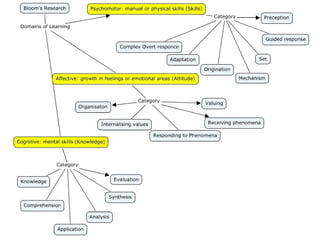
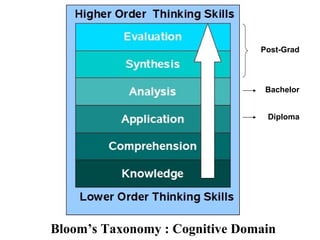
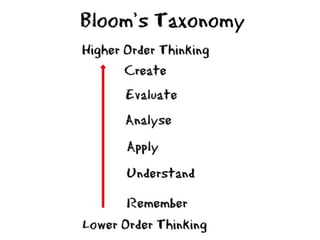
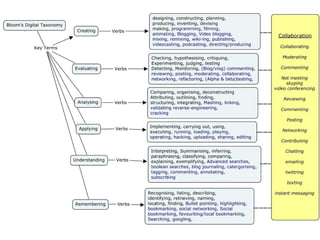
The document discusses the importance of learning outcomes in education. It explains that learning outcomes focus on what students can actually do after instruction rather than just covering content. Well-written learning outcomes provide direction for planning lessons, focus student behavior on skills to be developed, and clearly convey to students what they should learn. The document also contrasts learning outcomes with objectives and provides examples of verbs to use in writing measurable outcomes.