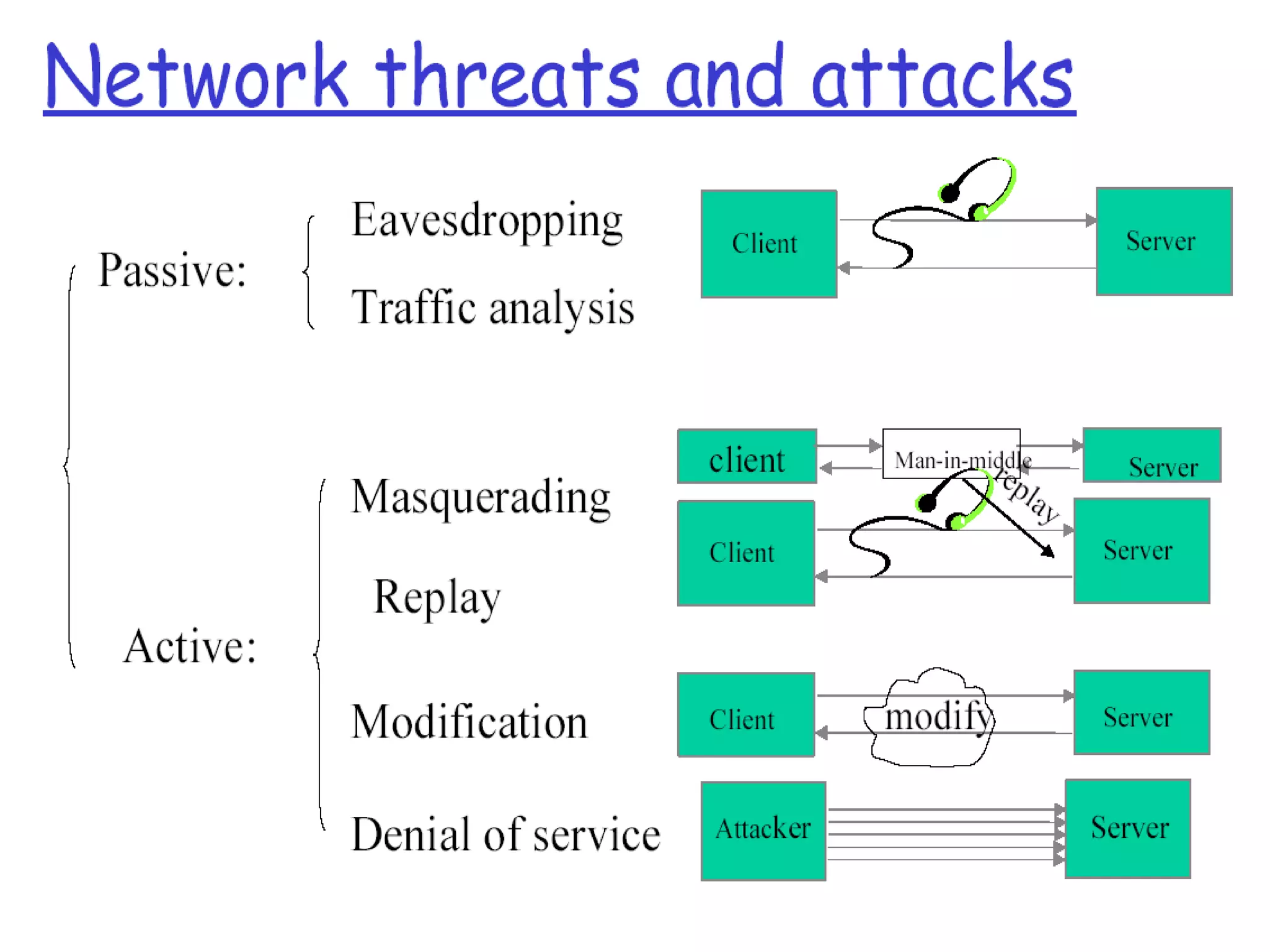
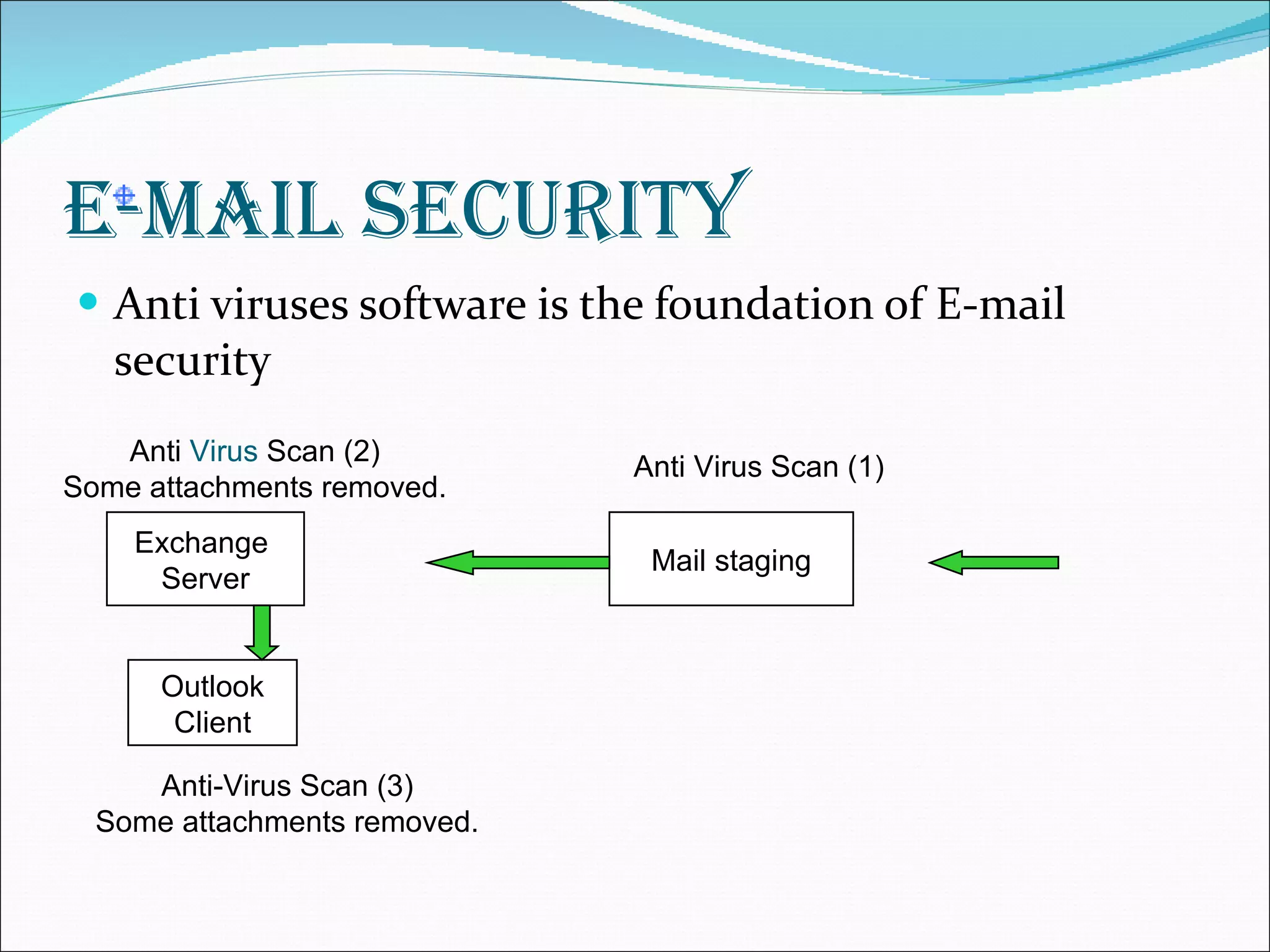
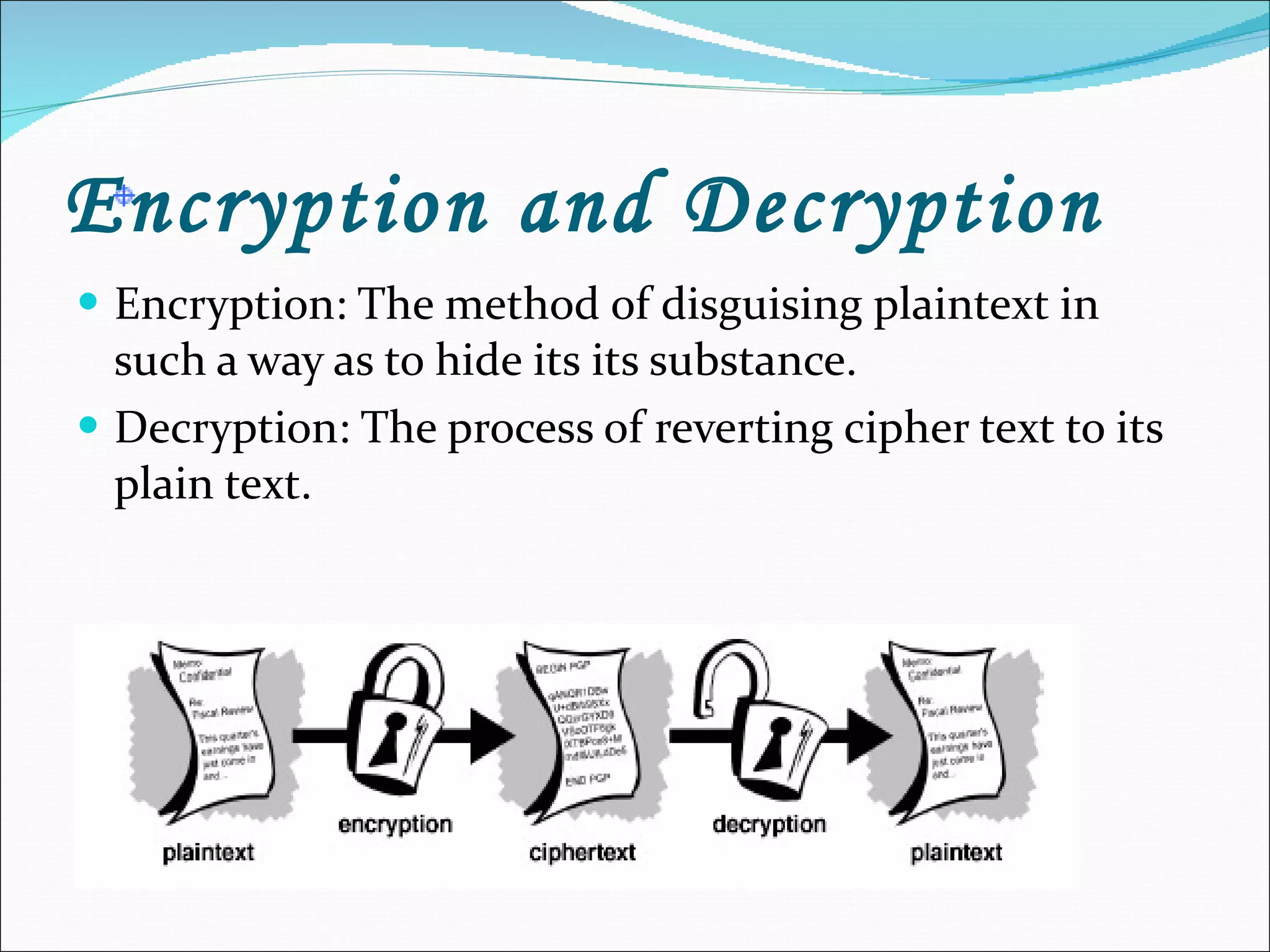
