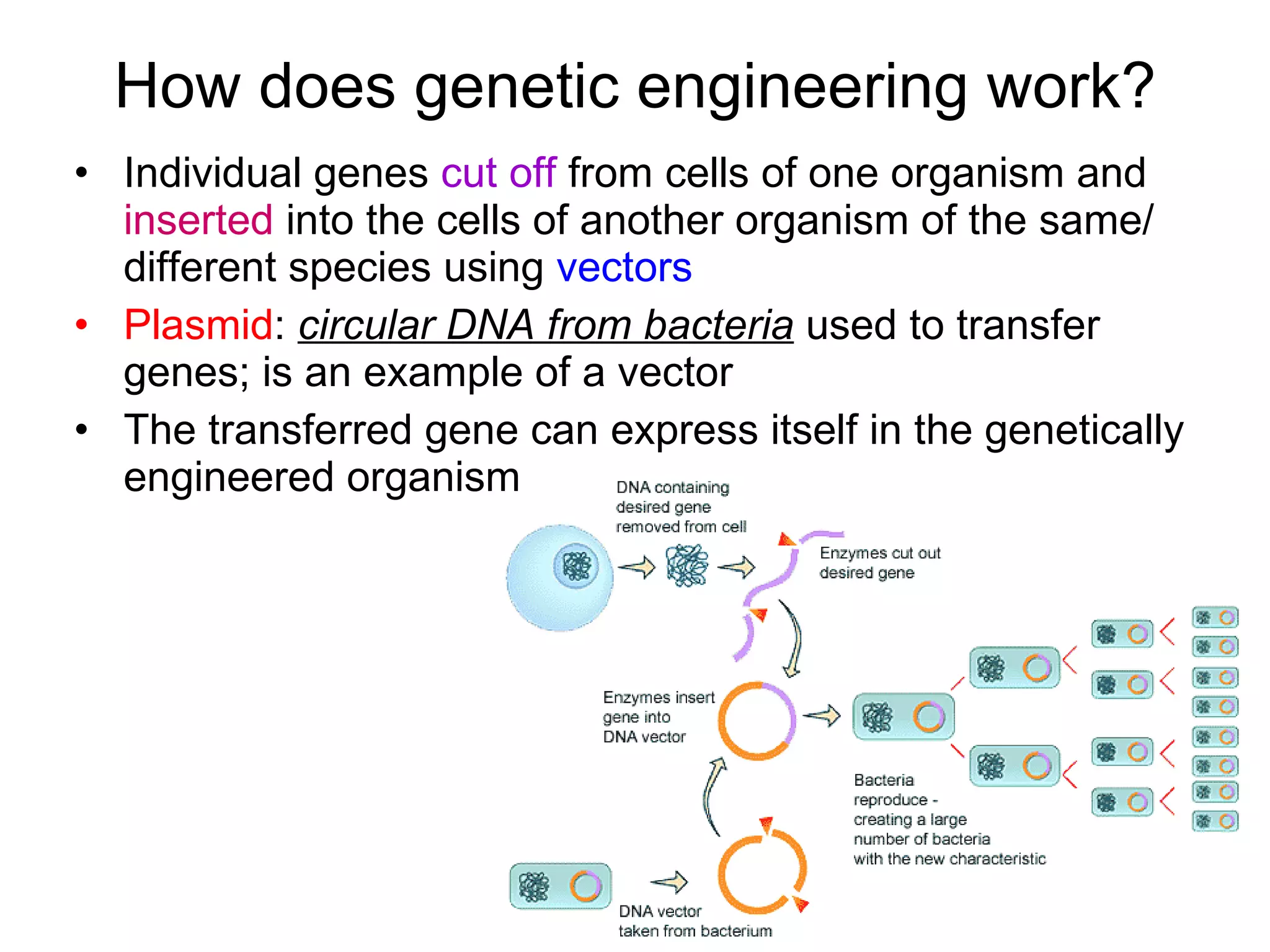
