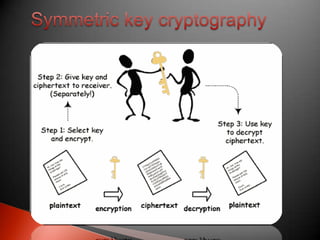
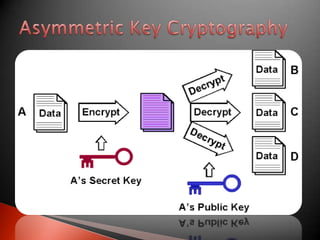
The document discusses the importance of securing information in the digital age. It states that information is a valuable asset that needs to be hidden from unauthorized access (confidentiality), protected from unauthorized changes (integrity), and available when needed (availability). It then discusses some key aspects of computer security including confidentiality, authentication, message integrity, and access/availability. The document goes on to define network security and some common network security threats. It lists components used for network security like antivirus software, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems. Finally, it briefly discusses encryption techniques including symmetric key algorithms and asymmetric/public-private key algorithms.