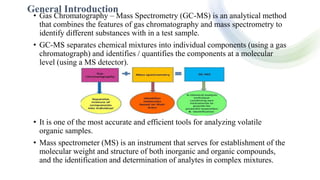
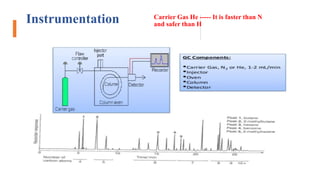
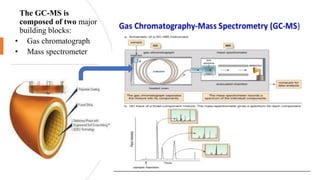
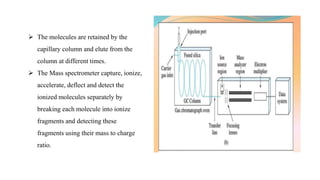
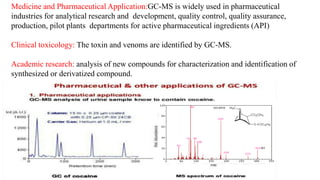
The document discusses hyphenated techniques in drug analysis, particularly the combination of gas chromatography and mass spectrometry (GC-MS). It explains the advantages of these techniques for fast, accurate analysis and their applications in various fields such as food analysis, environmental monitoring, and pharmaceuticals. Additionally, it covers the principles and instrumentation of GC-MS, emphasizing its effectiveness in identifying and quantifying substances.