Embed presentation

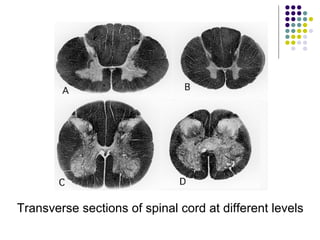
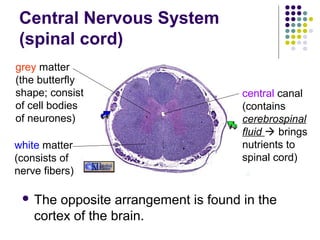
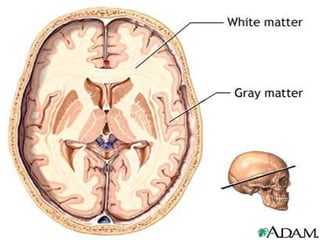
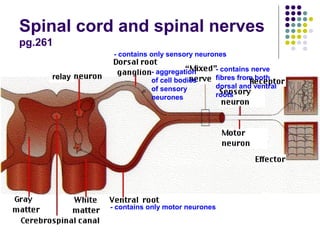

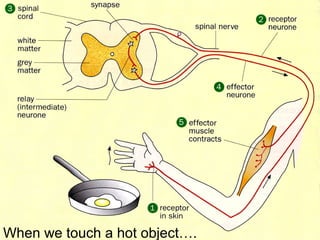


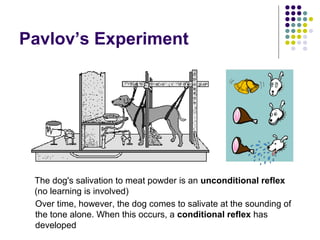
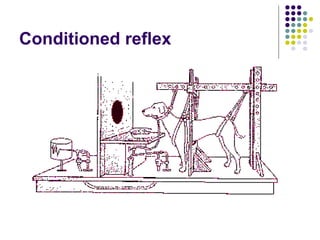


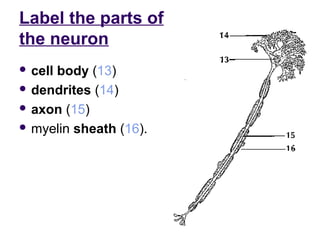
The document summarizes key aspects of the central nervous system, including: 1) The spinal cord contains grey matter on the inside consisting of neuron cell bodies, and white matter on the outside consisting of nerve fibers. 2) Reflex actions are immediate responses to a specific stimulus without conscious control, such as the knee jerk reflex. 3) A reflex arc consists of a receptor, sensory neuron, reflex center in the spinal cord or brain, motor neuron, and effector muscle or gland. 4) A conditioned reflex is a learned response acquired through experience that was originally not an effective stimulus, such as Pavlov's experiment where dogs learned to salivate at the sound of a tone through association with food.













