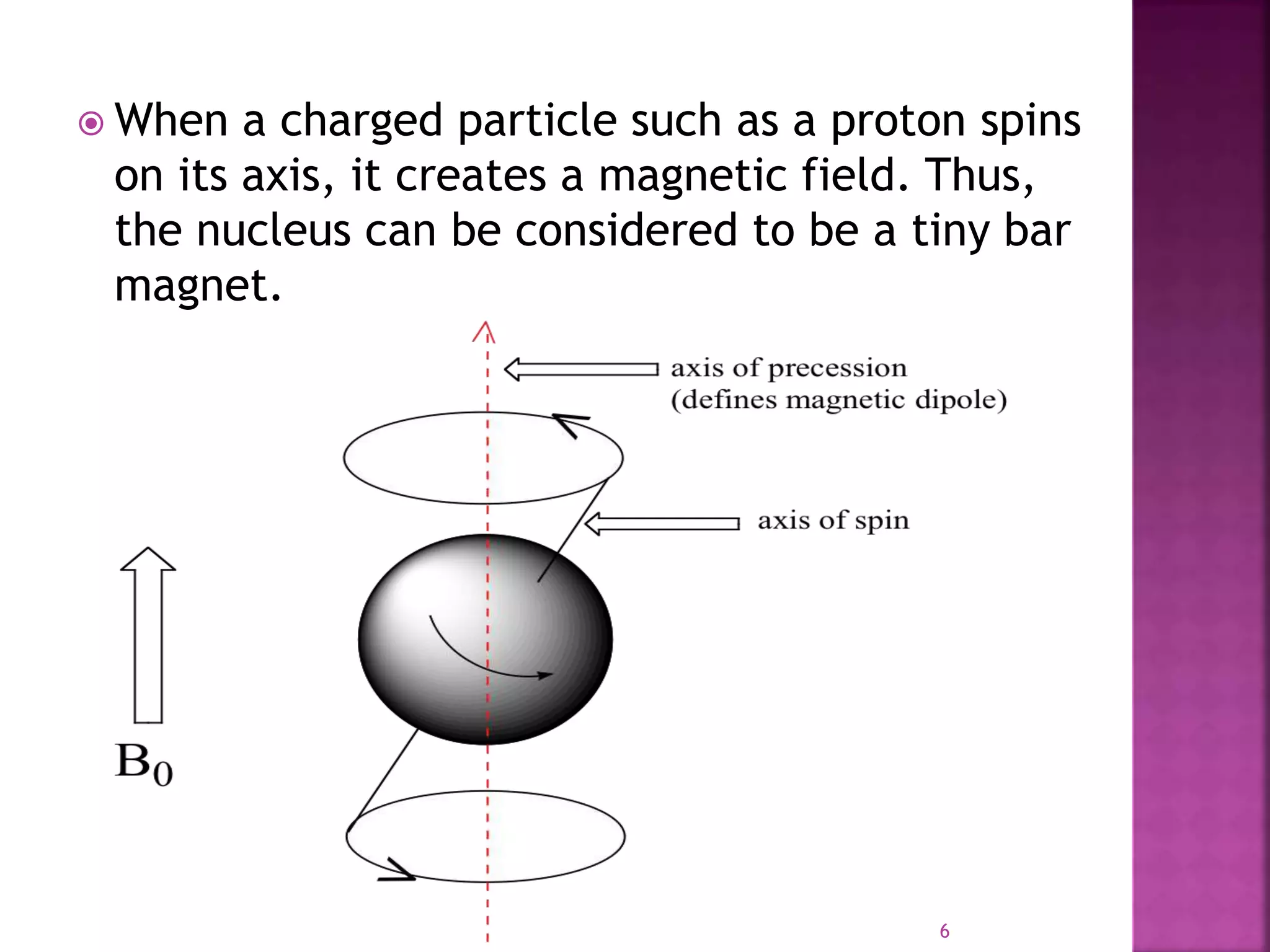
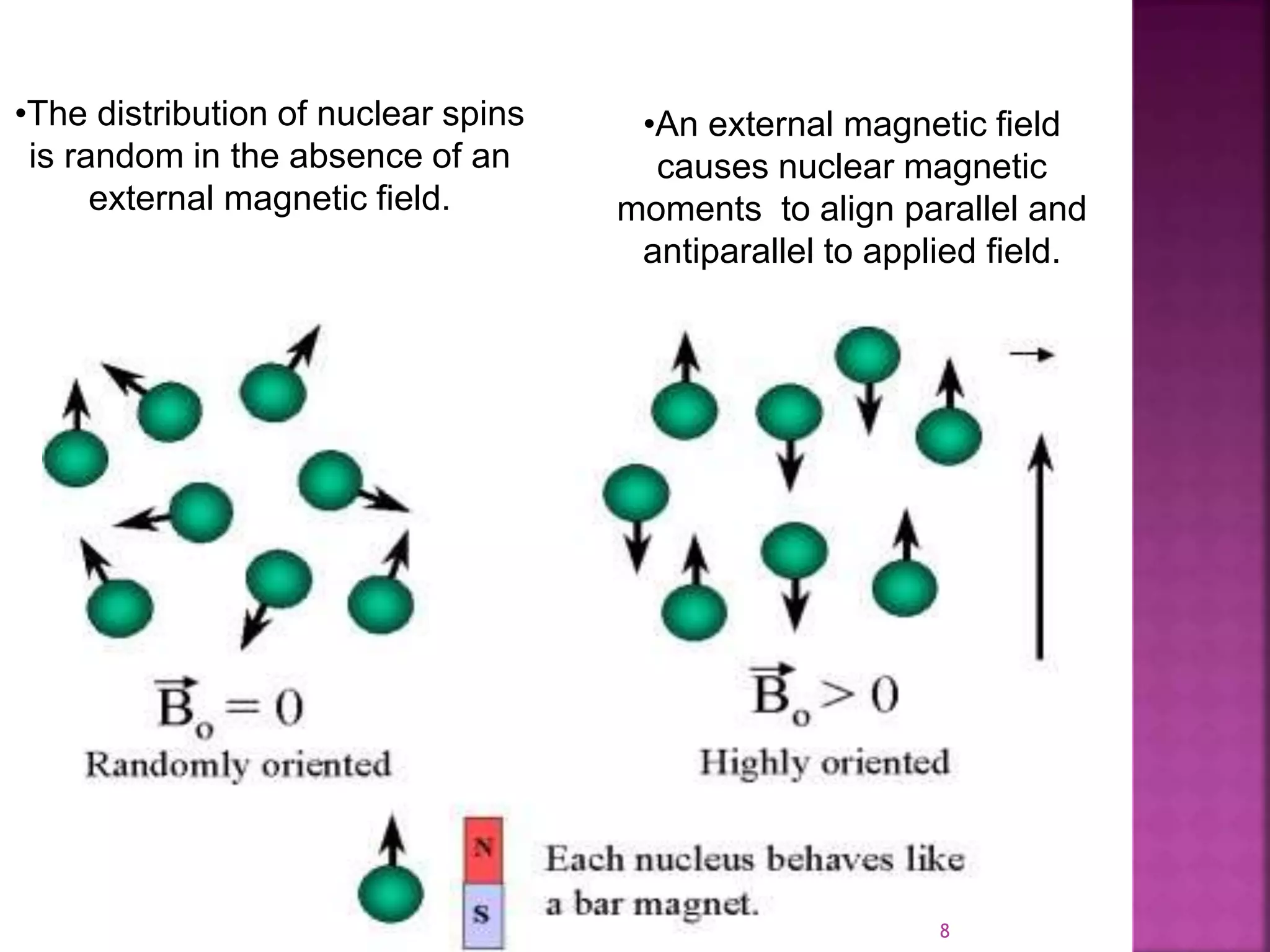
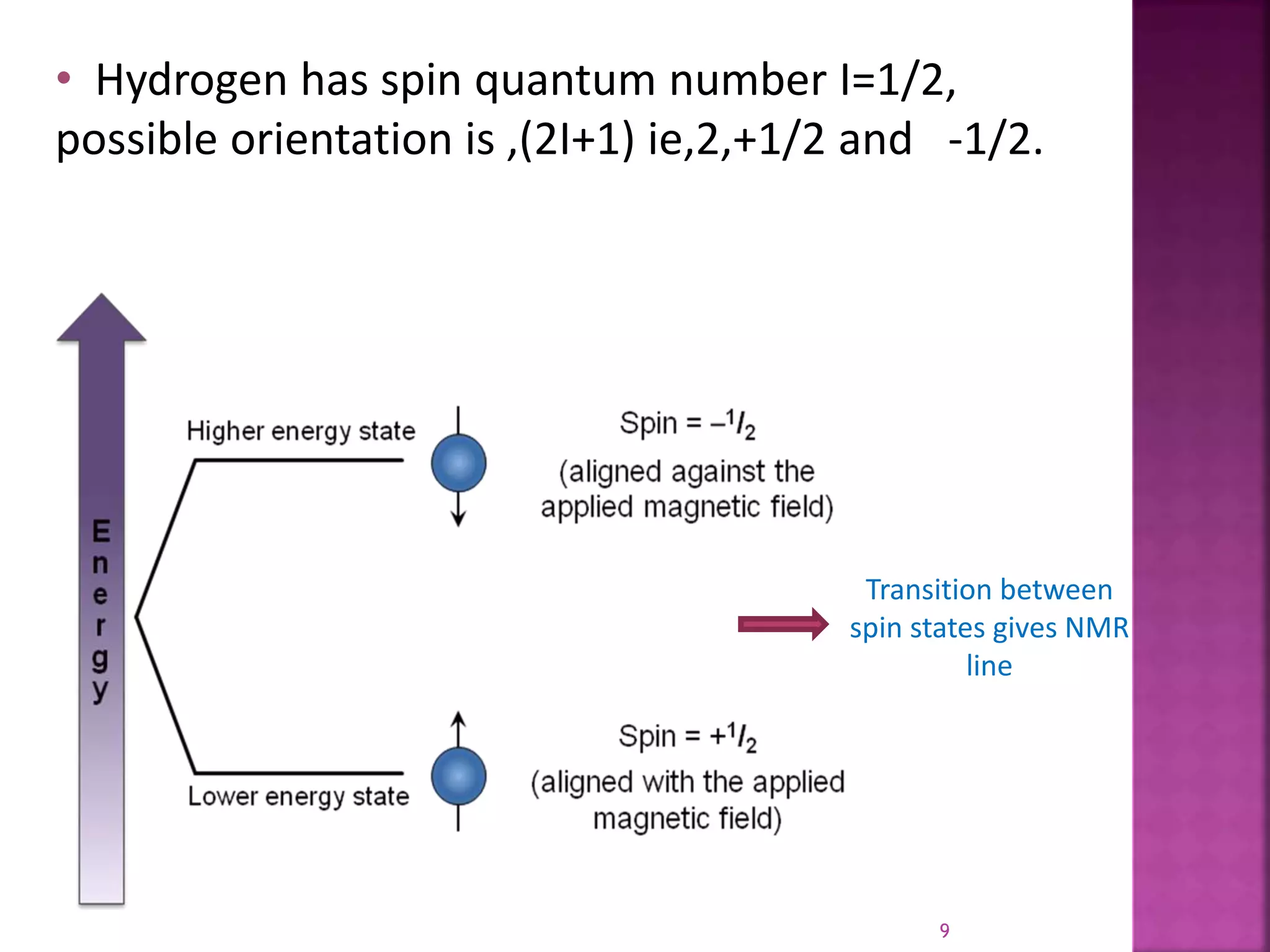
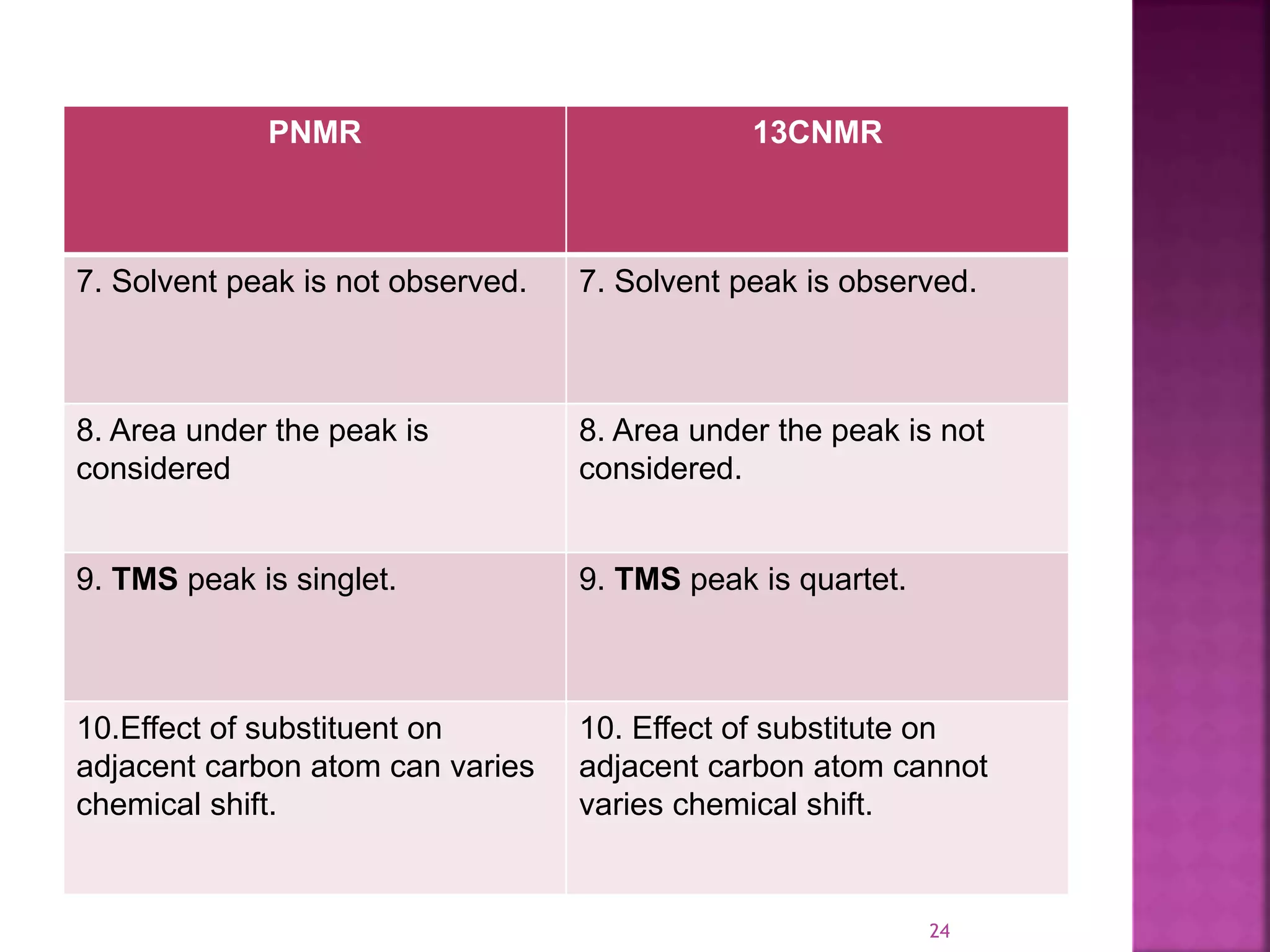
Proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (PNMR) is described. PNMR involves absorbing radiofrequency radiation by proton nuclei in a strong magnetic field. It is used to determine the type and number of hydrogen atoms in a molecule. The chemical shift range is 0-14 ppm and splitting is seen between non-equivalent protons. PNMR provides information on molecular structure and hydrogen bonding. Applications include structure elucidation of organic compounds, polymers, and biomolecules. Differences between PNMR and carbon-13 NMR are also outlined.