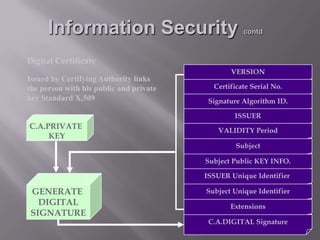
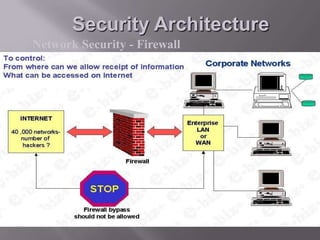
This document discusses information security and provides definitions and concepts related to protecting information systems. It defines information security as measures taken to protect information from unauthorized access, modification, or denial of service. It then outlines key aspects of information security management including security policies, risk analysis, contingency planning and more. Finally, it describes various information security threats like viruses, Trojan horses, and worms as well as methods of protecting information systems through encryption, authentication, firewalls, and other technical controls.