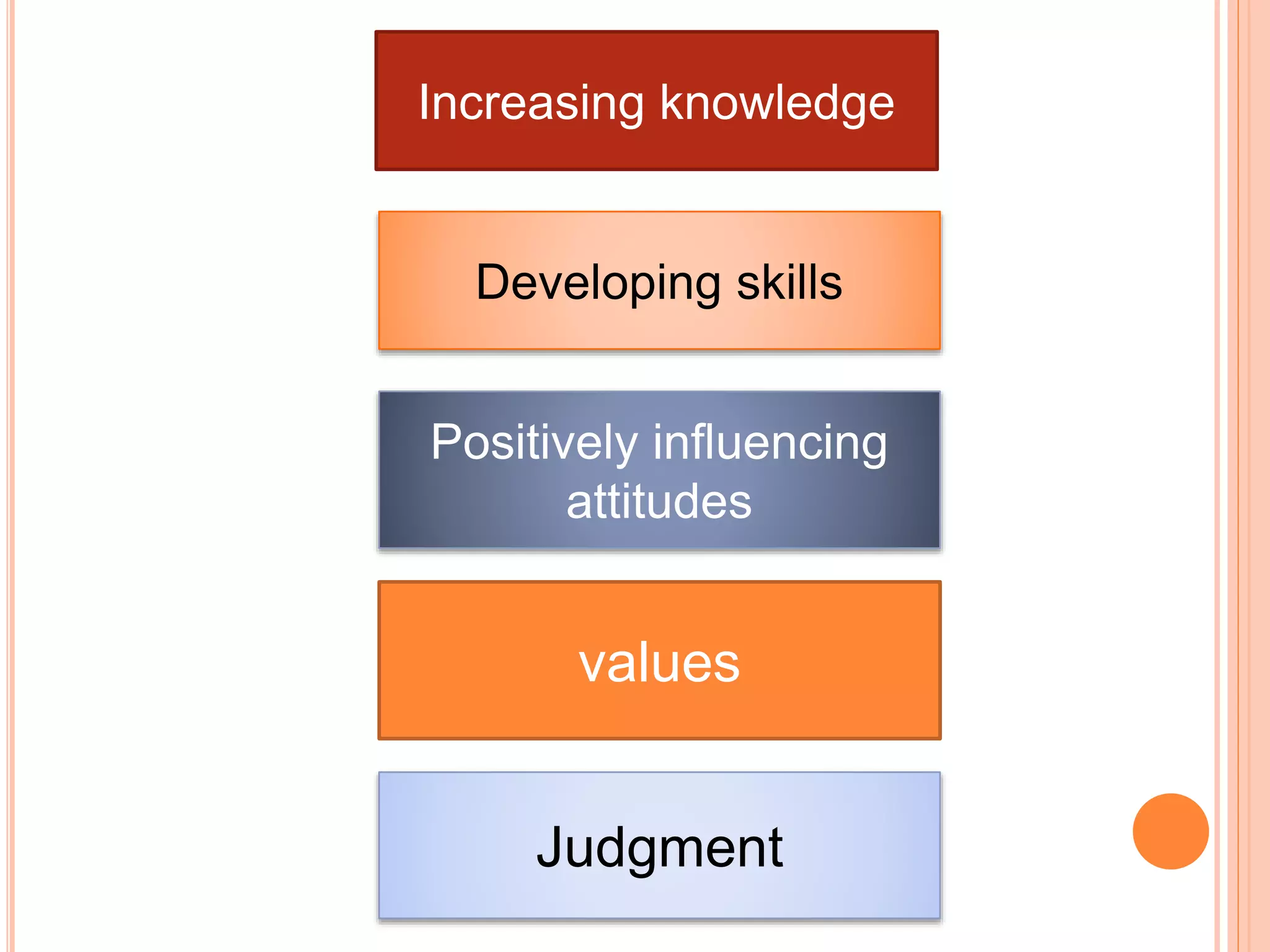
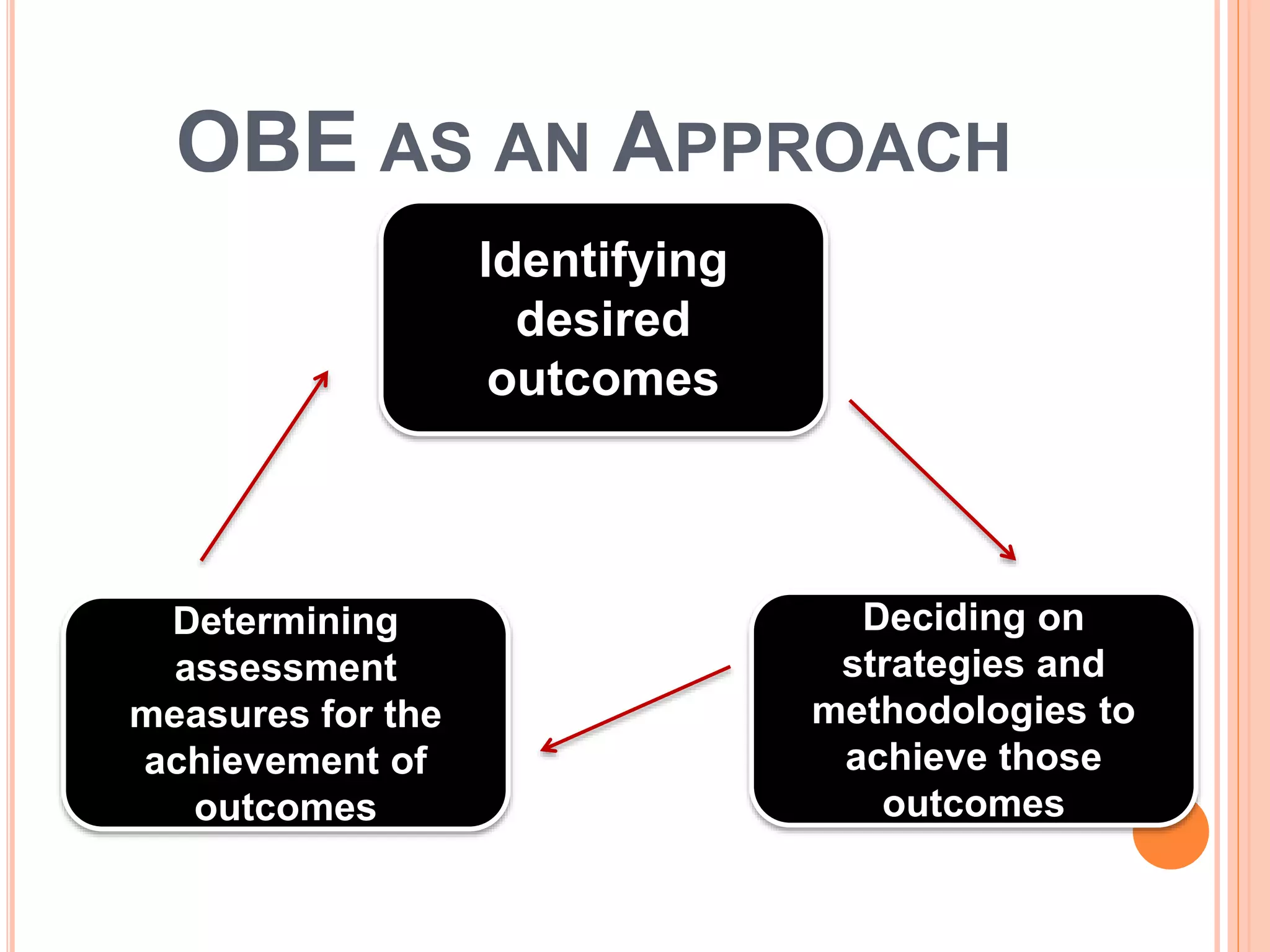
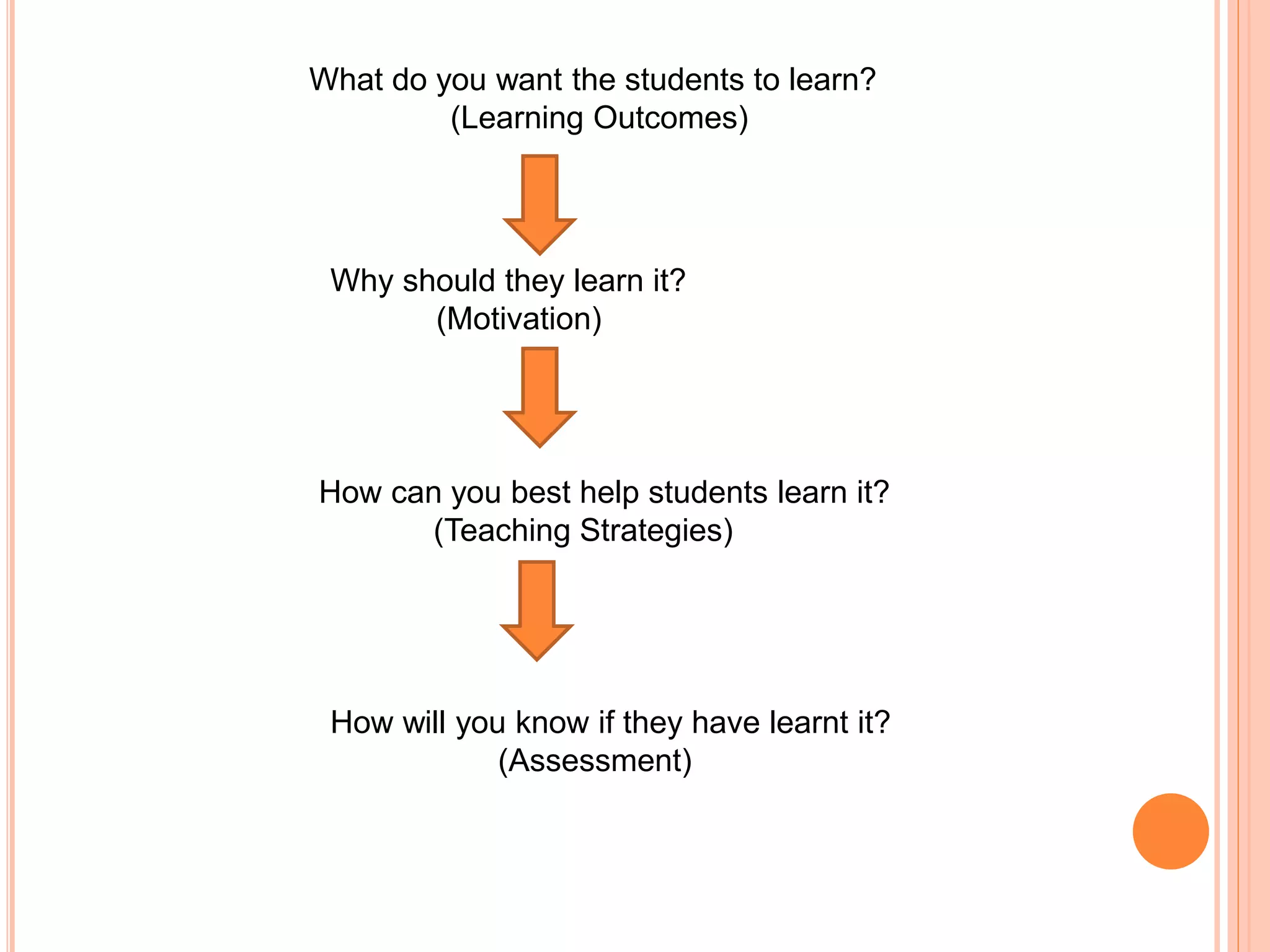
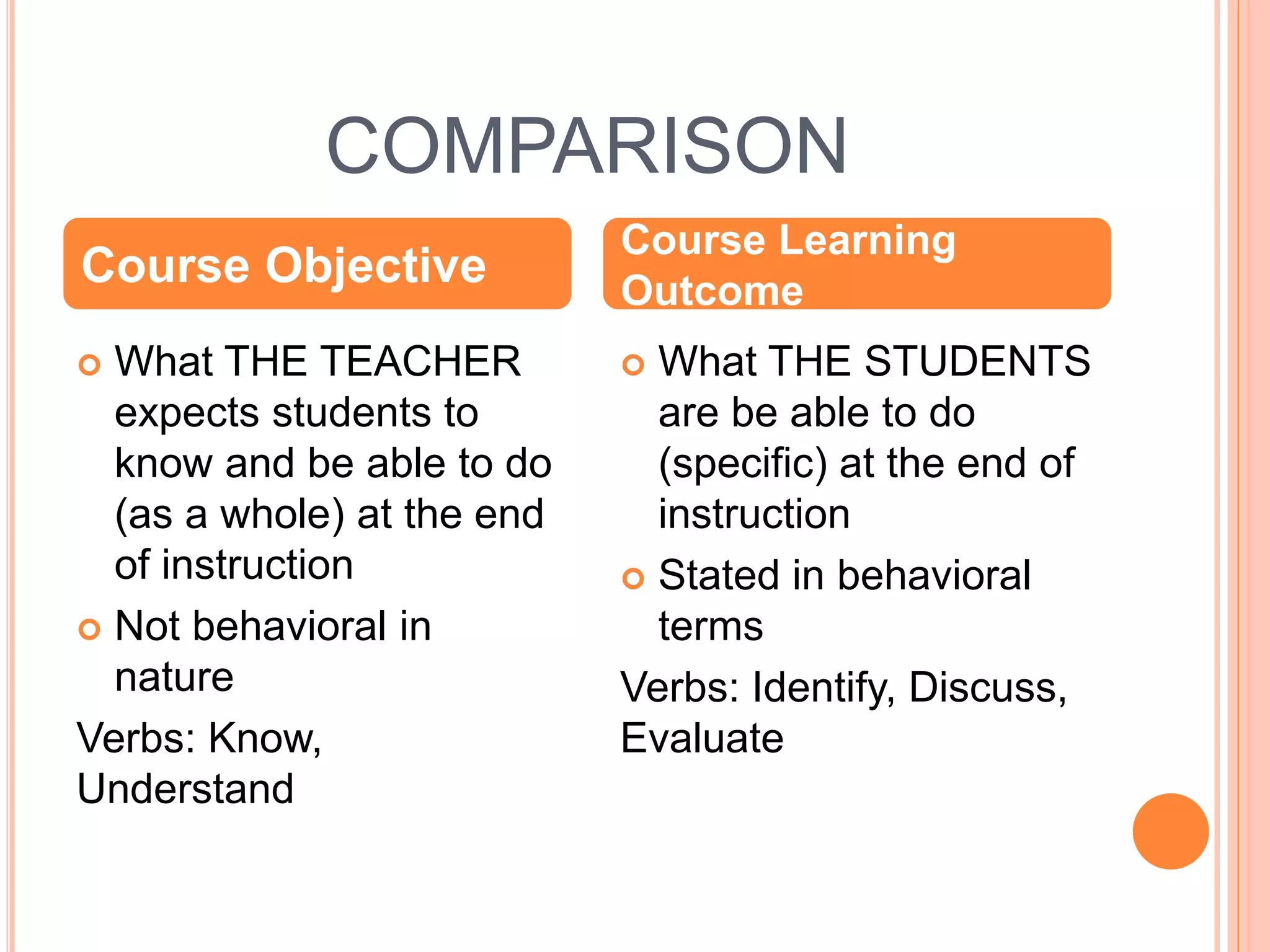
This document discusses outcomes-based education (OBE). It defines outcomes as the clear learning results that students must demonstrate after significant learning experiences. OBE focuses on intended learning outcomes from instruction rather than course credits. It is a student-centered approach defined by identifying desired outcomes, strategies to achieve them, and assessment measures. The document compares course objectives to learning outcomes and explains why defining outcomes prior to planning is important. It provides examples of OBE approaches and emphasizes that OBE focuses on long-term, cross-curricular outcomes related to students' future roles.