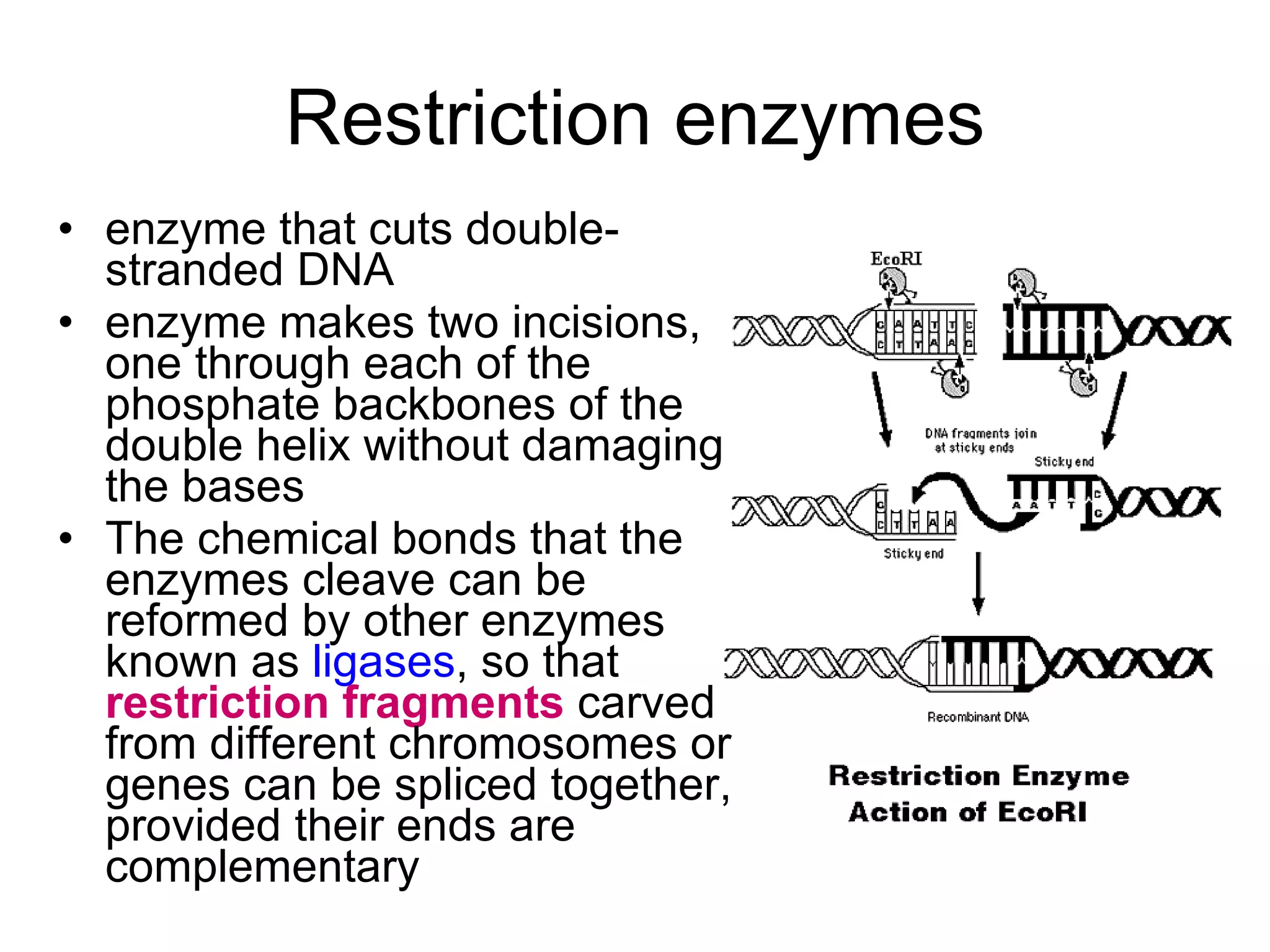
