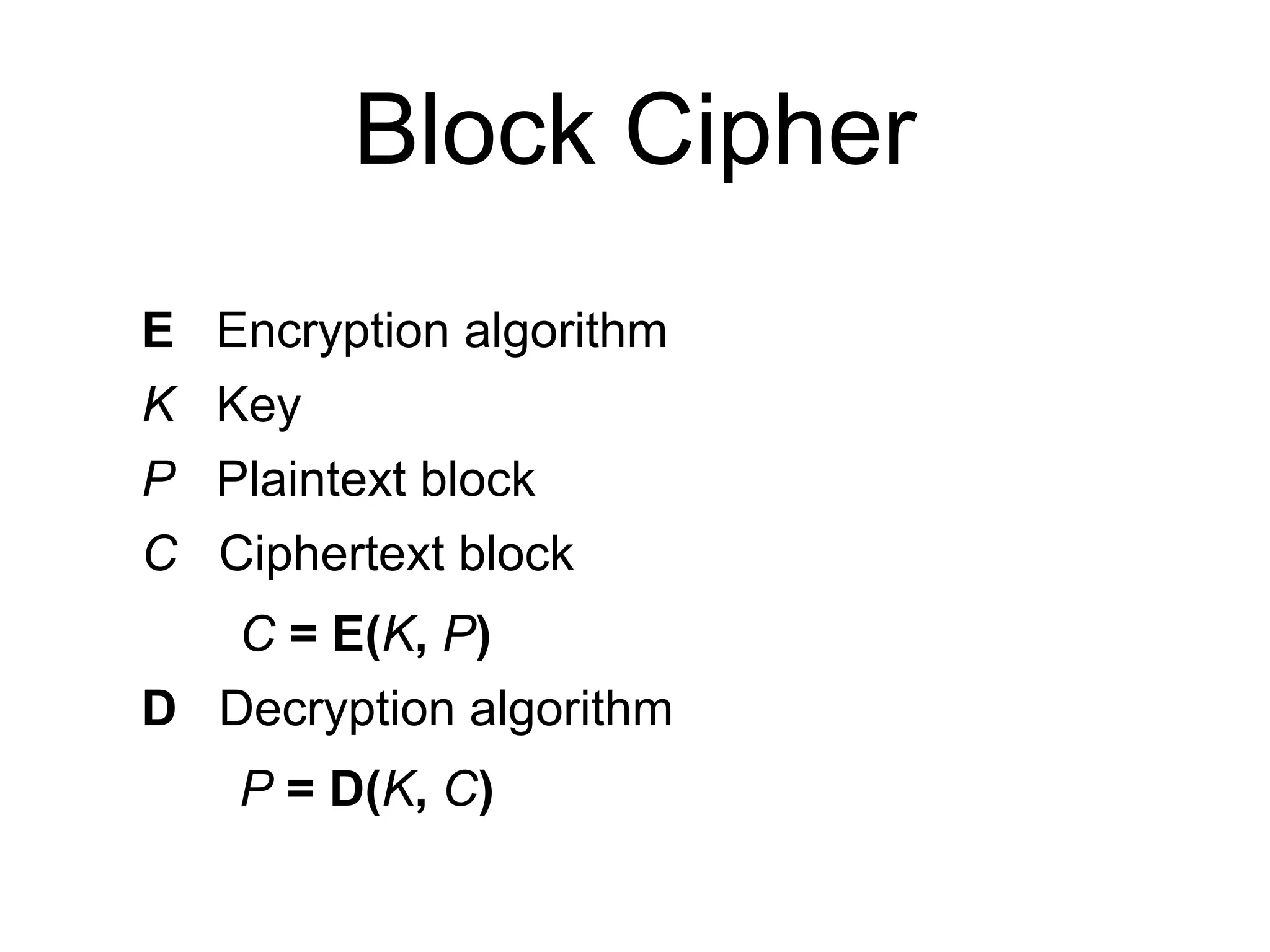
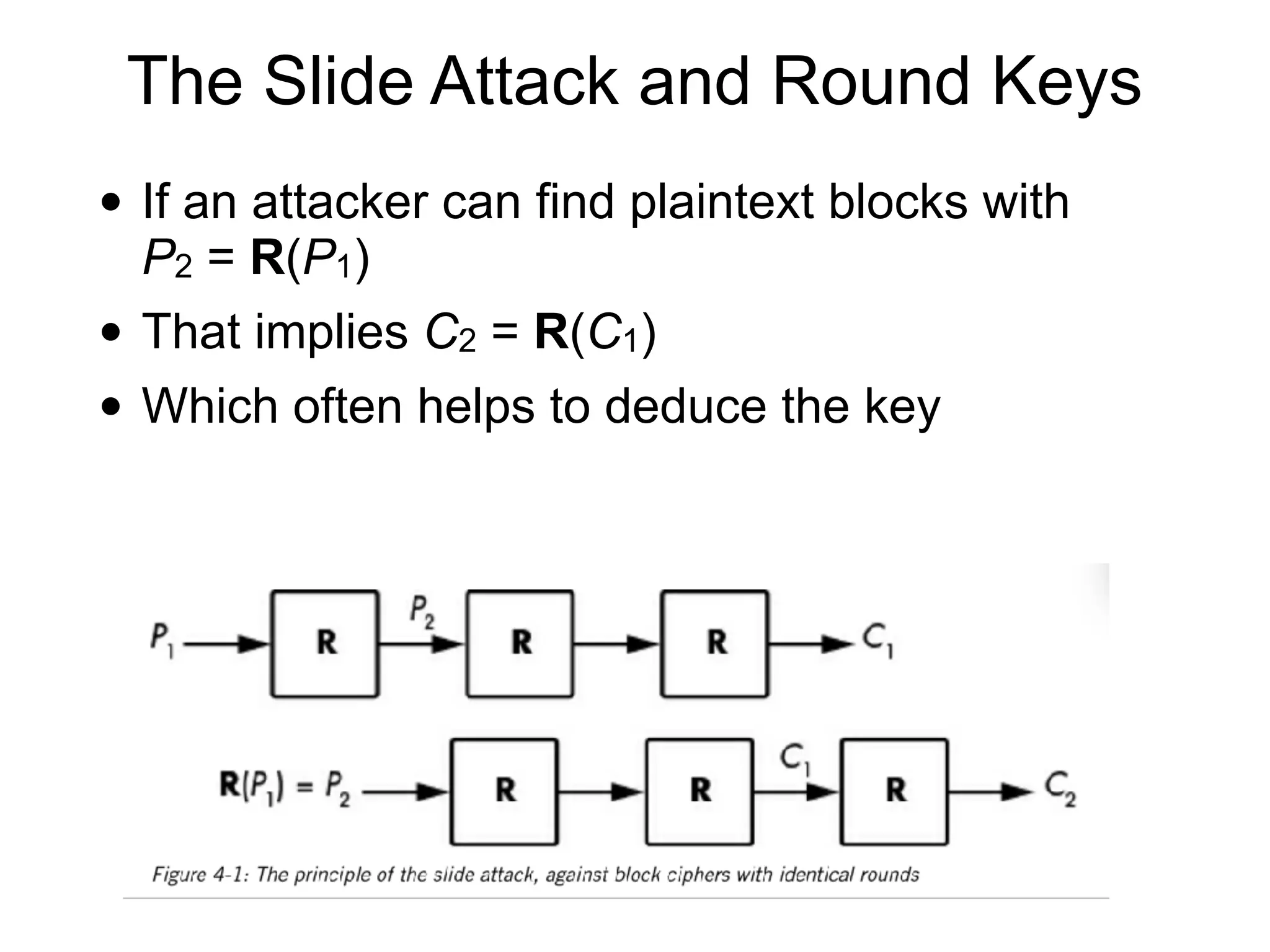
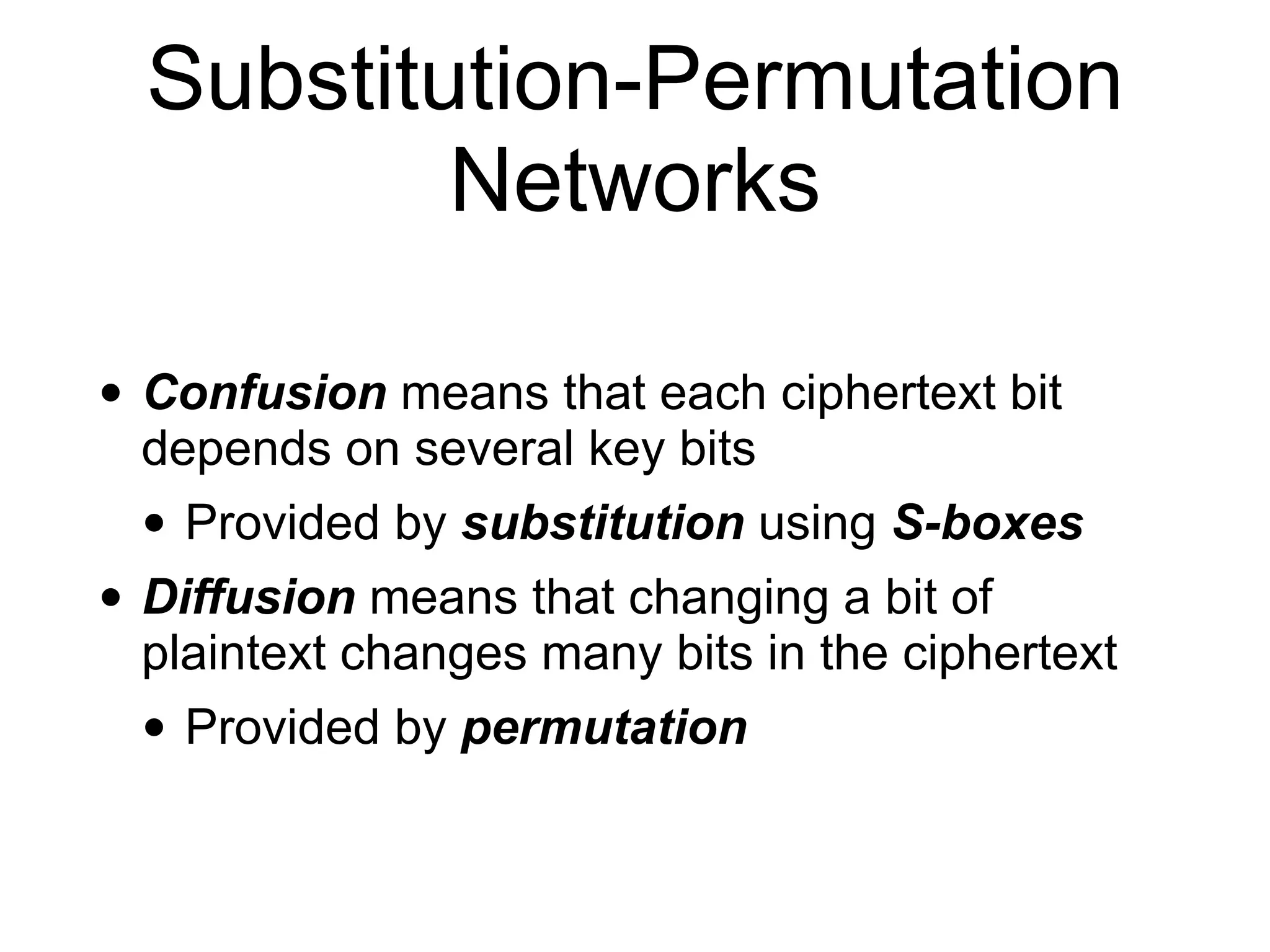
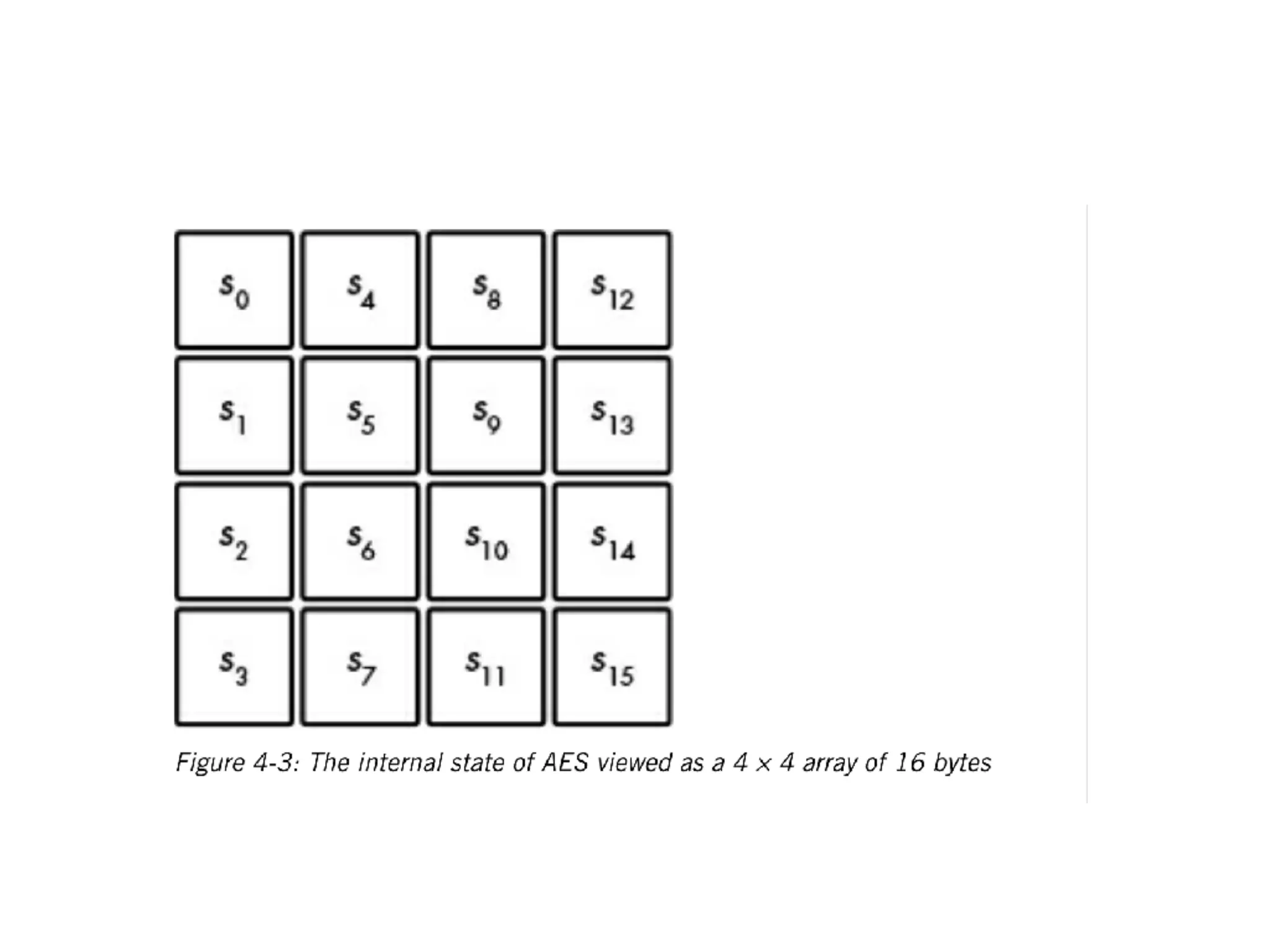
