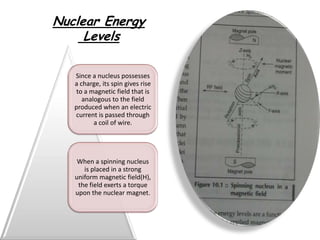
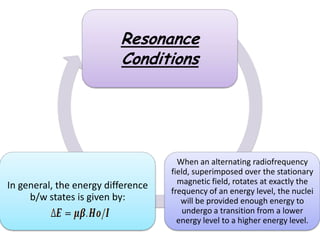
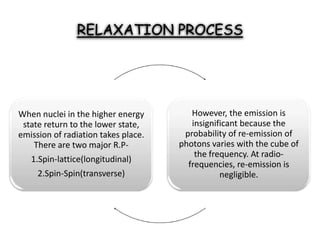
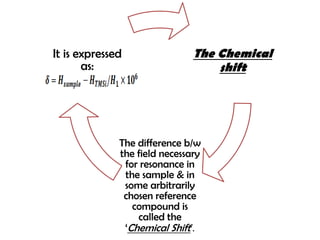
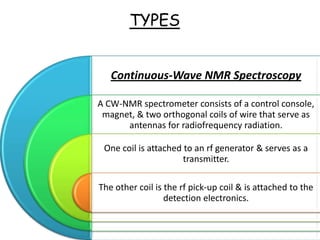
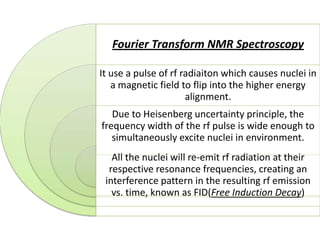
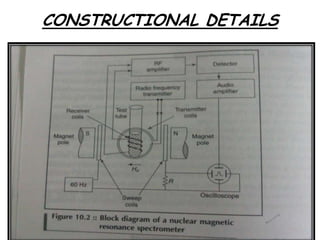
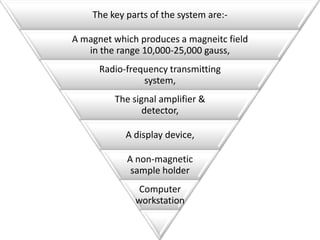
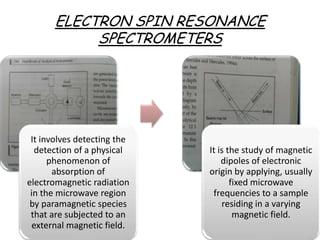
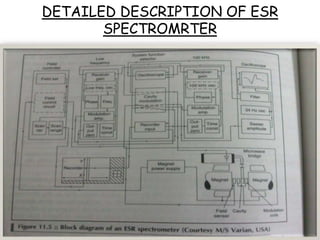
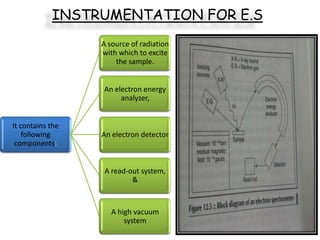
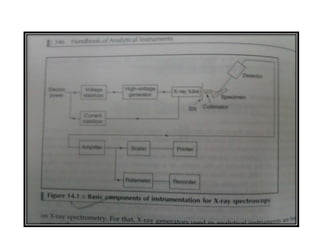
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy is a powerful technique for chemical analysis that involves the absorption of radiofrequency radiation by atomic nuclei in a magnetic field. It is useful for determining molecular structures and understanding how molecules function. The technique works by exciting atomic nuclei to higher energy states using radiofrequency pulses in a strong magnetic field. As the nuclei relax back to lower energy states, they emit radiofrequency signals that can be analyzed to provide information about molecular structure. NMR spectroscopy is widely used across many fields due to its applicability to a variety of sample sizes.