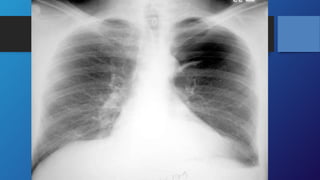
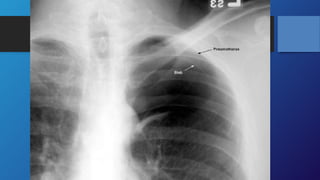
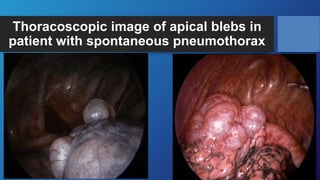
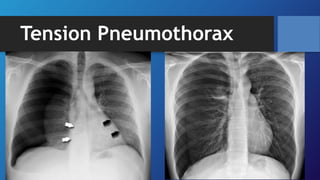
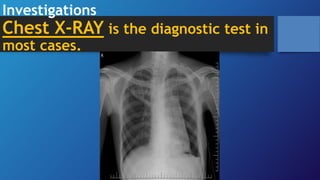
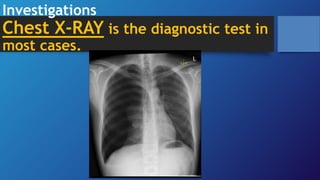
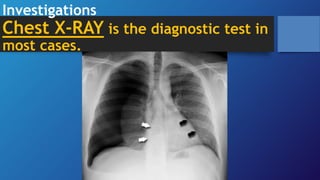
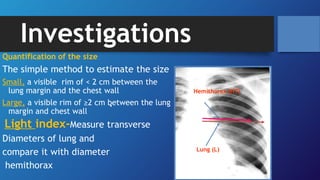
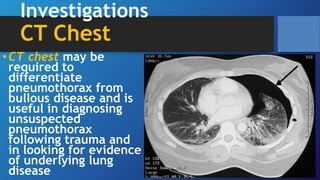
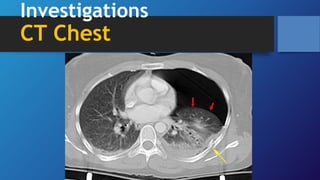
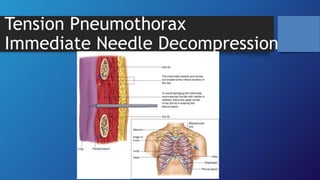
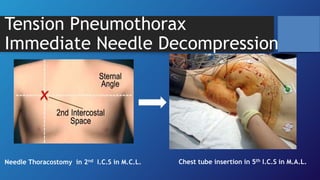
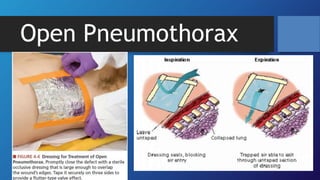
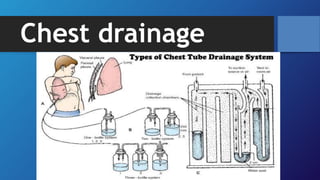
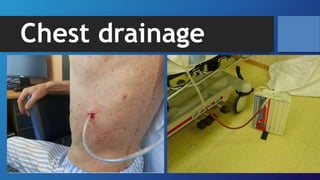
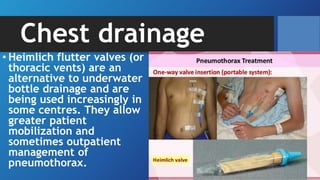
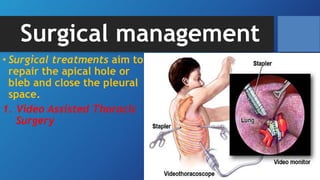
Pneumothorax is the presence of air in the pleural space. It can be classified as closed, open, or tension pneumothorax. The annual incidence is around 9 per 100,000 people. Risk factors include being a tall, thin male aged 20-40 who smokes cigarettes. Symptoms include chest pain and breathlessness. Chest x-ray is used for diagnosis and can classify pneumothorax as small or large based on rim size. Needle decompression is immediately needed for tension pneumothorax. Oxygen, aspiration, chest drain insertion, and surgery are treatment options depending on the severity of the case.