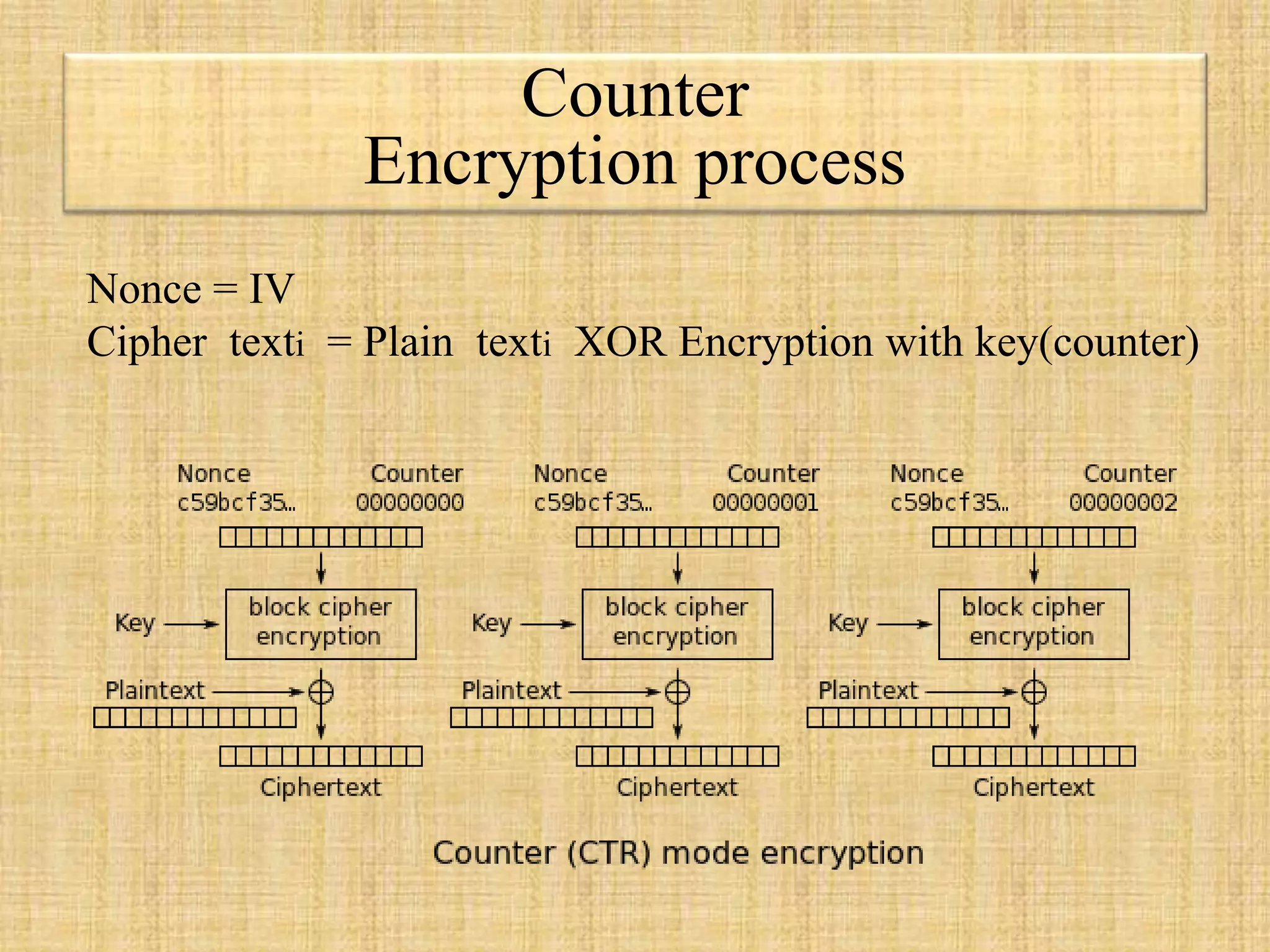
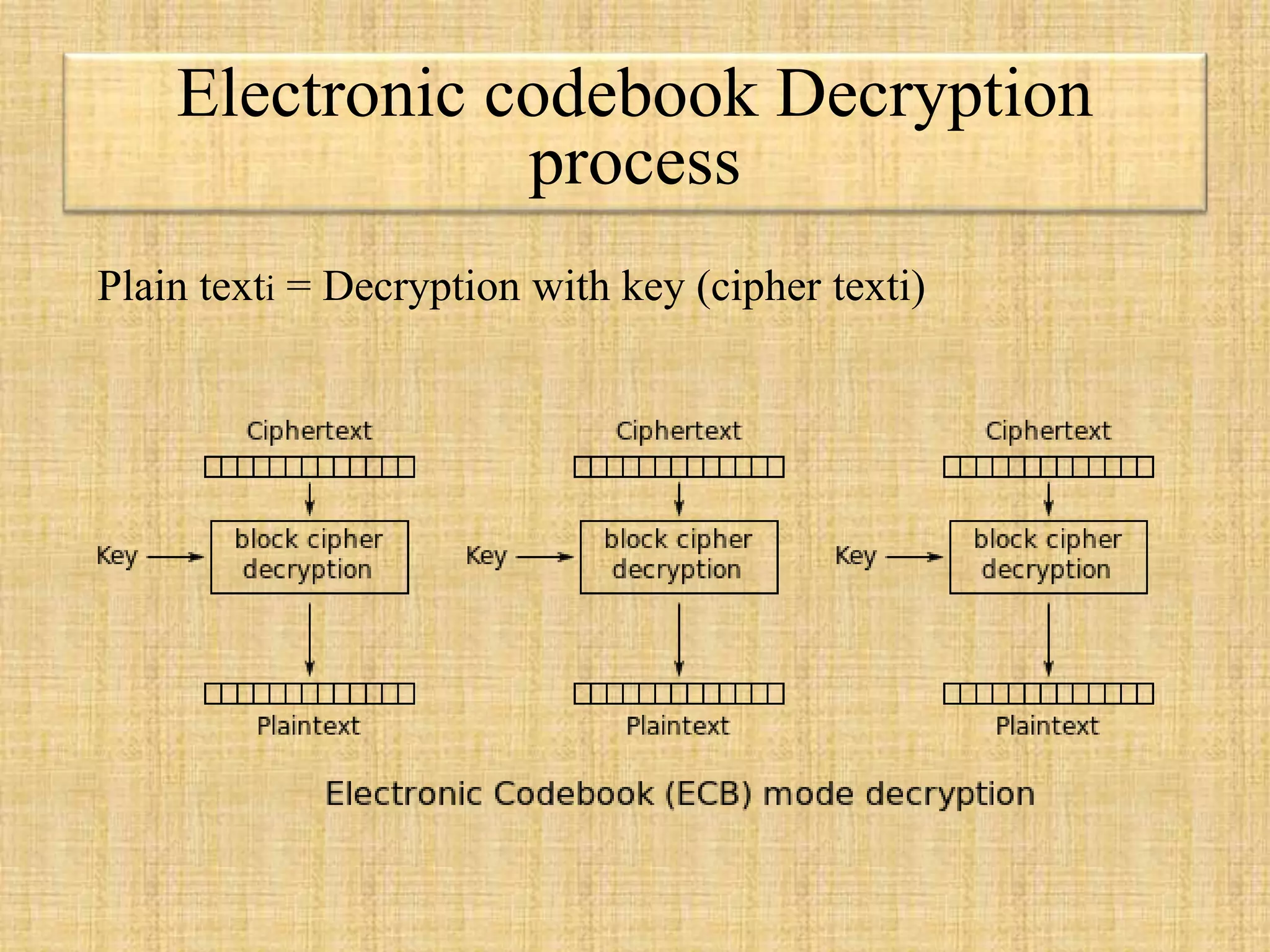
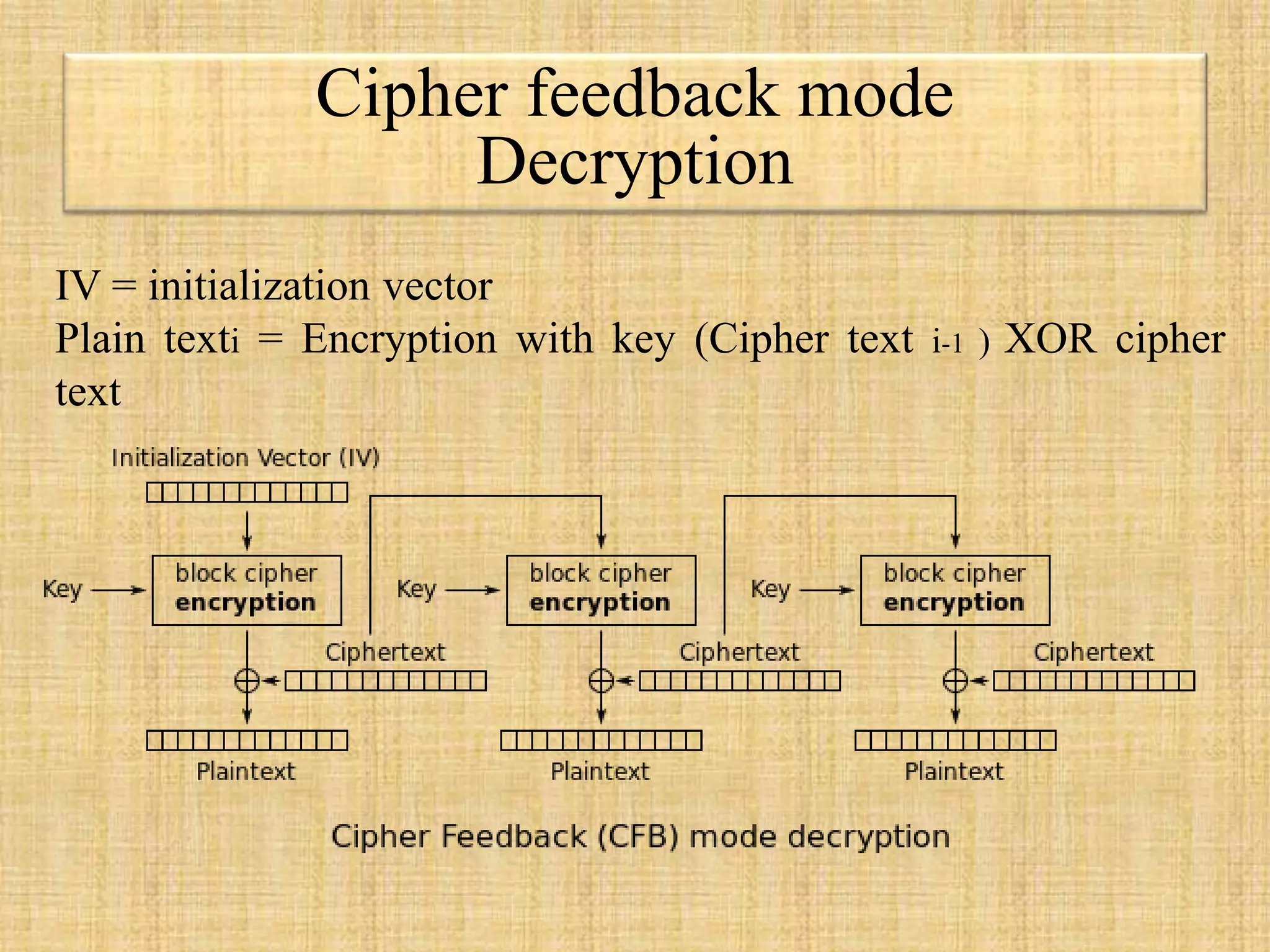
The document describes block ciphers, a foundational element in cryptography that encrypts fixed-length blocks of data using symmetric keys. It outlines five modes of operation defined by NIST to handle messages of varying lengths, including Electronic Codebook (ECB), Cipher Block Chaining (CBC), Cipher Feedback (CFB), Output Feedback (OFB), and Counter mode (CTR), each with specific encryption and decryption processes as well as security considerations. The text highlights the importance of initialization vectors (IVs) in ensuring encryption security and explains vulnerabilities associated with reusing IVs and patterns in ciphertext.


















![Cipher output feedback mode
encryption
IV = initialization vector
cipher texti =
plain texti XOR Encryption
(k , [cipher text i-1 XOR plain text i-1] )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/blockciphermodesofoperationpresentation-150831143925-lva1-app6892/75/Block-cipher-modes-of-operation-22-2048.jpg)
![Cipher output feedback mode
Decryption
IV = initialization vector
Plain texti =
cipher texti XOR Encryption
(k , [cipher text i-1 XOR plain text i-1] )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/blockciphermodesofoperationpresentation-150831143925-lva1-app6892/75/Block-cipher-modes-of-operation-23-2048.jpg)