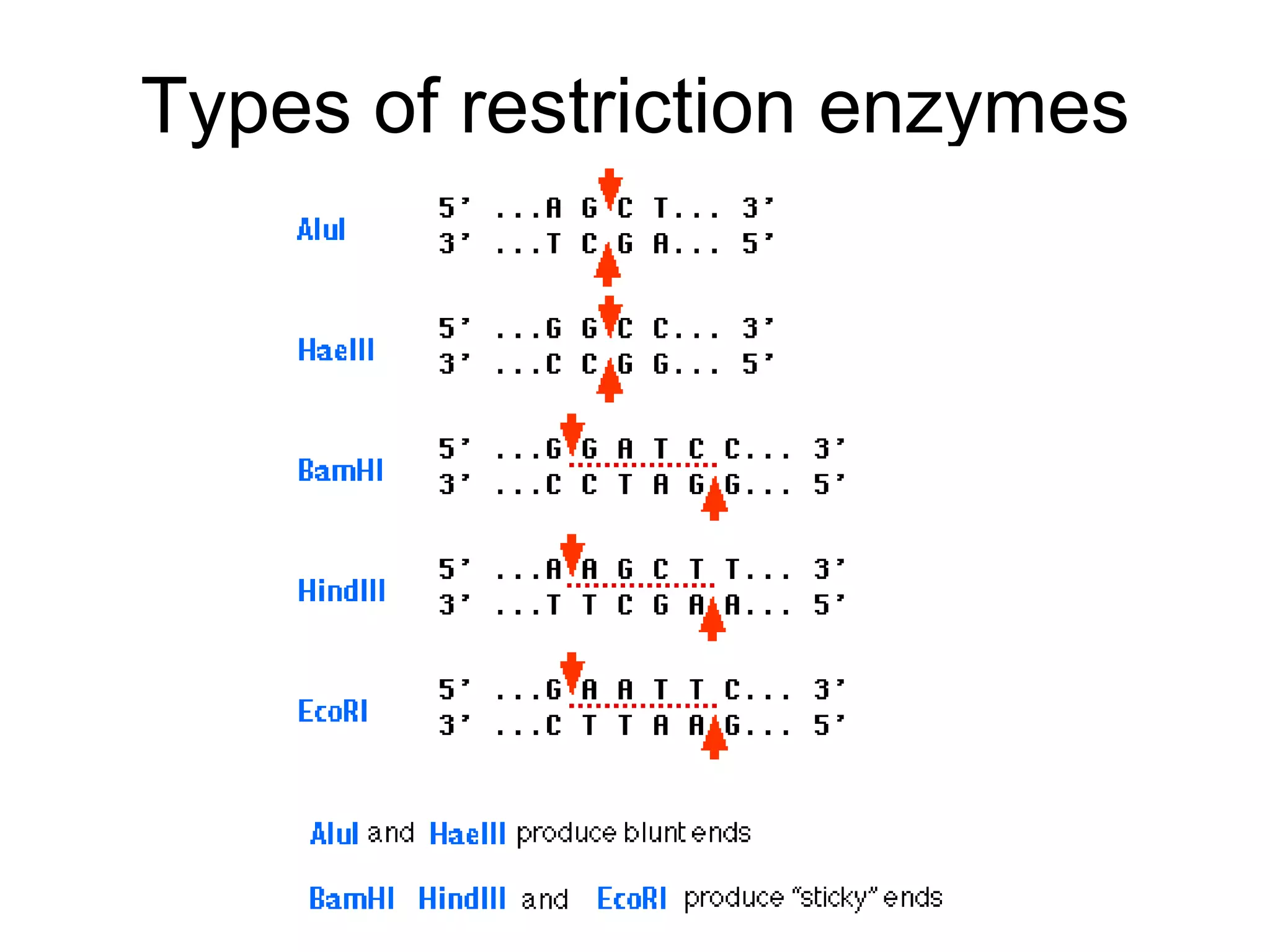
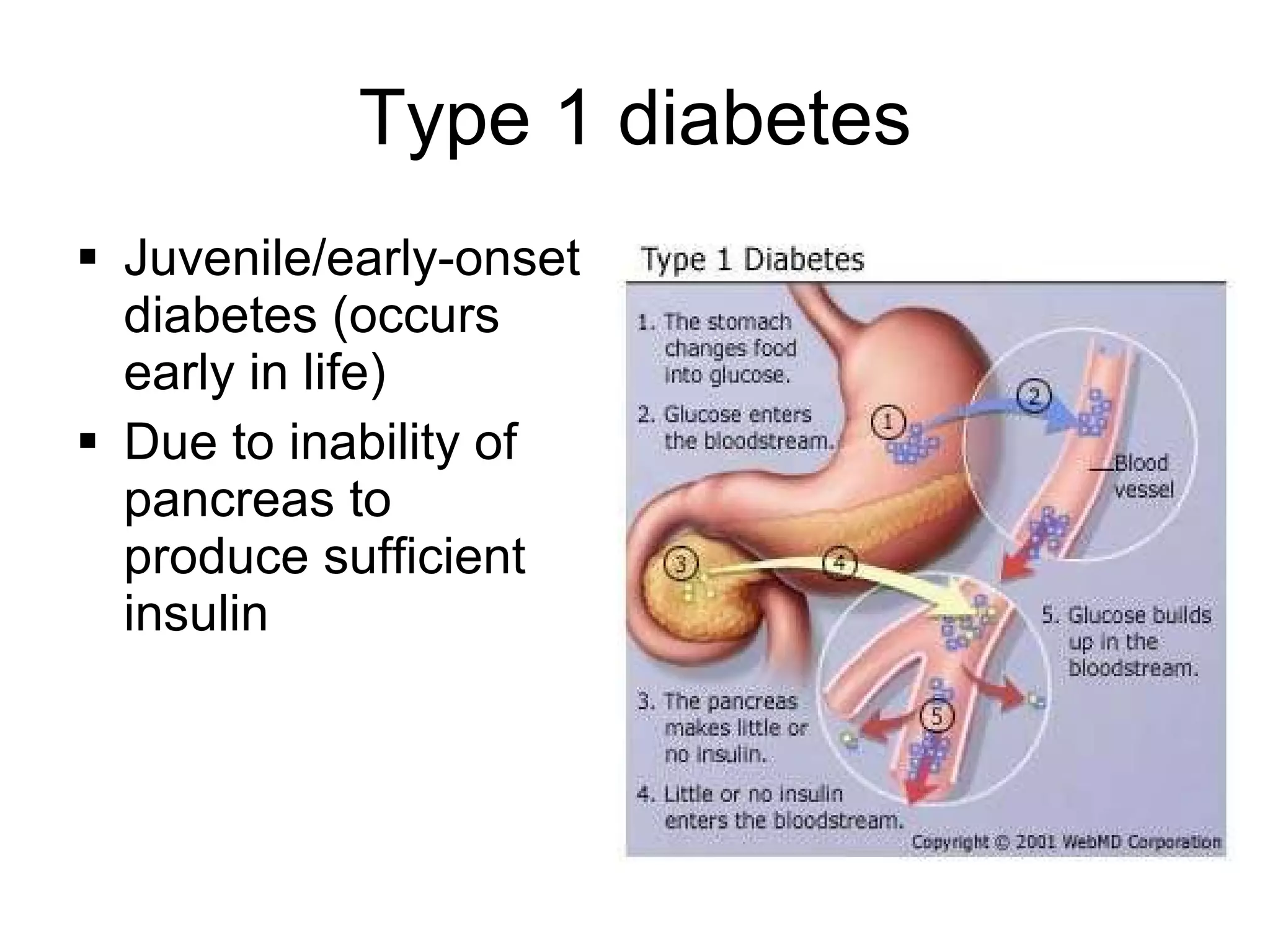
