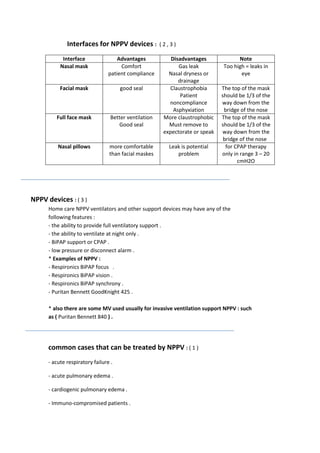
Non-invasive positive pressure ventilation (NPPV) provides ventilatory support without an endotracheal or tracheostomy tube. It uses inspiratory positive airway pressure and expiratory positive airway pressure to assist breathing. NPPV includes continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) and bilevel positive airway pressure (BiPAP). NPPV is used to treat acute and chronic respiratory failure, obstructive sleep apnea, and exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. It has advantages over invasive ventilation such as allowing speaking and swallowing. Common interfaces include nasal and full face masks. NPPV is delivered via home ventilators that can provide various modes and controls.