Theory of NMR (Ashis).pptx
•
0 likes•15 views
The document provides an overview of the theory of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. It discusses how nuclei with spin absorb electromagnetic radiation when placed in a magnetic field, creating distinct energy levels. When radio waves are applied at the resonance frequency, transitions between spin states occur, producing signals in the NMR spectrum. Chemical shifts arise from electrons shielding or deshielding nuclei from the magnetic field in different ways. Neighboring protons cause splitting of peaks according to spin-spin coupling rules.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
Recommended
Prabhakar Singh- II_SEM-Paper V_NMR and EPR SpectroscopyPrabhakar singh ii sem-paper v-nmr and epr spectroscopy

Prabhakar singh ii sem-paper v-nmr and epr spectroscopyDepartment of Biochemistry, Veer Bahadur Singh Purvanchal Univarsity, Jaunpur
More Related Content
Similar to Theory of NMR (Ashis).pptx
Prabhakar Singh- II_SEM-Paper V_NMR and EPR SpectroscopyPrabhakar singh ii sem-paper v-nmr and epr spectroscopy

Prabhakar singh ii sem-paper v-nmr and epr spectroscopyDepartment of Biochemistry, Veer Bahadur Singh Purvanchal Univarsity, Jaunpur
Similar to Theory of NMR (Ashis).pptx (20)
Prabhakar singh ii sem-paper v-nmr and epr spectroscopy

Prabhakar singh ii sem-paper v-nmr and epr spectroscopy
NMR, principle, chemical shift , valu,13 C, application

NMR, principle, chemical shift , valu,13 C, application
Recently uploaded
Recently uploaded (20)
A Giant Impact Origin for the First Subduction on Earth

A Giant Impact Origin for the First Subduction on Earth
Gliese 12 b: A Temperate Earth-sized Planet at 12 pc Ideal for Atmospheric Tr...

Gliese 12 b: A Temperate Earth-sized Planet at 12 pc Ideal for Atmospheric Tr...
Astronomy Update- Curiosity’s exploration of Mars _ Local Briefs _ leadertele...

Astronomy Update- Curiosity’s exploration of Mars _ Local Briefs _ leadertele...
Earliest Galaxies in the JADES Origins Field: Luminosity Function and Cosmic ...

Earliest Galaxies in the JADES Origins Field: Luminosity Function and Cosmic ...
FAIRSpectra - Towards a common data file format for SIMS images

FAIRSpectra - Towards a common data file format for SIMS images
BLOOD AND BLOOD COMPONENT- introduction to blood physiology

BLOOD AND BLOOD COMPONENT- introduction to blood physiology
The importance of continents, oceans and plate tectonics for the evolution of...

The importance of continents, oceans and plate tectonics for the evolution of...
platelets- lifespan -Clot retraction-disorders.pptx

platelets- lifespan -Clot retraction-disorders.pptx
Mammalian Pineal Body Structure and Also Functions

Mammalian Pineal Body Structure and Also Functions
SAMPLING.pptx for analystical chemistry sample techniques

SAMPLING.pptx for analystical chemistry sample techniques
Musical Meetups Knowledge Graph (MMKG): a collection of evidence for historic...

Musical Meetups Knowledge Graph (MMKG): a collection of evidence for historic...
National Biodiversity protection initiatives and Convention on Biological Di...

National Biodiversity protection initiatives and Convention on Biological Di...
Predicting property prices with machine learning algorithms.pdf

Predicting property prices with machine learning algorithms.pdf
GLOBAL AND LOCAL SCENARIO OF FOOD AND NUTRITION.pptx

