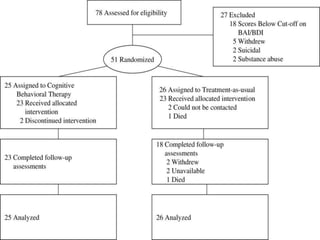
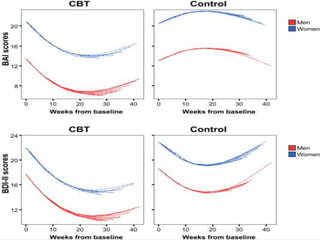
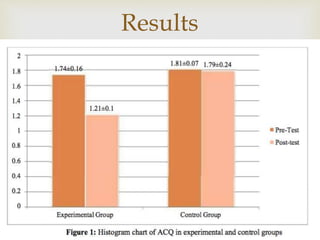
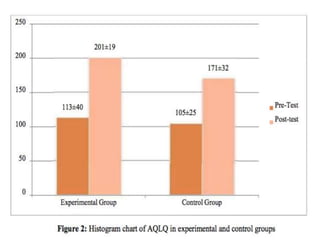
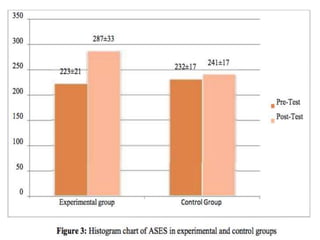
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a psychotherapy that addresses maladaptive thoughts and behaviors, aiming to improve emotional well-being by promoting positive changes. It has shown effectiveness in treating anxiety and depression in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma, highlighting the need for mental health integration in medical care. Various techniques such as modeling and computer-assisted therapy are utilized in CBT, contributing to significant symptom relief and improved psychological outcomes.