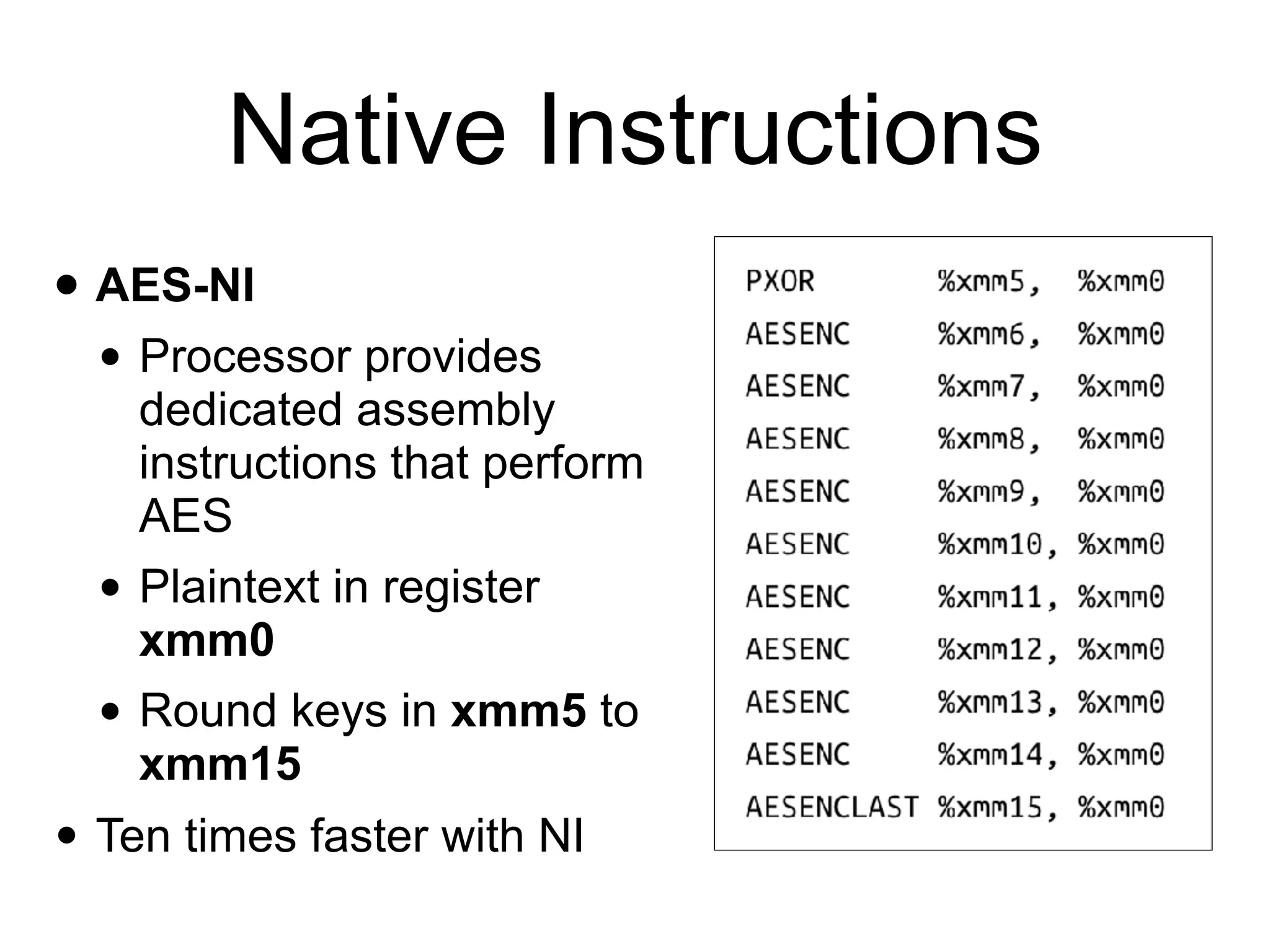
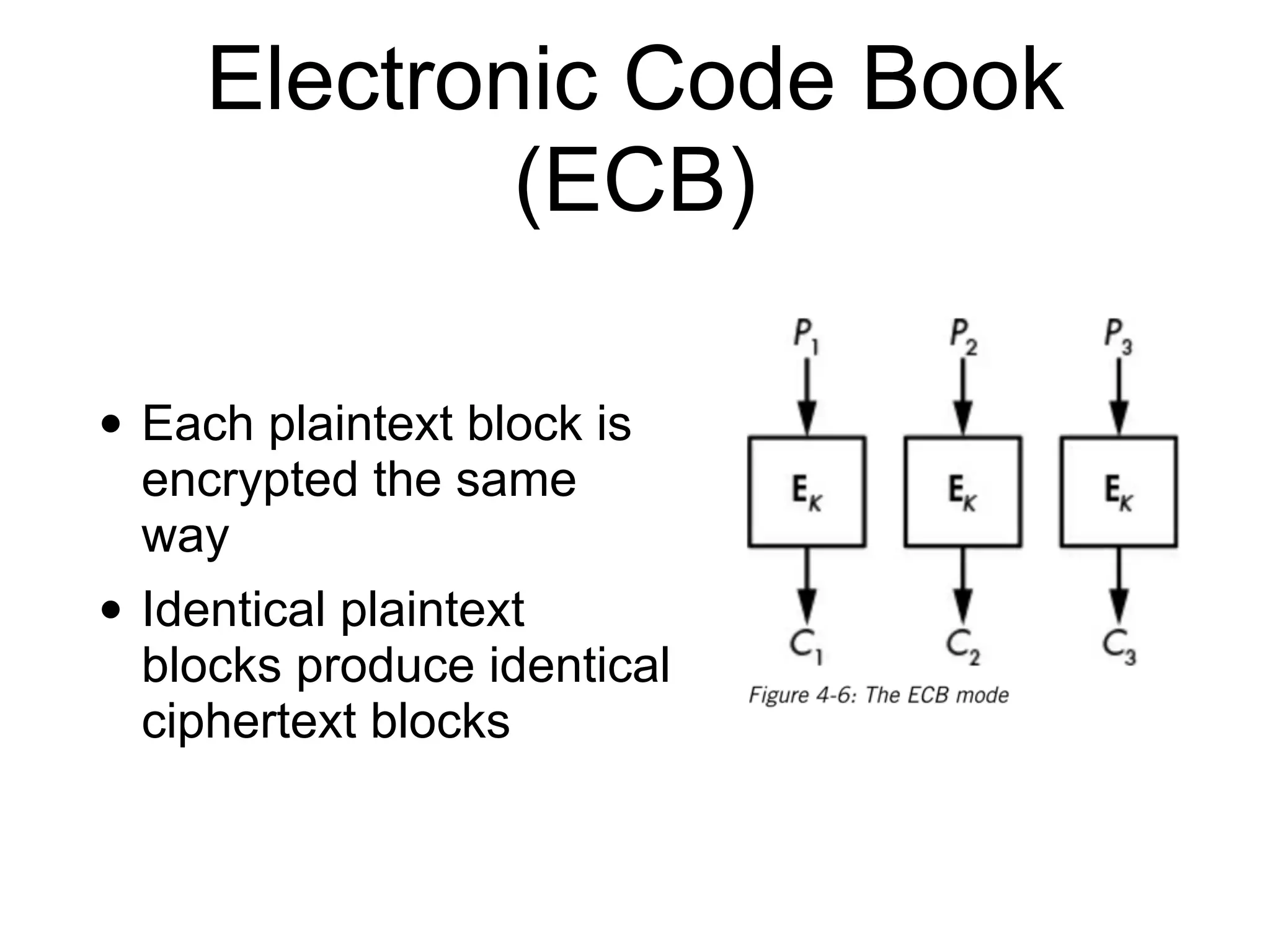
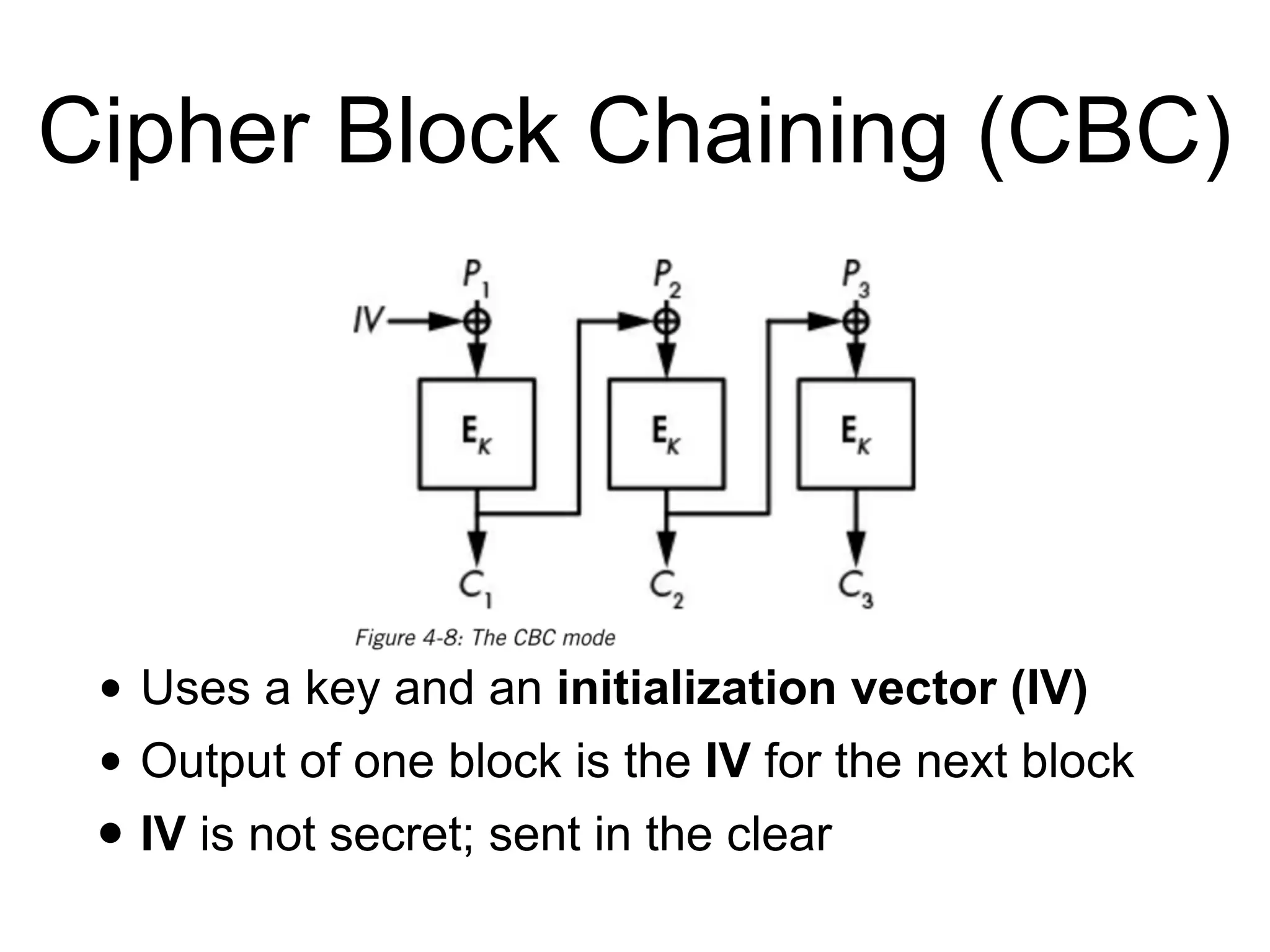