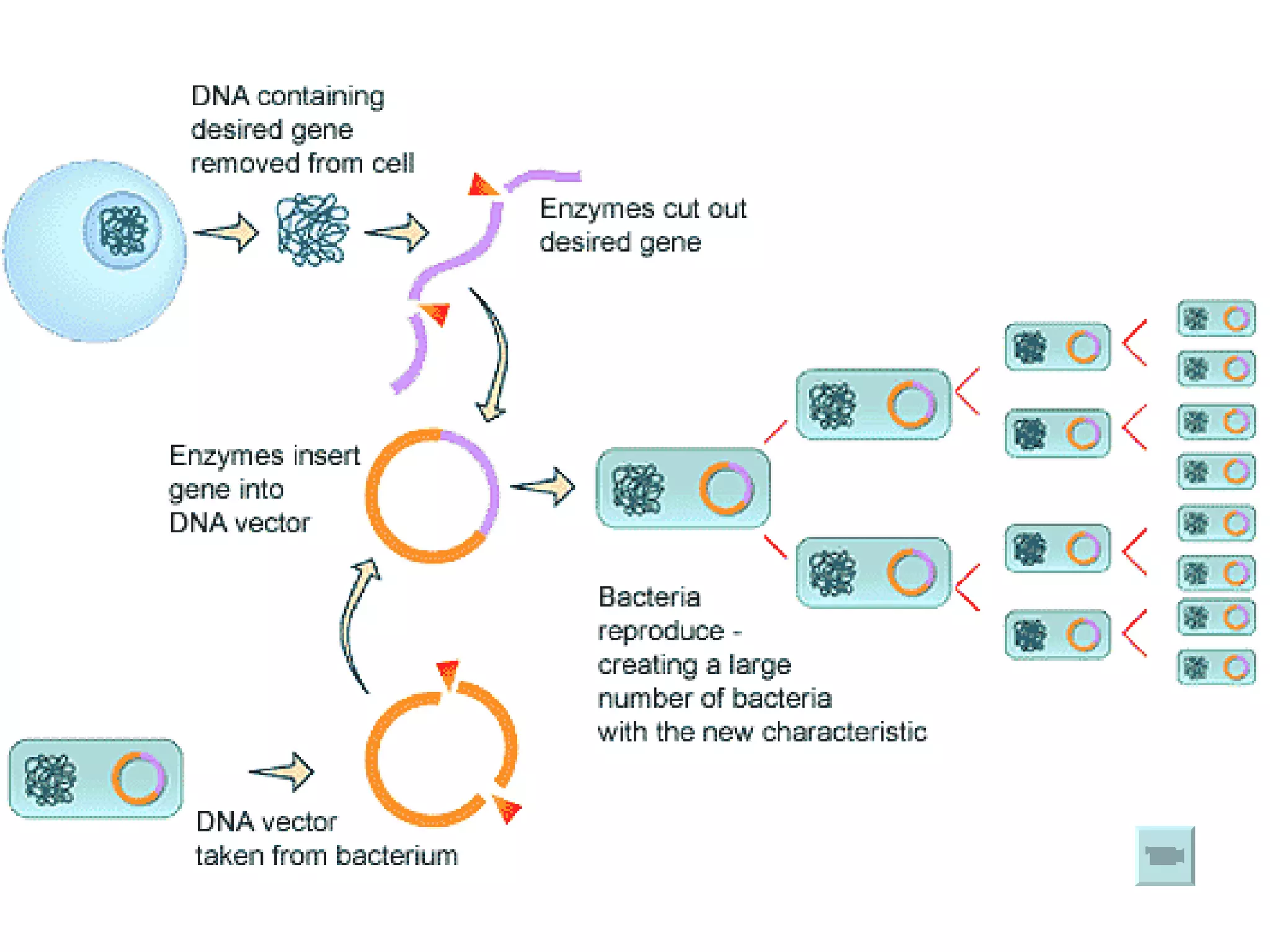