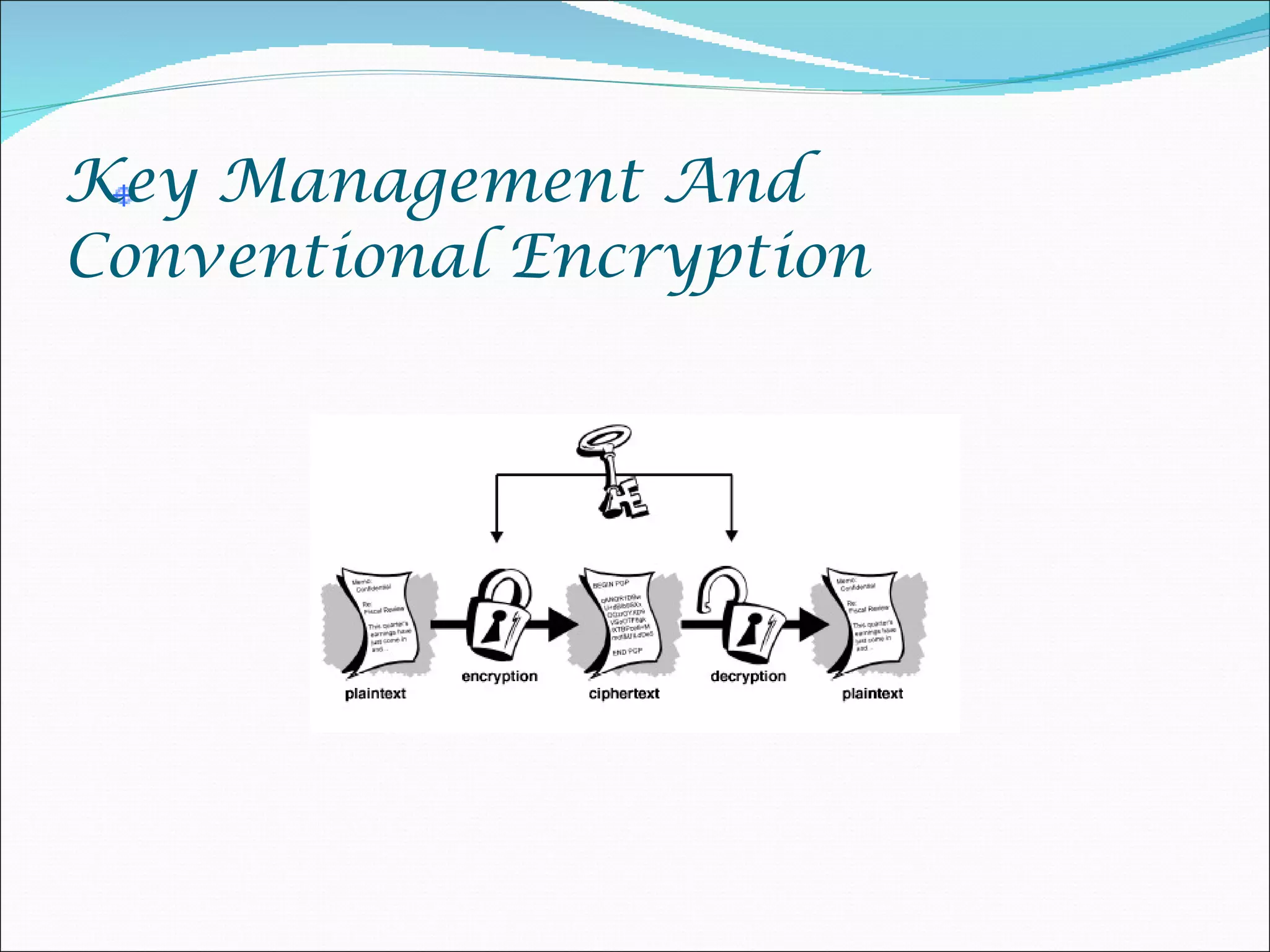
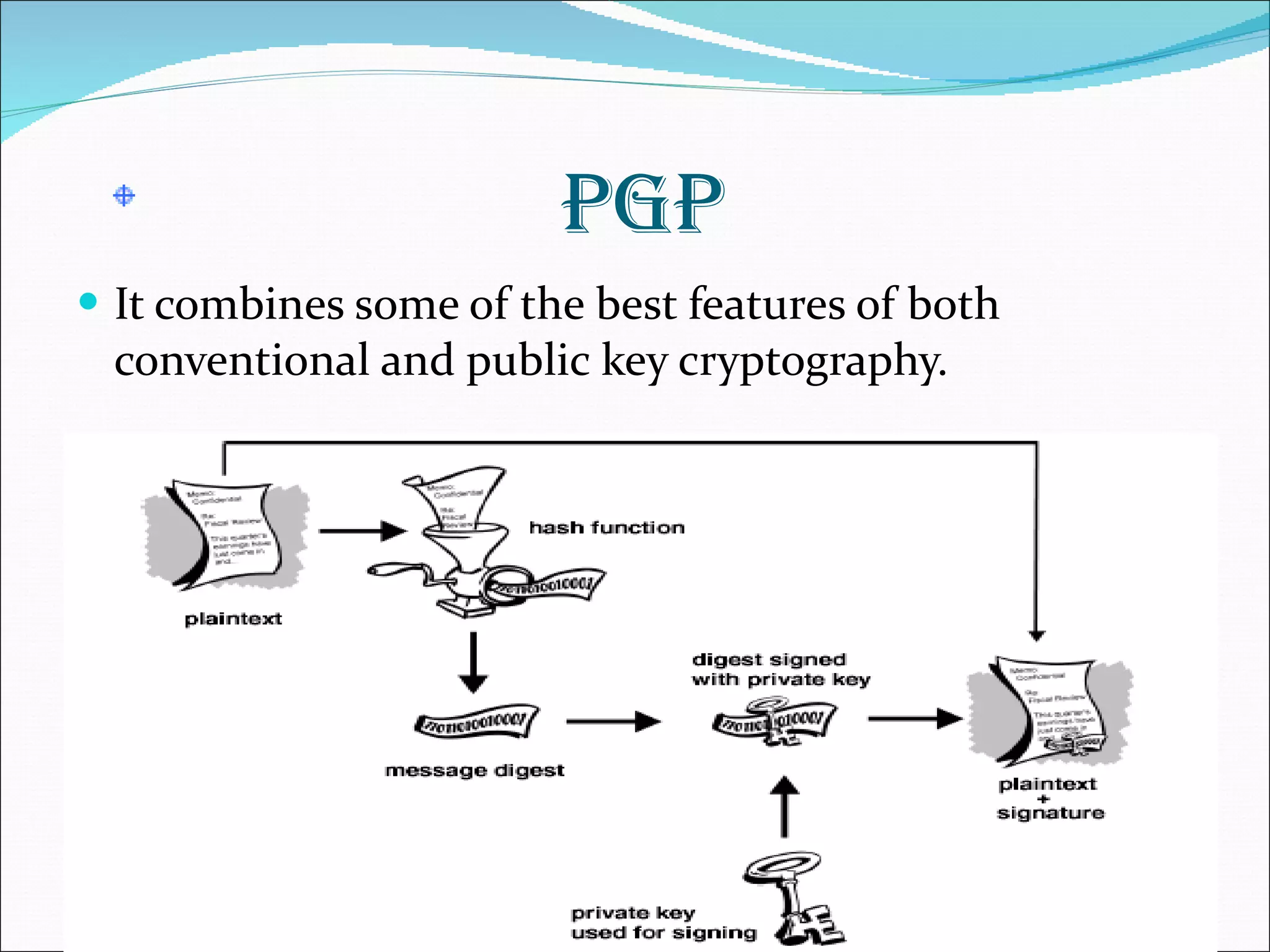
The document discusses various aspects of network and computer security. It covers topics like password security guidelines, email security measures using antivirus software, evolving online threats like blended attacks and identity theft. It also explains cryptography concepts like encryption, decryption, conventional and public key cryptography. Security is a shared responsibility and requires cooperation from everyone through intelligent policies and consistent practices.