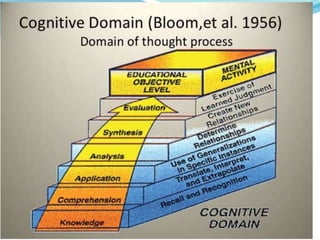
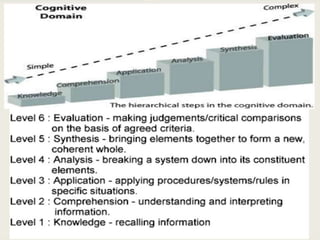
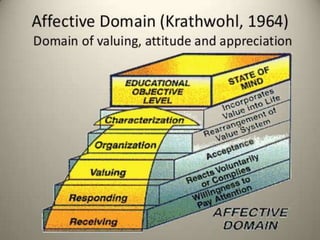
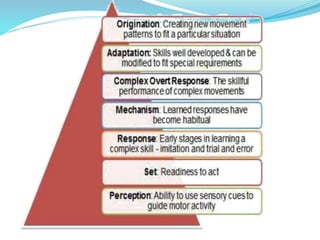
The document discusses aims, goals, and objectives in curriculum development. It defines aims as the most general level of educational outcomes, goals as reflecting purpose with outcomes in mind, and objectives as the most specific levels. Aims provide direction to educational action and inspire an ideal vision. Goals are statements of intent to be accomplished and have some outcomes in mind. Objectives delineate expected changes in students and intended behaviors. The document also outlines examples of aims, goals, and objectives for different levels of education.