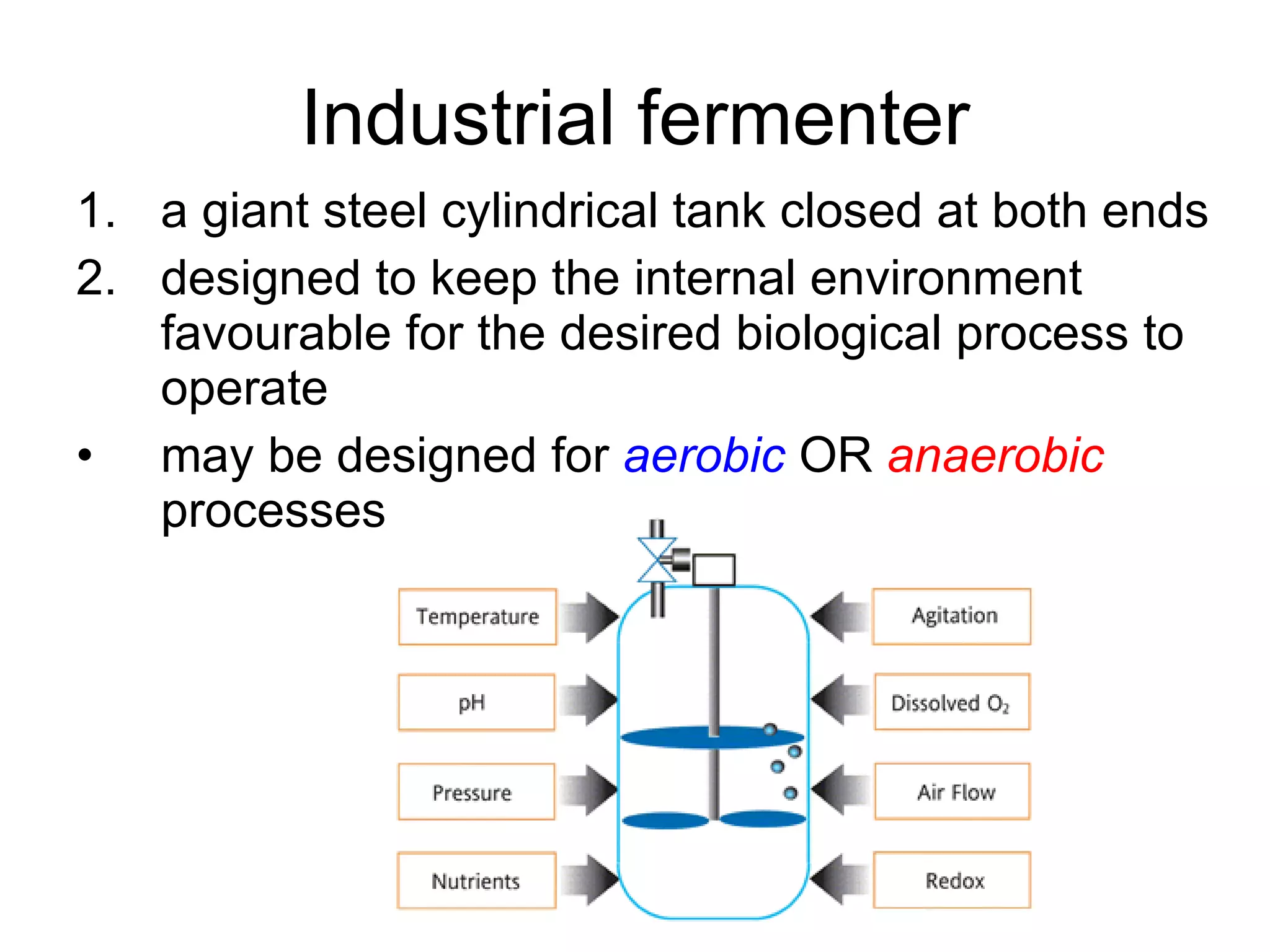
