Embed presentation
Downloaded 191 times





![•
•
•
•
for i = 0 to 255
do
S[i] = i;
T[i] = K[i mod keylen];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rc4-170821143257/85/Rc4-7-320.jpg)
![•
•
j = 0;
for i = 0 to 255
do
j = (j + S[i] + T[i]) mod 256;
Swap (S[i], S[j]);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rc4-170821143257/85/Rc4-8-320.jpg)
![•
i, j = 0;
for (int x = 0; x < byteLen; x++)
do
i = (i + 1) mod 256;
j = (j + S[i]) mod 256;
Swap (S[i], S[j]);
t = (S[i] + S[j]) mod 256;
k = S[t];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rc4-170821143257/85/Rc4-9-320.jpg)
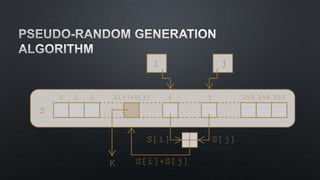











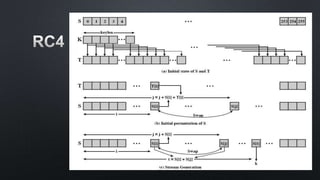






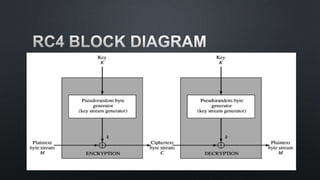
The document discusses cryptographic algorithms and keys. It describes the RC4 algorithm which uses a key stream to encrypt plaintext into ciphertext. It involves initializing a state array S with permutations, then generating a pseudo-random key stream by swapping array bytes based on the key and indices i and j. The key stream is then combined with plaintext to produce ciphertext. The document also mentions SSL and provides several references on RC4, WEP attacks, and cryptographic algorithm breakdowns.






![•
•
•
•
for i = 0 to 255
do
S[i] = i;
T[i] = K[i mod keylen];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rc4-170821143257/85/Rc4-7-320.jpg)
![•
•
j = 0;
for i = 0 to 255
do
j = (j + S[i] + T[i]) mod 256;
Swap (S[i], S[j]);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rc4-170821143257/85/Rc4-8-320.jpg)
![•
i, j = 0;
for (int x = 0; x < byteLen; x++)
do
i = (i + 1) mod 256;
j = (j + S[i]) mod 256;
Swap (S[i], S[j]);
t = (S[i] + S[j]) mod 256;
k = S[t];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rc4-170821143257/85/Rc4-9-320.jpg)


















