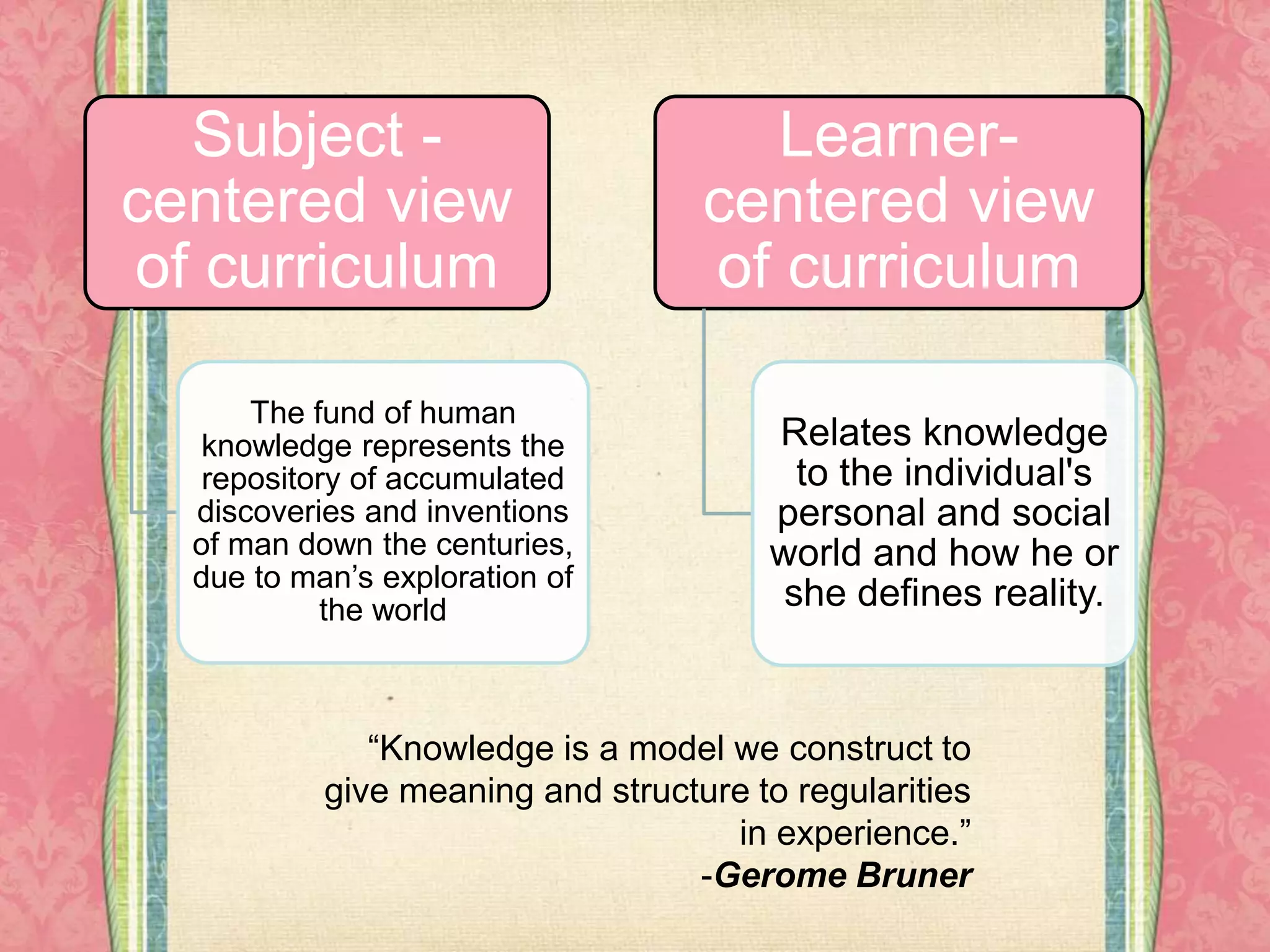
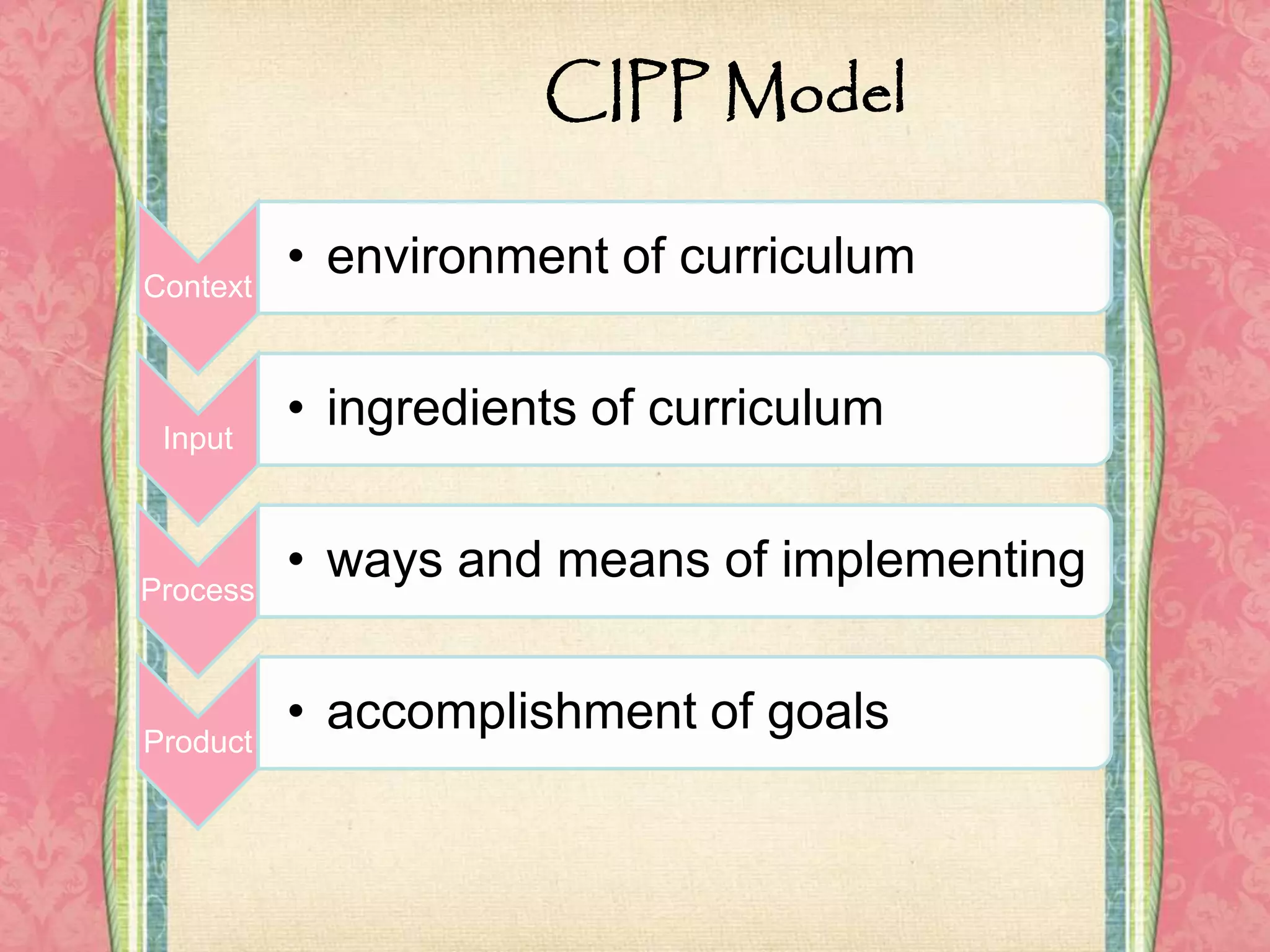
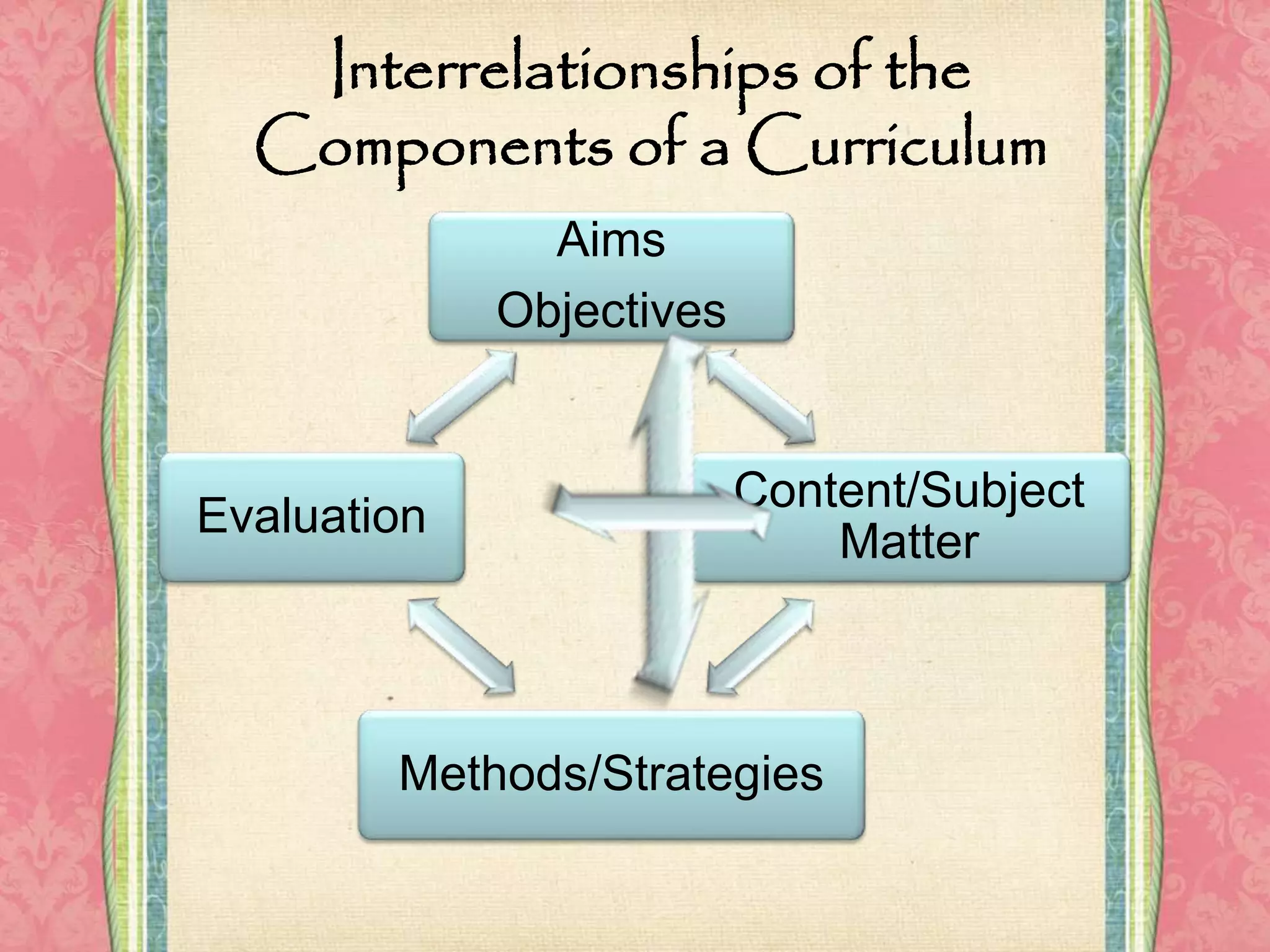
The document outlines the four major components of curriculum: 1) aims, goals and objectives which define what is to be achieved; 2) subject matter/content which determines what topics should be included; 3) learning experiences which are the instructional strategies that link goals to content; and 4) evaluation approaches to assess the quality, effectiveness and outcomes of the curriculum. It also discusses different views of curriculum being either subject-centered or learner-centered and introduces Stufflebeam's CIPP model as a widely used evaluation method.