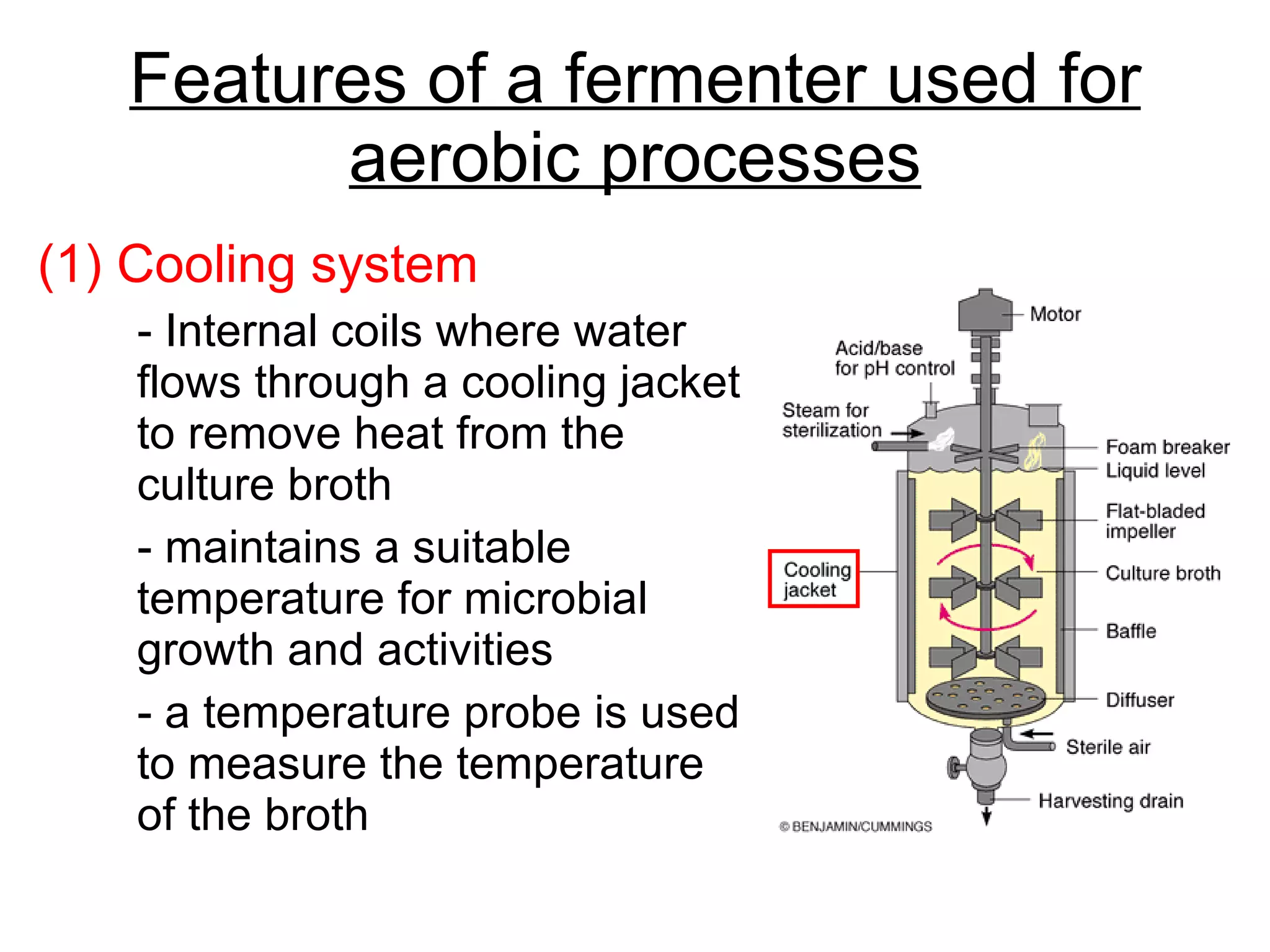
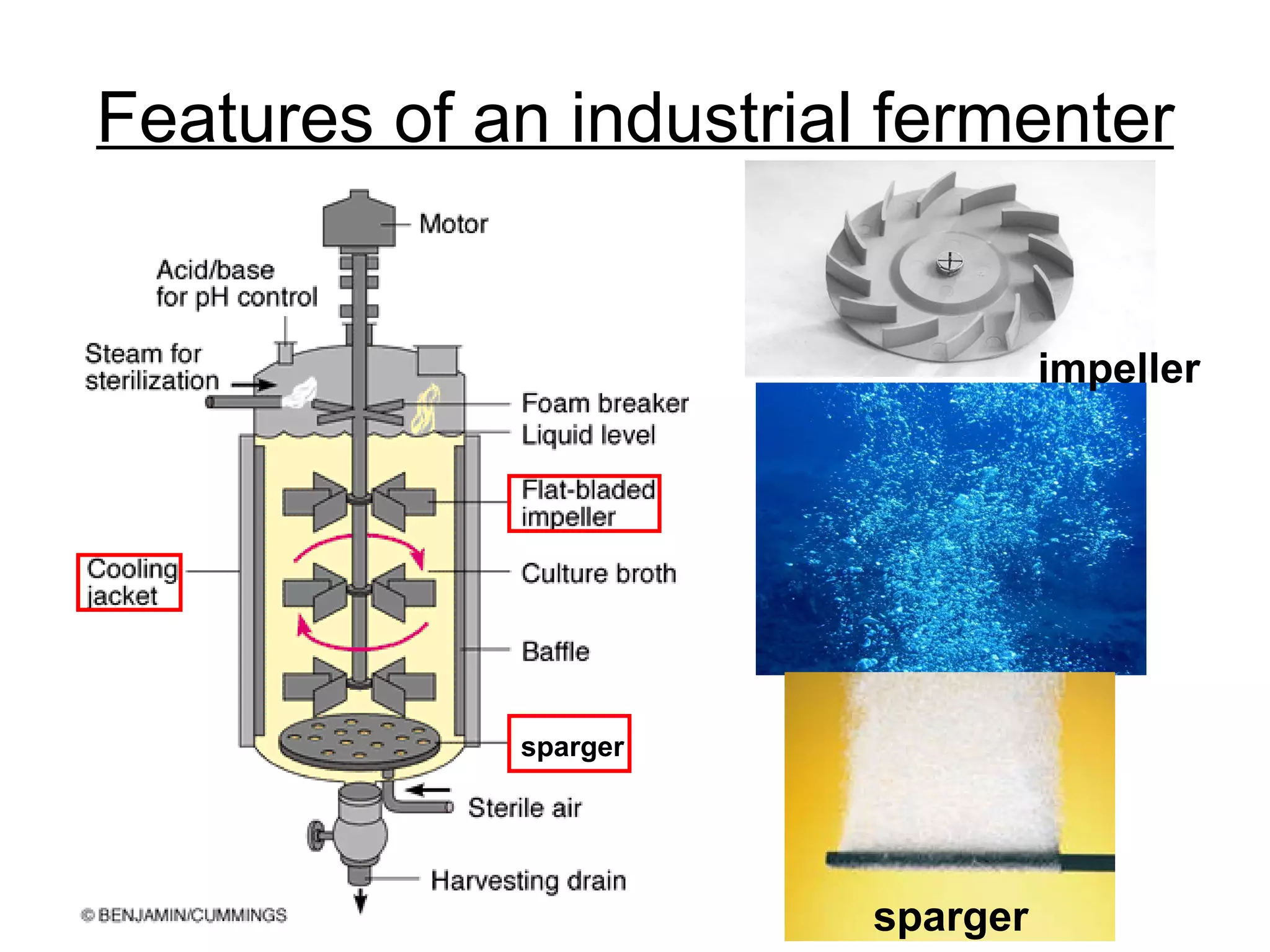