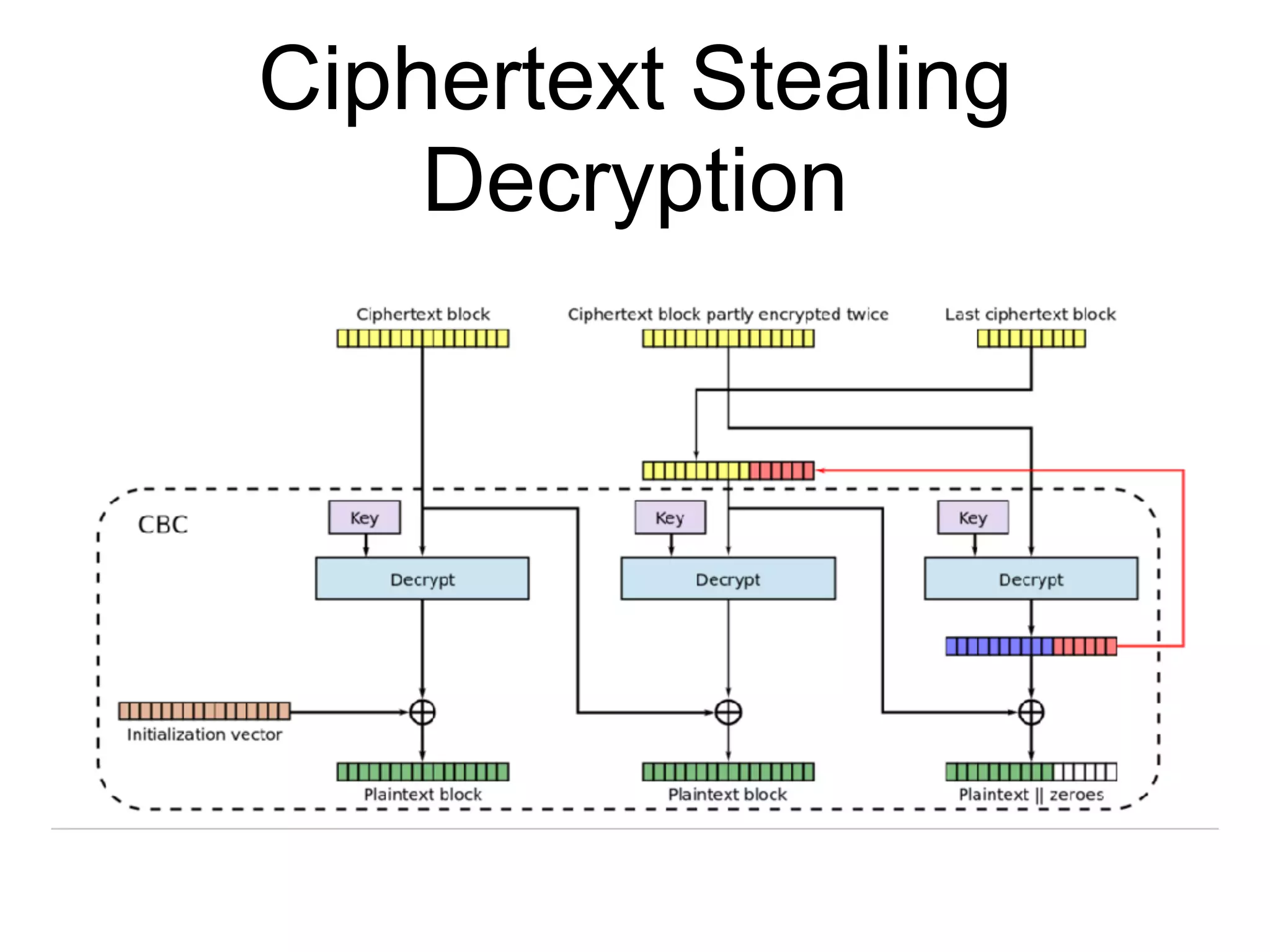
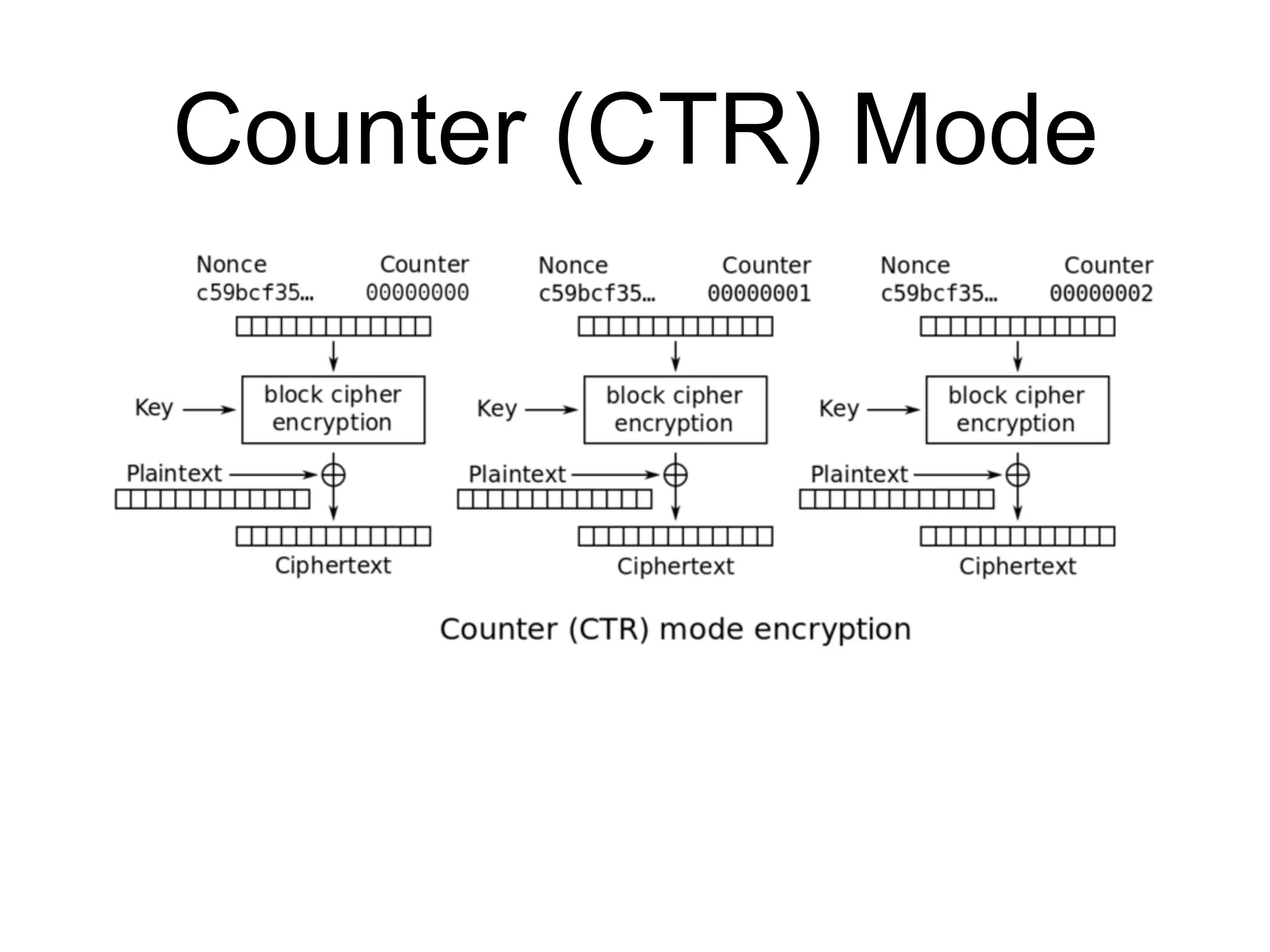
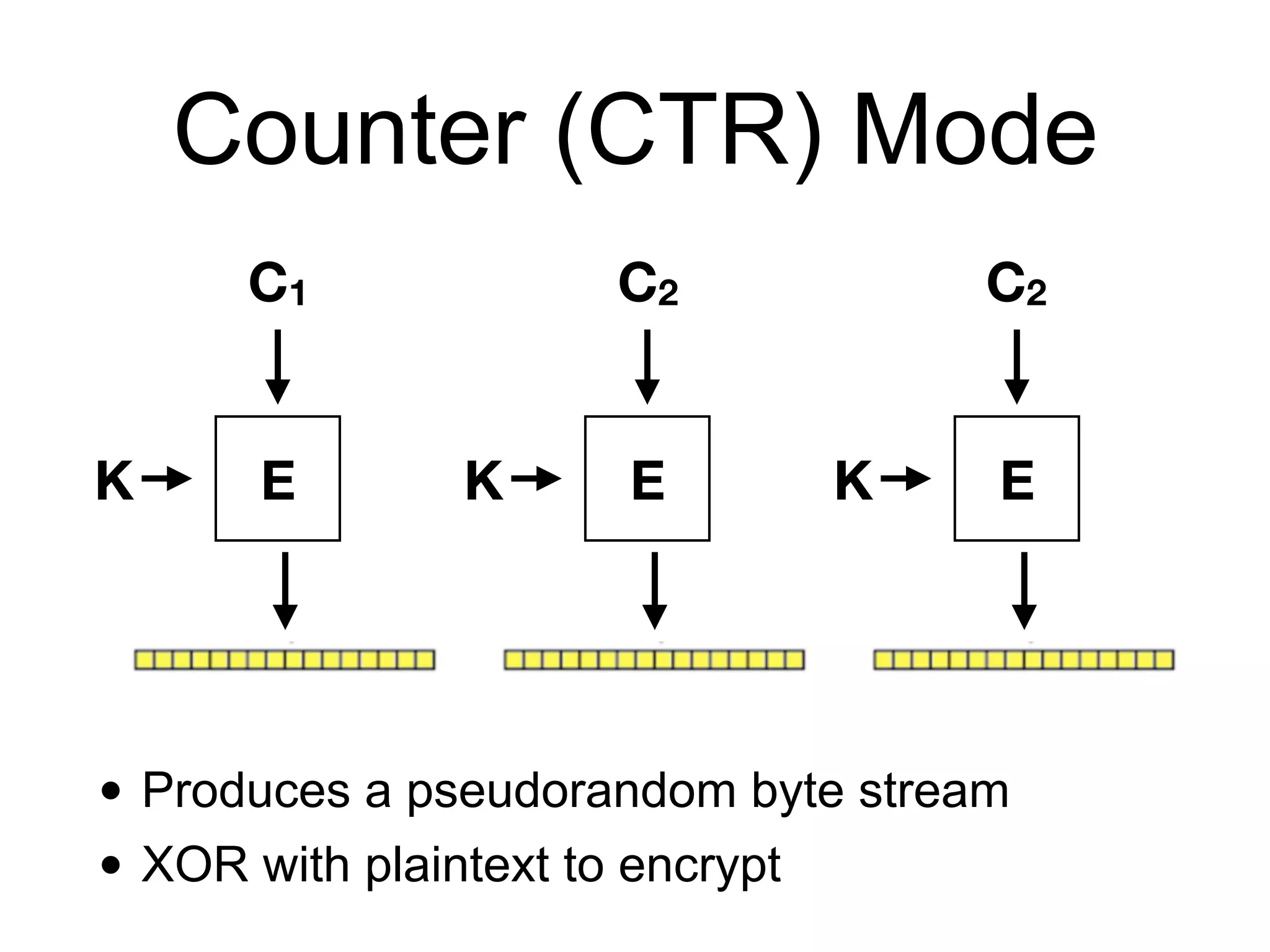
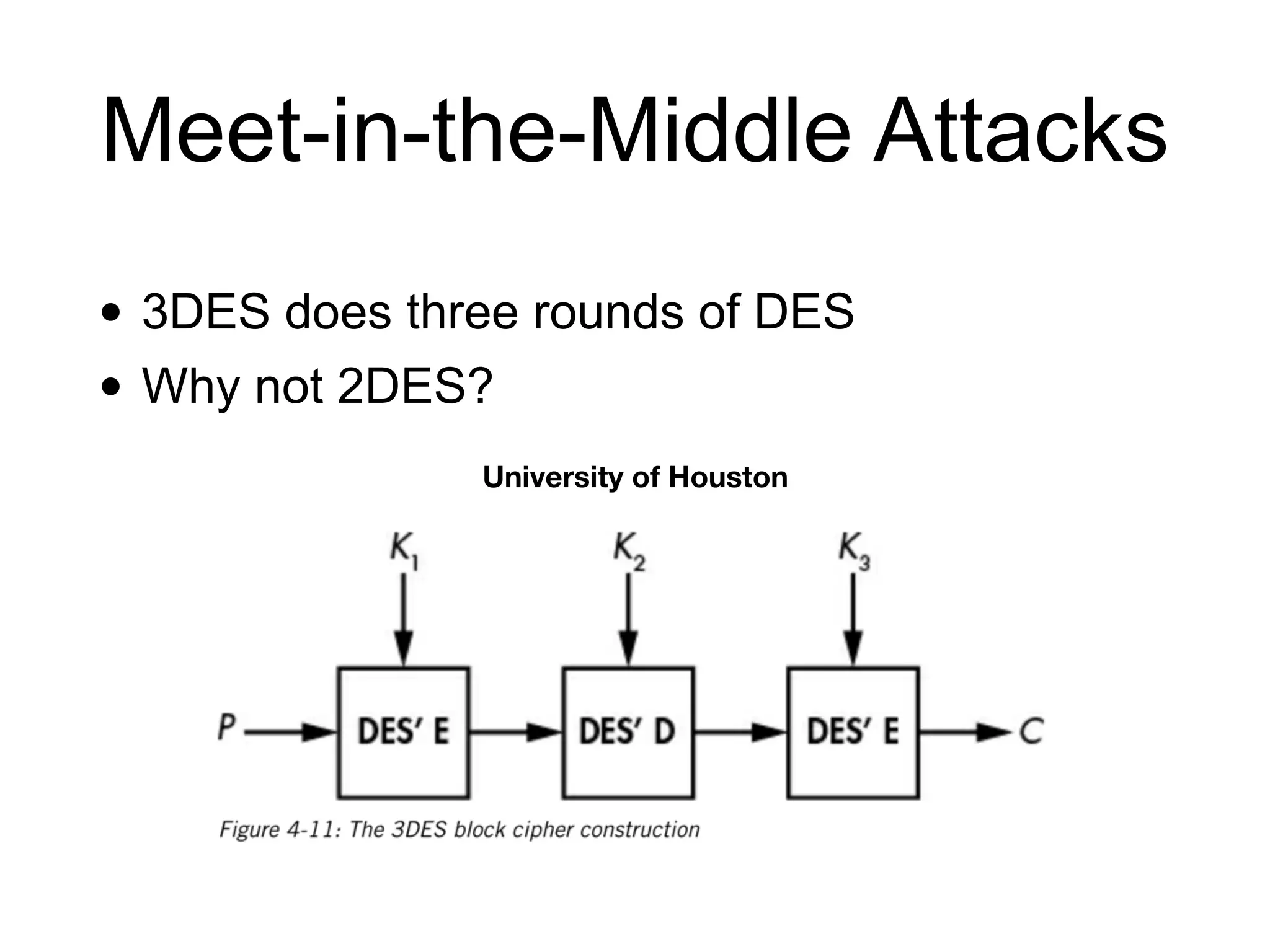
