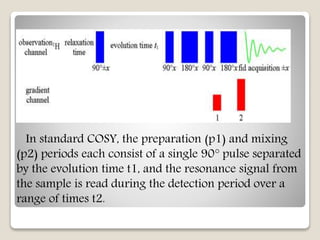
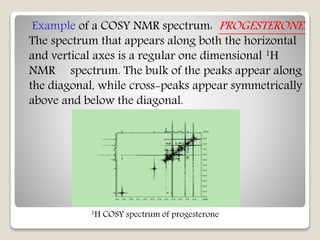
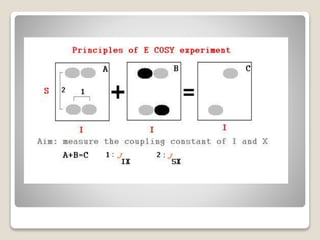
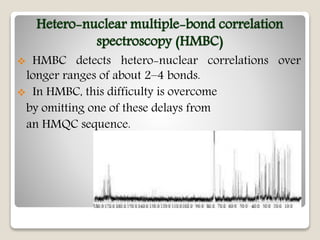
The document discusses two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (2D NMR). 2D NMR provides more structural information about molecules than 1D NMR. There are several types of 2D NMR experiments that provide different information, including COSY, TOCSY, HSQC, and NOESY. These experiments establish correlations between nuclei that are directly bonded or spatially close. 2D NMR is useful for determining molecular structures, especially of complex biomolecules like proteins.