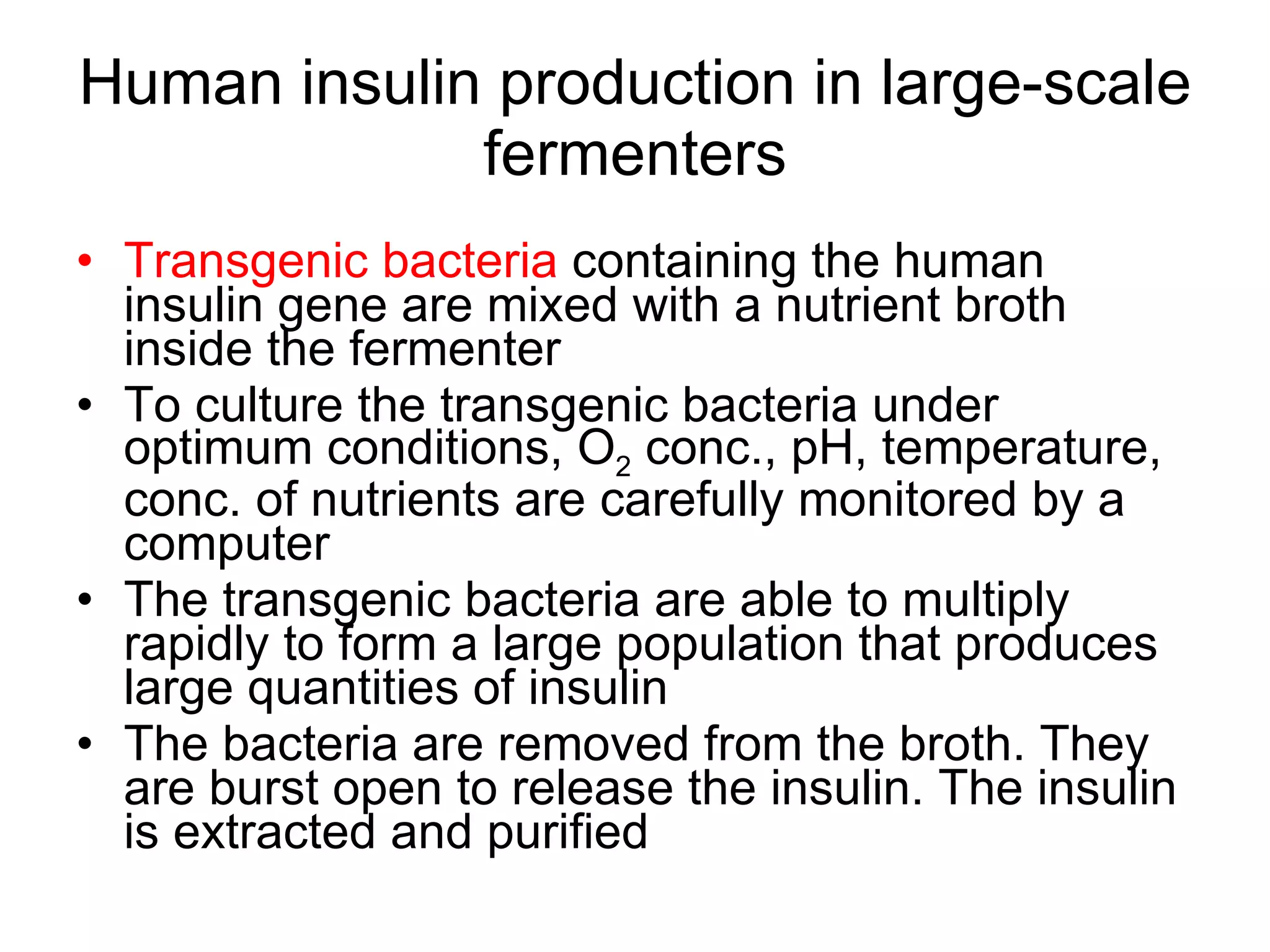
