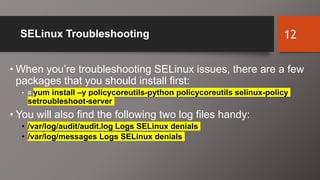
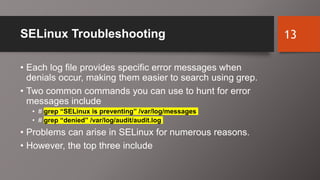
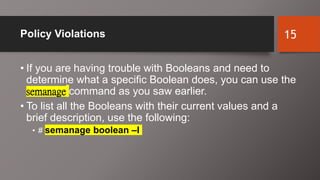
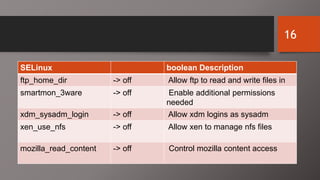
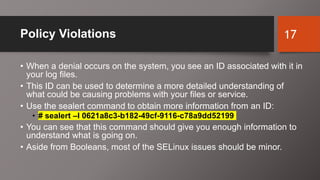
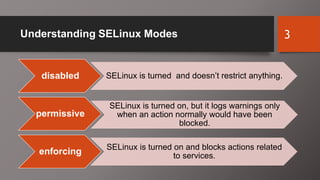
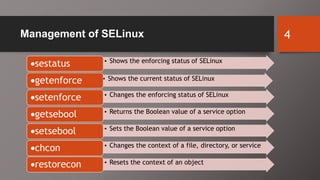
SELinux is an additional layer of security for Linux that confines applications and protects files. It can run in different modes like enforcing or permissive. Administrators use commands like sestatus, setenforce, and getsebool to check and configure the SELinux mode and boolean settings. When issues arise, logs and troubleshooting commands help identify labeling problems, incorrect contexts, or confined services that require boolean changes.


![sestatus command.
• Syntax: sestatus [options]
• Options:
• -b Displays all Booleans and their statuses
• -v Provides verbose output
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/11-selinux-231003052537-aa18bbd0/85/11-SELinux-in-Red-Hat-5-320.jpg)

![config file
• Aside from editing the config file, you can also use the setenforce
command to change the status.
• Syntax: setenforce [ Enforcing | Permissive | 1 | 0 ]
• If the current mode is permissive, you can change it to enforcing with
the following:
• # setenforce enforcing
• Regardless of which method you use when changing the mode in
which SELinux runs, you are still required to reboot the system.
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/11-selinux-231003052537-aa18bbd0/85/11-SELinux-in-Red-Hat-7-320.jpg)
![Service and Boolean Options
• To view the Boolean options, you can use the getsebool command
combined with grep to look for specific options.
• Syntax: getsebool [-a | boolean]
• Although you have not installed a web server yet, let’s look at the
Boolean options from it anyway.
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/11-selinux-231003052537-aa18bbd0/85/11-SELinux-in-Red-Hat-8-320.jpg)

![Service and Boolean Options
• After deciding which Boolean you’d like to change, you need to
enable or disable the value appropriately.
• To enable or disable a Boolean option, you can use the
setsebool command.
• When using the command, you also need to use the -P option
for the change to be persistent.
• Syntax: setsebool [options] [boolean = <on (1) | (0)>]
• options
• -P Makes the changes persistent
10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/11-selinux-231003052537-aa18bbd0/85/11-SELinux-in-Red-Hat-10-320.jpg)