GLOBAL AND LOCAL SCENARIO OF FOOD AND NUTRITION.pptx
Theory of NMR (Ashis).pptx
- 1. Theory of NMR Name -Ashis Kumar Dash Regd no- 210705100034
- 2. Outline • Introduction • Theory of NMR • Energy levels of nucleus in applied magnetic field • Role of radio frequency • Chemical shift • Shielding and Deshielding • Downfieild shift • General principles for spin – spin interactions
- 3. Introduction • Nuclear magnetic resonance involves absorption of electromagnetic radiation in the radio frequency region. • Absorption of radiowaves in the presence of magnetic field is accompanied by a special type of nuclear transition,and for this reason we call this type of spectroscopy nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. • NMR was first discovered in 1946 by F.Bloch (Stanford University) and E.M Purcell of (Havard University). They shared noble prize in 1952 for this discovery.
- 4. Theory • All the nuclei carry positive charge. Each proton and neutron inside the nucleus have their own spin about their axis,and give rise to a resultant spin of the nucleus called nuclear spin. • All nuclei carry a charge , since a charged particle spinning around its axis gives rise to a magnetic moment and generates a magnetic field. • When such nuclei placed in an applied magnetic field, magnetic interaction takes place (i.e –attrraction / repulsion) leading to creation of magnetic energy levels in the nuclei. • The proton and neutron each has spin ½ , thus the nuclear spin is the resultant spin of protons and neutrons. Ex- Deuteron contains one proton and neutron. (⇈) or (⇵) Nuclear spin=1 ↲ ↳ Nuclear spin =0
- 5. (a) Nucleus which doesn’t have mechanical spin, i.e – Spin quantum number(I)=0. Such nucleus has no magnetic properties. (b) Nuclei having either an odd number of protons or an odd number of neutrons, exhibit half integral I. i.e – I=1/2, 3/2, 5/2 . (c) Odd proton and odd neutrons, exhibits integral spin quantum no- 1,2,3 etc. (d) Even proton and neutrons have no angular momentum(I=0), have no magnetic properties.
- 6. Energy levels of a spinning nucleus in an applied magnetic field • Spinning nucleus (I>0) acts as a tiny magnet. When such nucleus is placed in magnetic field , magnetic interaction takes place and magnetic energy levels are created. • Without applied magnetic field, the spin states of nuclei are degenerate and energy level transition doesn’t arise. • Magnetic nucleus can take up different energy levels or orientations with respect to the direction of applied field. • For a nucleus, there are (2I+1) possible orientations. Ex- For Hydrogen the spin quantum no(I)=1/2.when it is placed in a magnetic field of strength (Ho) have orientations (2×1/2+1)=2.(i.e.-1/2 and +1/2). - Among these two types of orientations one is parallel orientation (low energy state /magnetic moment is alligned parallel with the field). Another one is anti parallel (high energy state / magnetic moment is against the applied field).
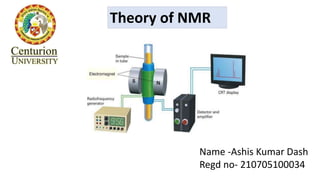
- 8. Role of radio frequency on the spinning nucleus • Spinning nucleus under the influence of the applied magnetic field rotates about it’s axis at a definite frequency. • When an alternating radio frequency field is applied to the spinning nucleus at right angle to the applied field, if the radio frequency is exactly equal to the frequency of the spinning nucleus , then these frequencies are said to be in resonance ( resonance frequency). • In the state of resonance, absorption or emission of the radiation takes place by the nucleus which leads to transition between nuclear spin states. The absorbed frequency flips the nucleus from low energy spin state to high energy spin state. This absorption process produces a signal which is recorded as a band in the spectrum called the NMR spectrum.
- 9. • Chemical shift – Nuclei are essential parts of molecules held together by the electrons of-the chemical bonds.The magnetic field at which a free or ‘bare’ nucleus resonates is quite different from the field at which the same nucleus in a molecule resonates. Electrons in a molecule affects the NMR.The electrons may shield or dishield a nucleus from the applied magnetic field. The difference between the magnitude of magnetic field at which a free nuclei and a molecular nuclei resonate is called chemical shift. • Shielding and Deshielding of protons – A bare or pure proton when exposed to a radio frequency, it flips it’s spin from lower energy level(⇈) to a higher energy level (⇵). However all the protons don’t flip their spin. The magnetic field “sensed” by the nucleus isn’t same as the applied magnetic field. • The electrons present near to the bond / protons induce their own magnetic field, which may reinforce or oppose the applied magnetic field.
- 10. General rules for spin spin interactions- • Protons of the same group don’t interact with each other to give splitting signal. Ex- 3 protons in the -CH3 group don’t interact with each other. • The multiplicity of a peak of group of equivalent protons is determined by the neighbouring protons. If “n” number of protons present in the adjacent carbon atom then the peak split into (n+1) signals. • The intensities of the peak are symmetric at the mid point. Pascal’s triangle formed. Downfield shift – most of the organic Compounds are less shielded than those of TMS and therefore require less energy for resonance. Thus the peaks appear at lower fields or downfields of the TMS reference peak.
- 13. Thank you