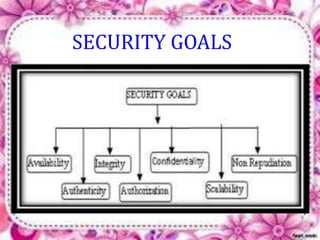
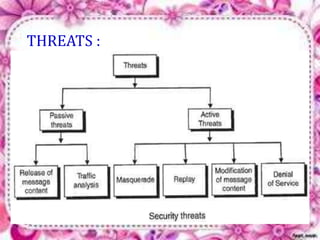
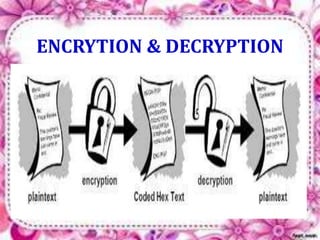
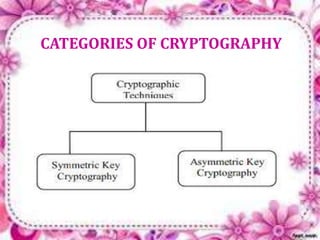
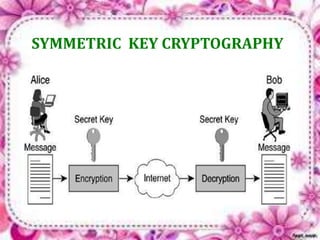
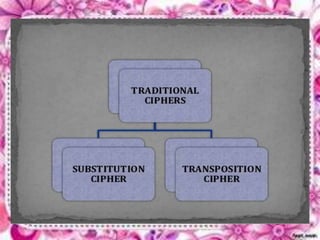
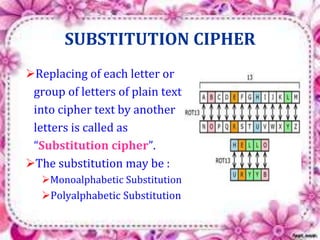
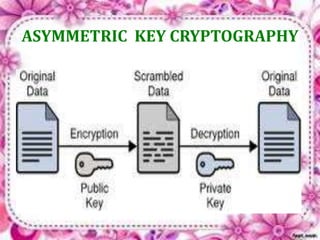
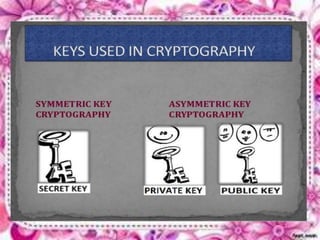
This document discusses network security and cryptography. It begins by defining a network and some common network threats. It then discusses network security goals like avoiding denial of service attacks. The document outlines different cryptography techniques like symmetric and asymmetric key cryptography. Symmetric cryptography uses a shared key while asymmetric uses public and private keys. Specific algorithms like RSA and DES are described. The document proposes combining numerals and alphabets in encryption to increase security. It concludes cryptography can securely hide and transmit data through encryption and decryption.
![NETWORK SECURITY
CRYPTOGRAPHY
Presented BY
Sankari.P(B.Sc[CS] S/F)
Sadakathullah Appa College
Tirunelveli -11.
Guided by:
Mrs.J .Jannathul Firthous ,M.sc,M.phil](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/network-141012234335-conversion-gate01/75/Network-security-and-cryptography-1-2048.jpg)