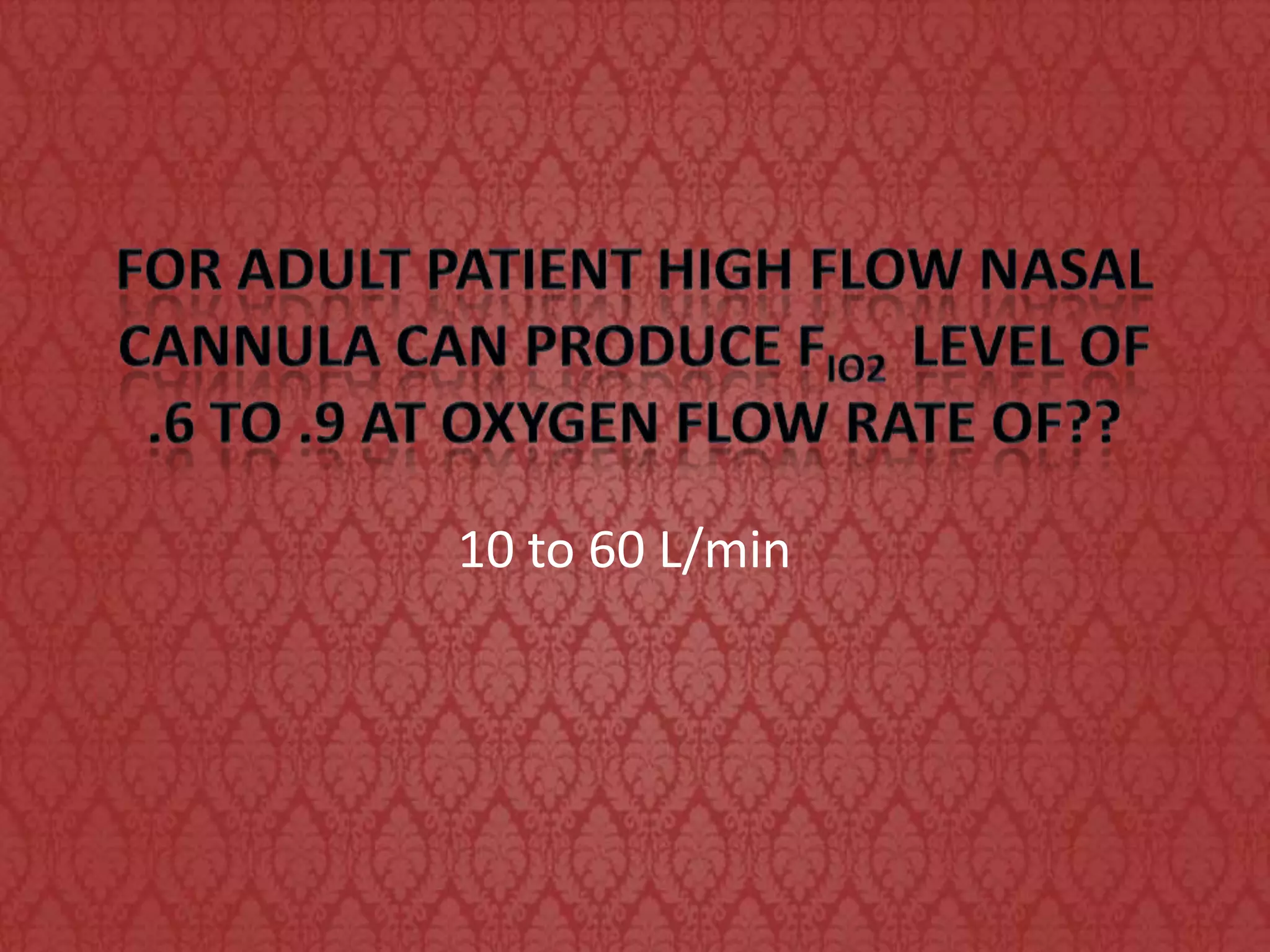
The document discusses high flow nasal cannula (HFNC) therapy, its components, benefits, and applications in respiratory care for adults and infants. It highlights the importance of humidified oxygen delivery for improved patient outcomes and comfort, as well as the evolution of equipment used for this therapy. Additionally, it contrasts HFNC with low flow nasal cannula therapy (LFNC) regarding cost and performance.