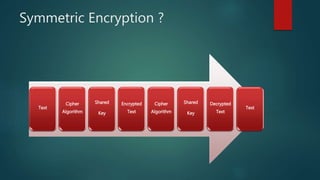
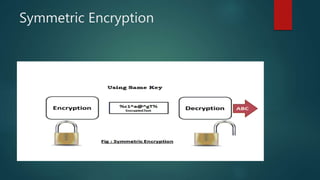
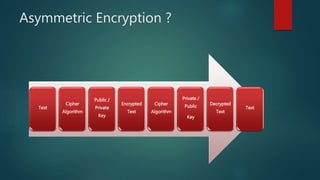
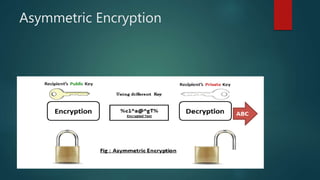
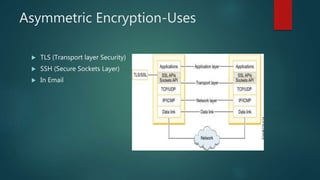
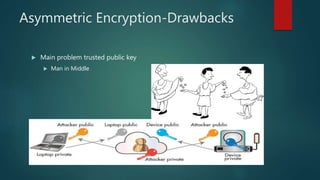
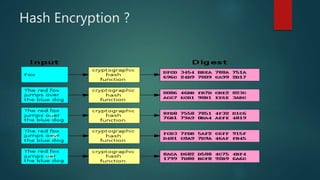
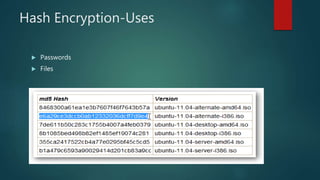
The document outlines types of encryption, specifically symmetric and asymmetric encryption, along with their uses and drawbacks. It also explains hashing, its properties, uses, and distinctions from encryption. The discussion highlights the challenges associated with each method, such as key management and security vulnerabilities.