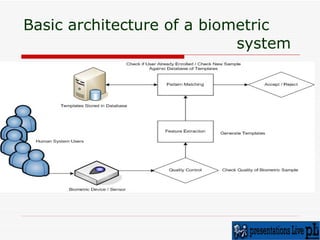
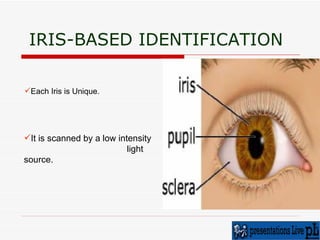
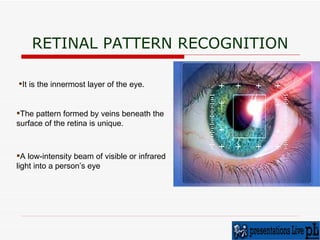
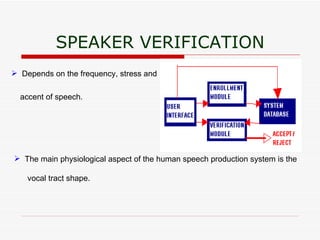
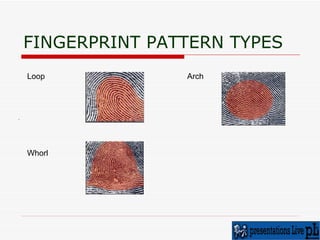
The document discusses various biometric techniques for identifying individuals, including fingerprint recognition, hand geometry analysis, iris scanning, retinal pattern recognition, facial recognition, signature analysis, and speaker verification. It provides a brief history of biometrics and describes the basic components of a biometric system. Fingerprint recognition is described as the oldest technique, examining ridge and furrow patterns. Factors like pressure and skin condition affect fingerprint scanning accuracy. Multimodal biometrics that combine techniques can provide more reliable identification. Biometrics have various applications and also some drawbacks depending on the specific technique used.











![REFERENCES [Bigun, 1997] Bigun, E.S., J. Bigun, Duc, B.: “Expert conciliation for multi modal person authentication systems by Bayesian statistics,” In Proc. 1st Int. Conf. On Audio Video-Based Personal Authentication [Brunelli et al, 1995] R. Brunelli, and D. Falavigna, "Personal identification using multiple cues," IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence. [Dieckmann]Dieckmann, U.Plankensteiner, P., and Wagner, T.: “SESAM: A biometric person identification system using sensor fusion,” In Pattern Recognition Letters, Vol. 18, No. 9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spatternmatchingusingbiometrictechniques-101227075922-phpapp02/85/Spattern-matching-using-biometric-techniques-21-320.jpg)

