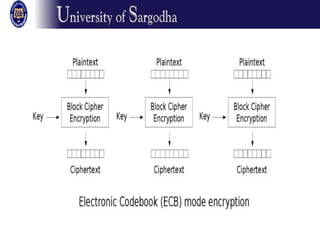
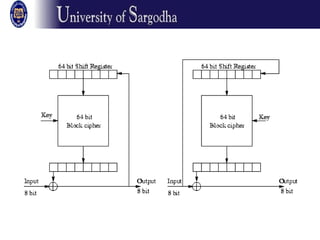
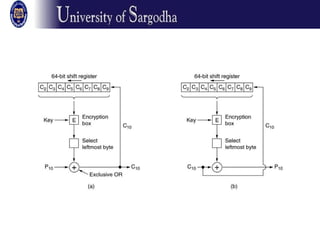
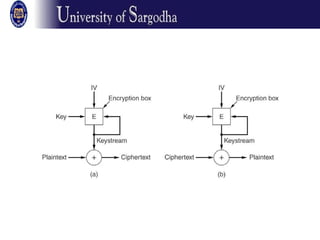
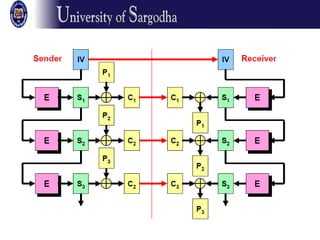
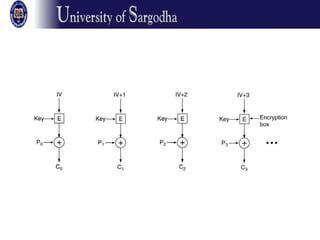
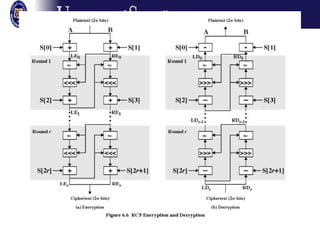
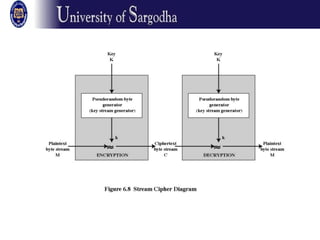
The document discusses several modes of operation for block ciphers and stream ciphers. It explains that block cipher modes like CBC, CFB, OFB, and Counter Mode require an initialization vector (IV) to provide randomization and prevent identical plaintext blocks from encrypting to the same ciphertext. The IV must be transmitted along with the ciphertext and never reused with the same key. Stream ciphers like RC4 generate a pseudorandom key stream that is XORed with plaintext bytes to produce ciphertext.













![RC4 algorithm
• Key length is variable: from 1 to 256 bytes
• Based on the key initialize a 256-byte
state vector S: S[0…255]
• At all times S contains a permutation of
the numbers 0, 1, …, 255
• For encryption and decryption a byte k is
selected from S and the entries in S are
permuted](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ns4-150126141536-conversion-gate02/85/Block-Ciphers-Modes-of-Operation-22-320.jpg)