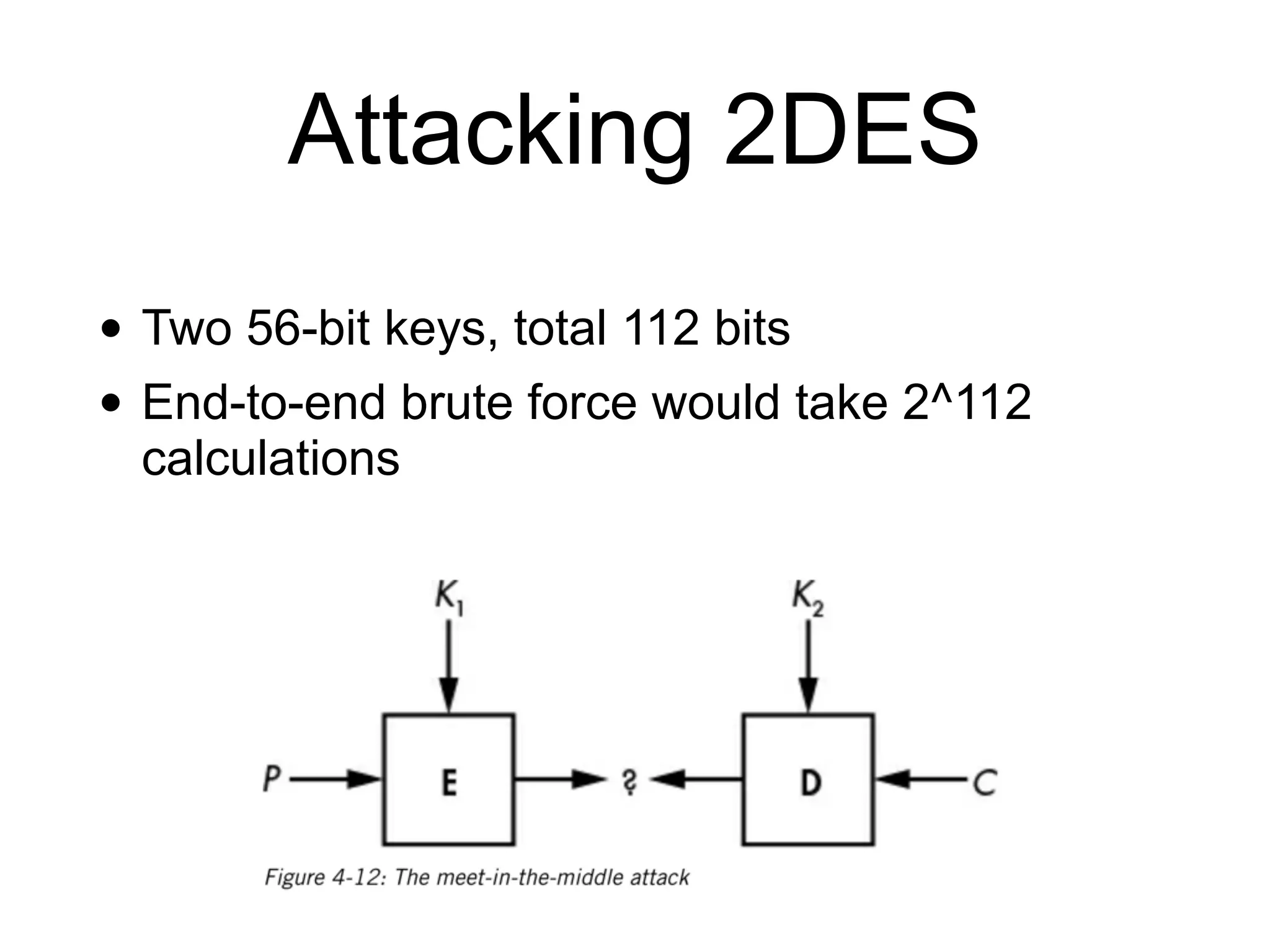
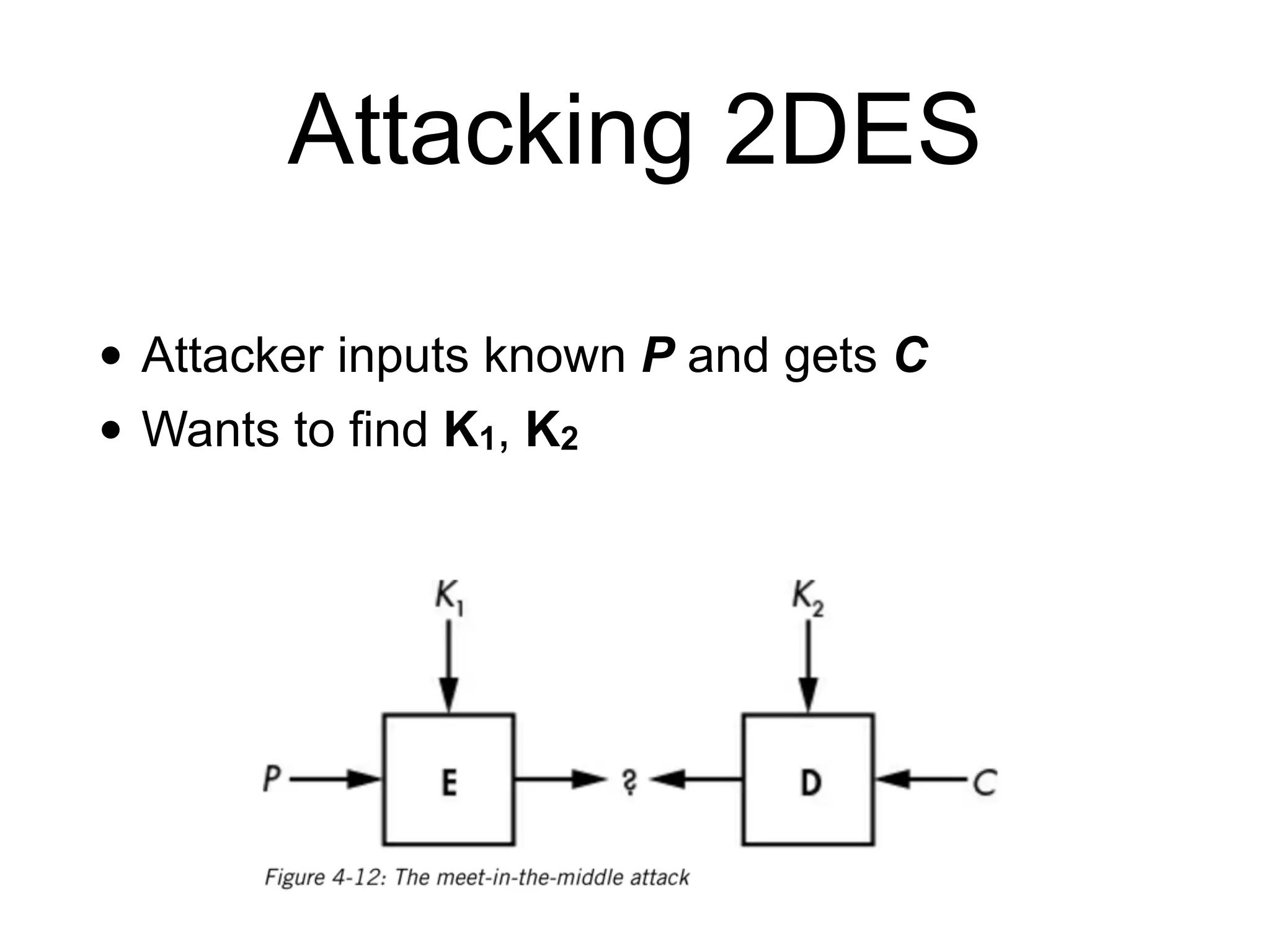
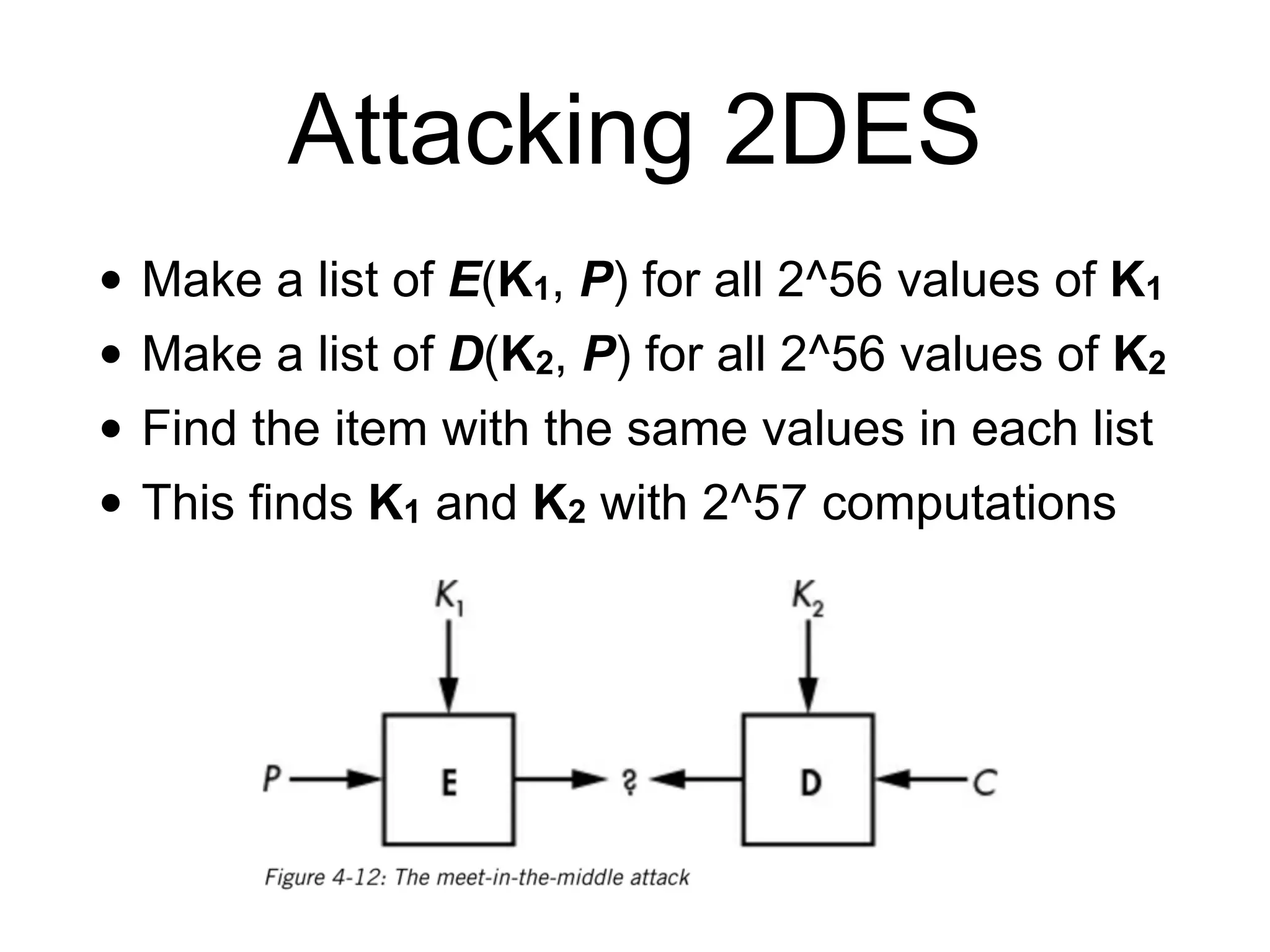
