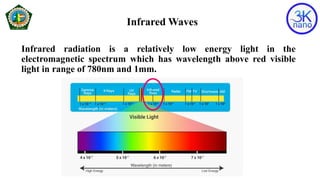
FTIR spectroscopy is a technique that uses infrared radiation to identify chemical bonds in molecules. An FTIR spectrometer simultaneously collects high-resolution spectral data over a wide spectral range. When molecules are exposed to infrared radiation, they selectively absorb specific wavelengths that cause molecular vibrations. This produces a characteristic infrared absorption spectrum that acts as a molecular fingerprint. The positions of absorption peaks in the spectrum correspond to the energies of bond vibrations and can be used to determine a sample's chemical composition and structure.