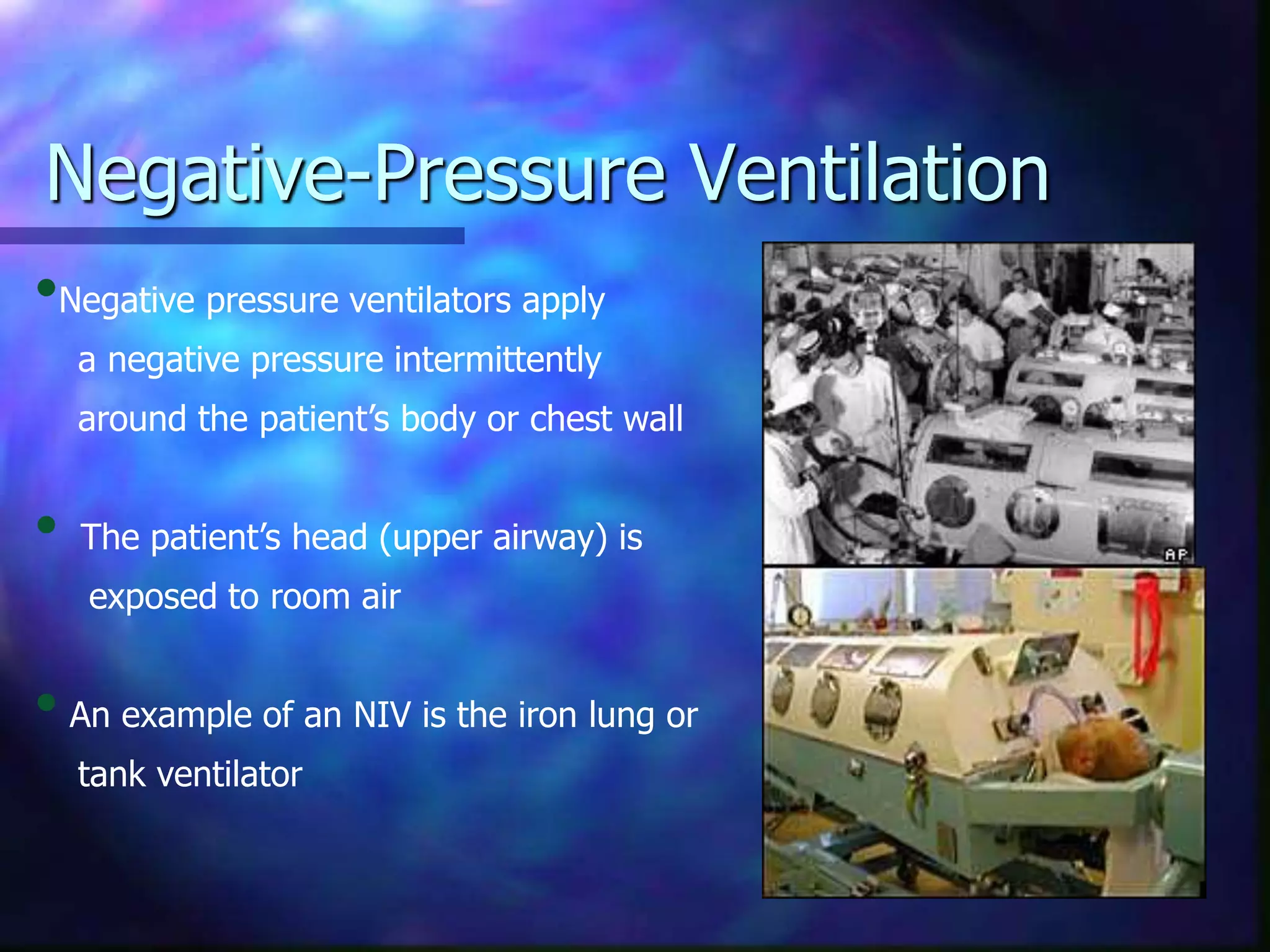
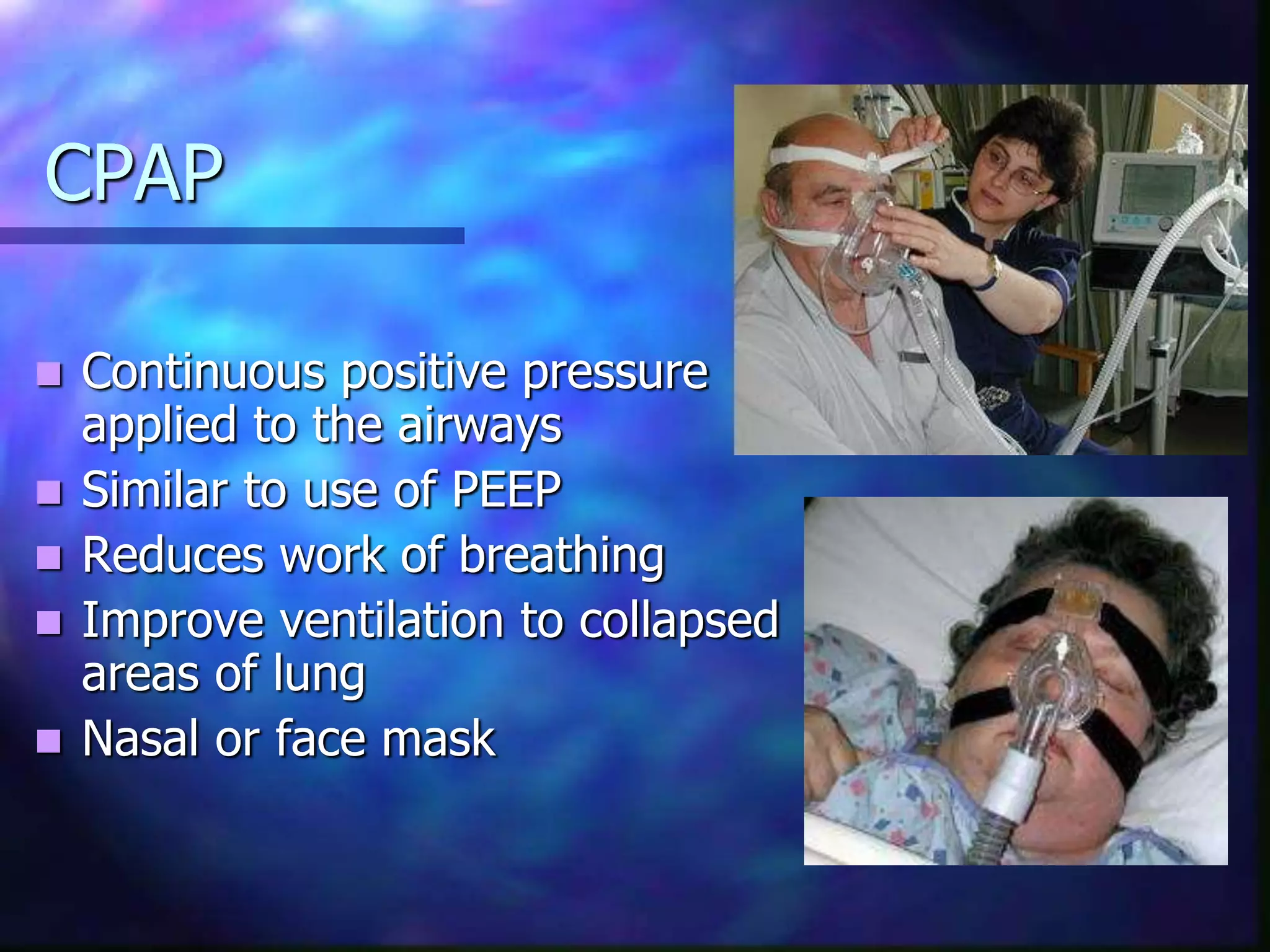
Non-invasive ventilation (NIV) delivers ventilatory support without an invasive artificial airway. It has benefits over invasive ventilation like preserving airway function and reducing risks. NIV is indicated for exacerbations of COPD, respiratory failure, cardiac pulmonary edema, and other conditions. Contraindications include coma, inability to protect airway. NIV includes CPAP, bilevel PAP and negative pressure devices. Settings are tailored to the condition but aim to reduce work of breathing and improve ventilation and oxygenation without overdistending the lungs. Response is monitored closely and NIV may be switched to invasive support if the patient deteriorates.