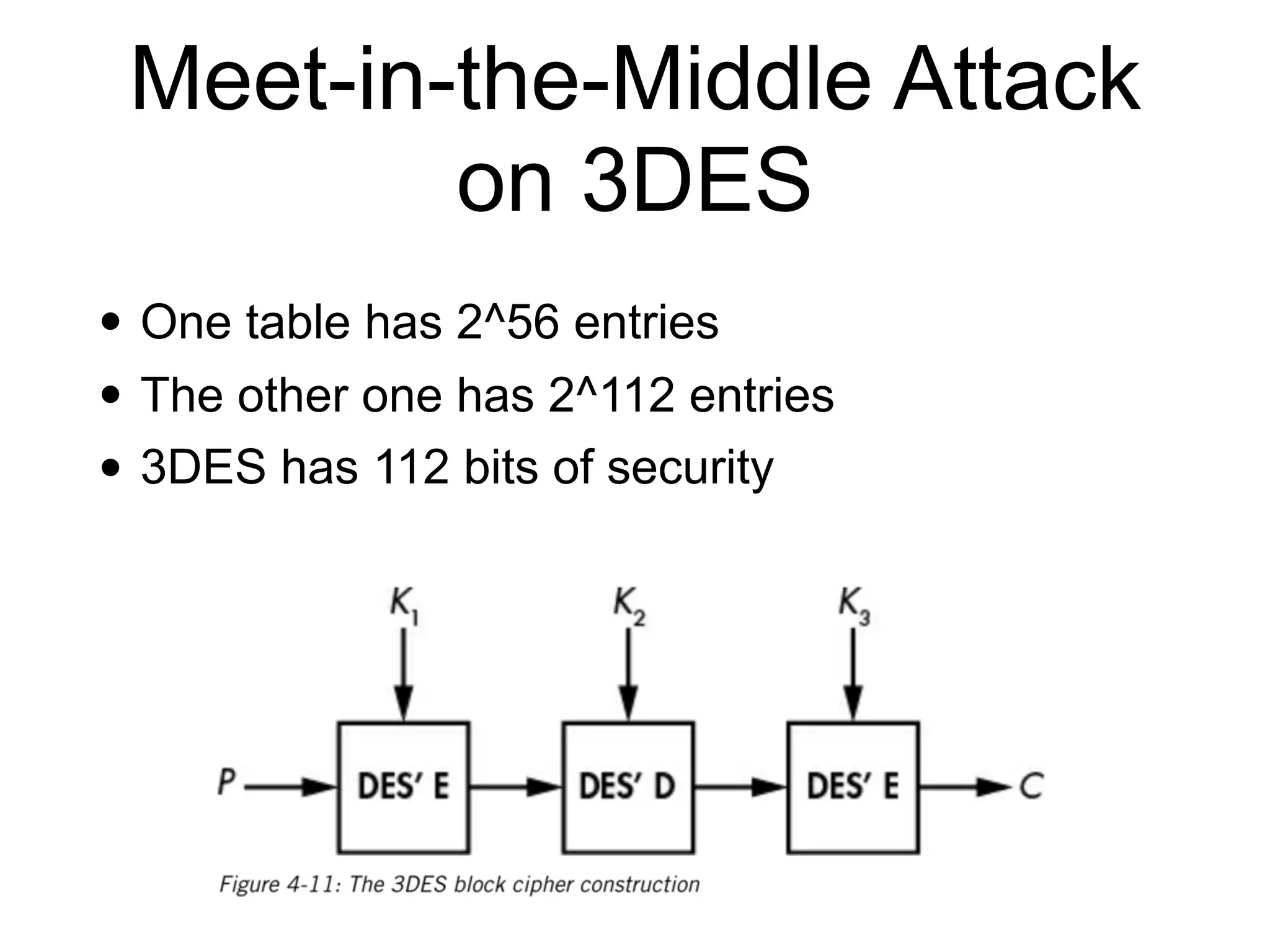
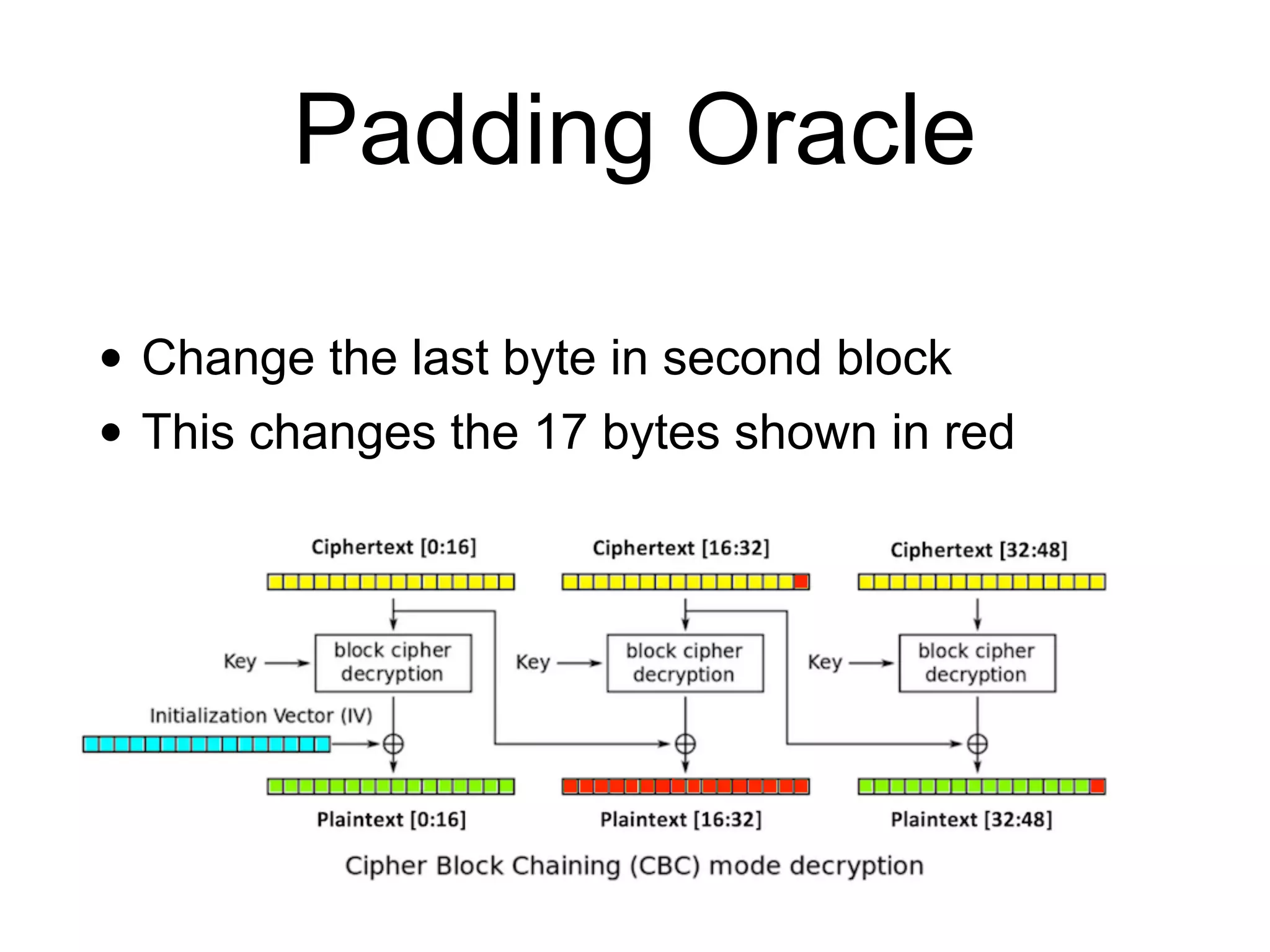
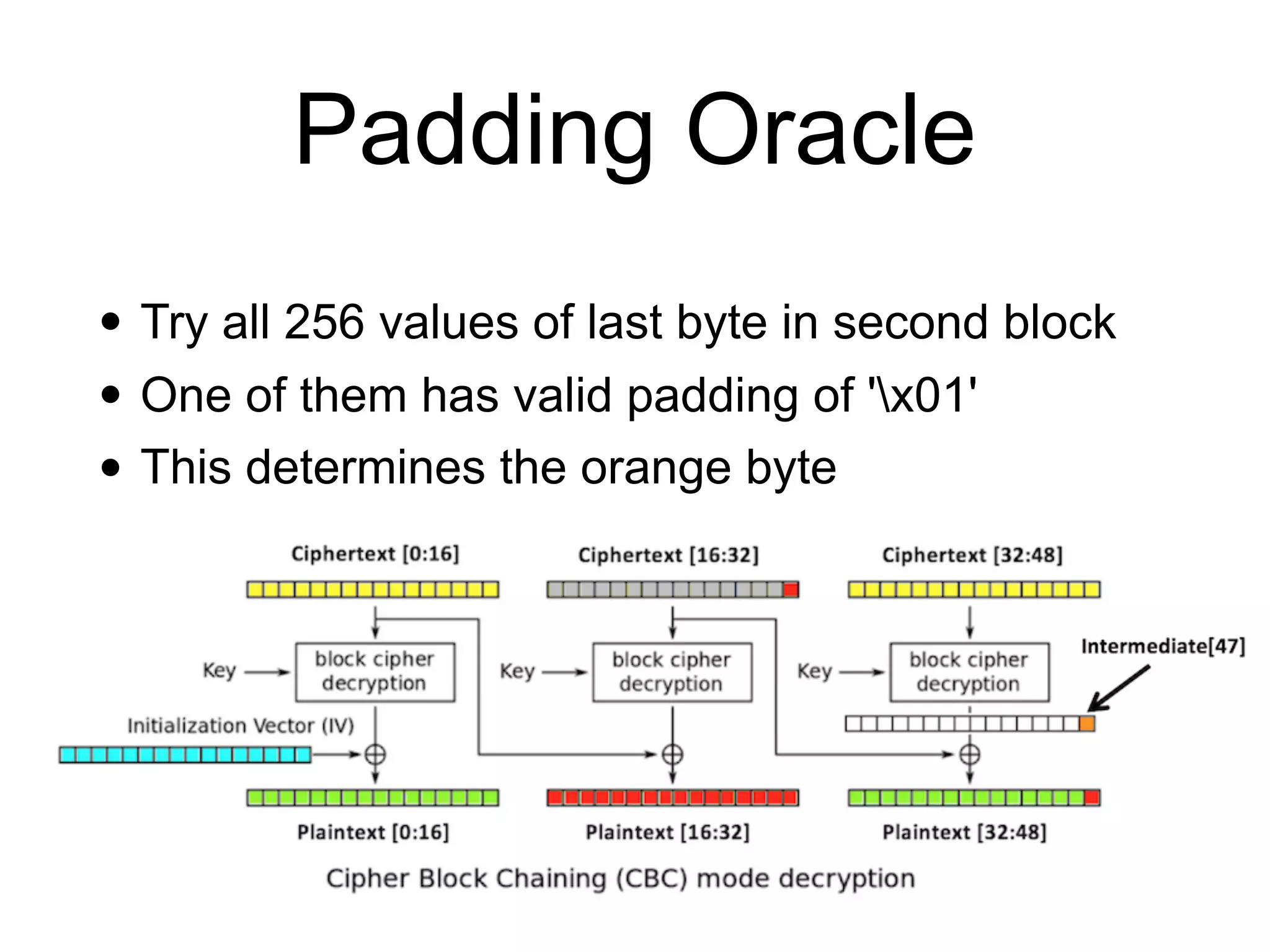
The document discusses the fundamentals of block ciphers, specifically focusing on the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) and its implementation. It covers the construction of block ciphers, security goals, modes of operation including ECB and CBC, and the efficiency improvements in AES implementations. Additionally, it highlights potential vulnerabilities and attacks against encryption methods, such as padding oracle attacks and meet-in-the-middle attacks.