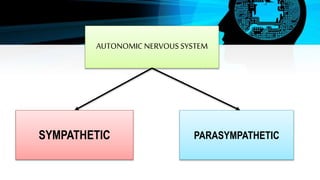
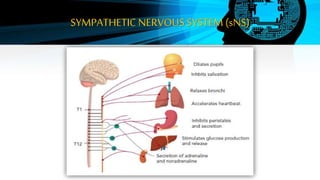
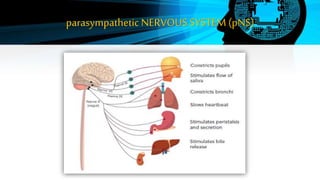
The document discusses the autonomic nervous system (ANS), which regulates involuntary body functions. The ANS has two divisions - the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. The sympathetic system activates the body's fight or flight response and increases functions like heart rate. The parasympathetic system calms the body and increases functions like digestion when the body is at rest.