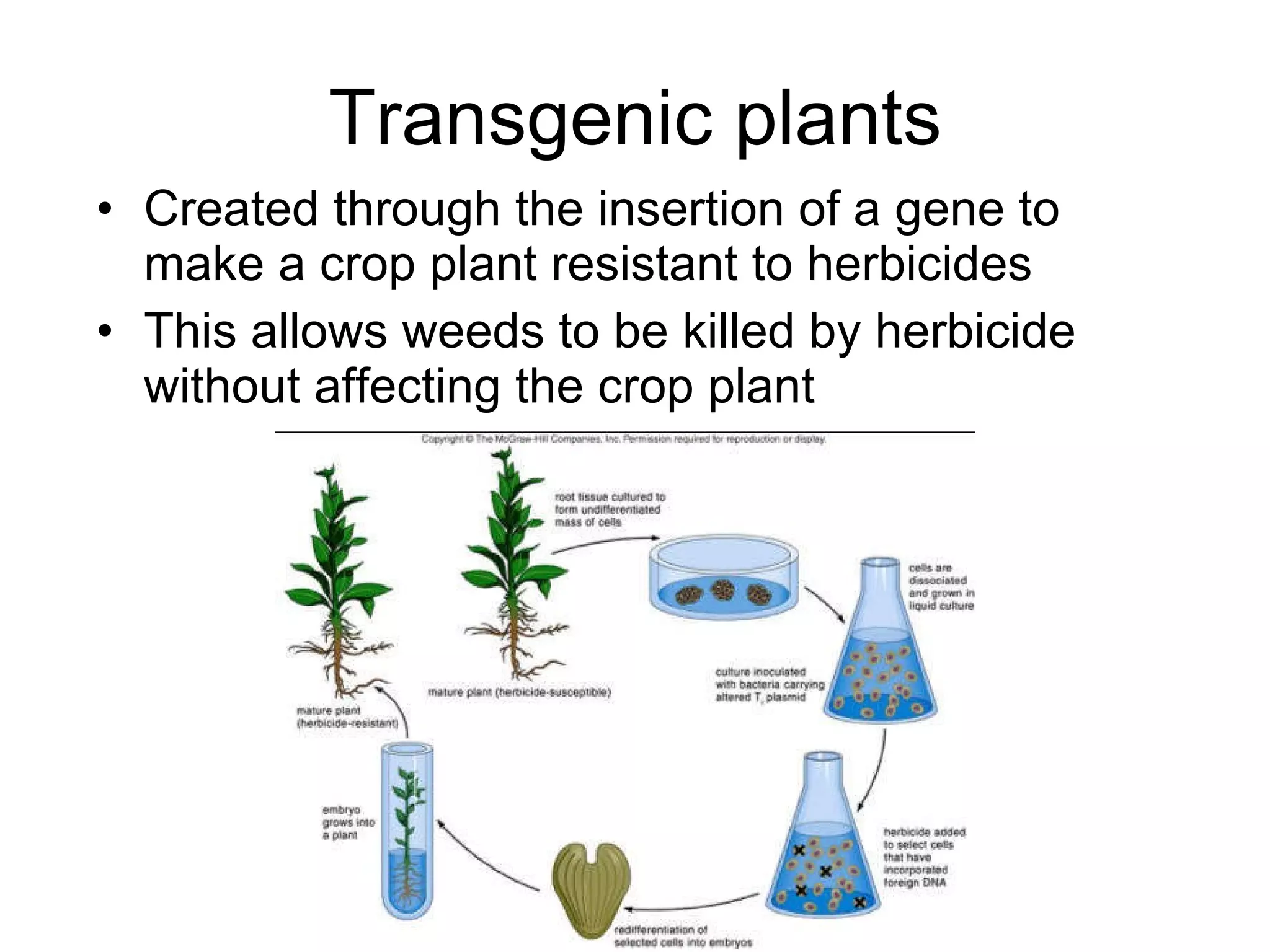
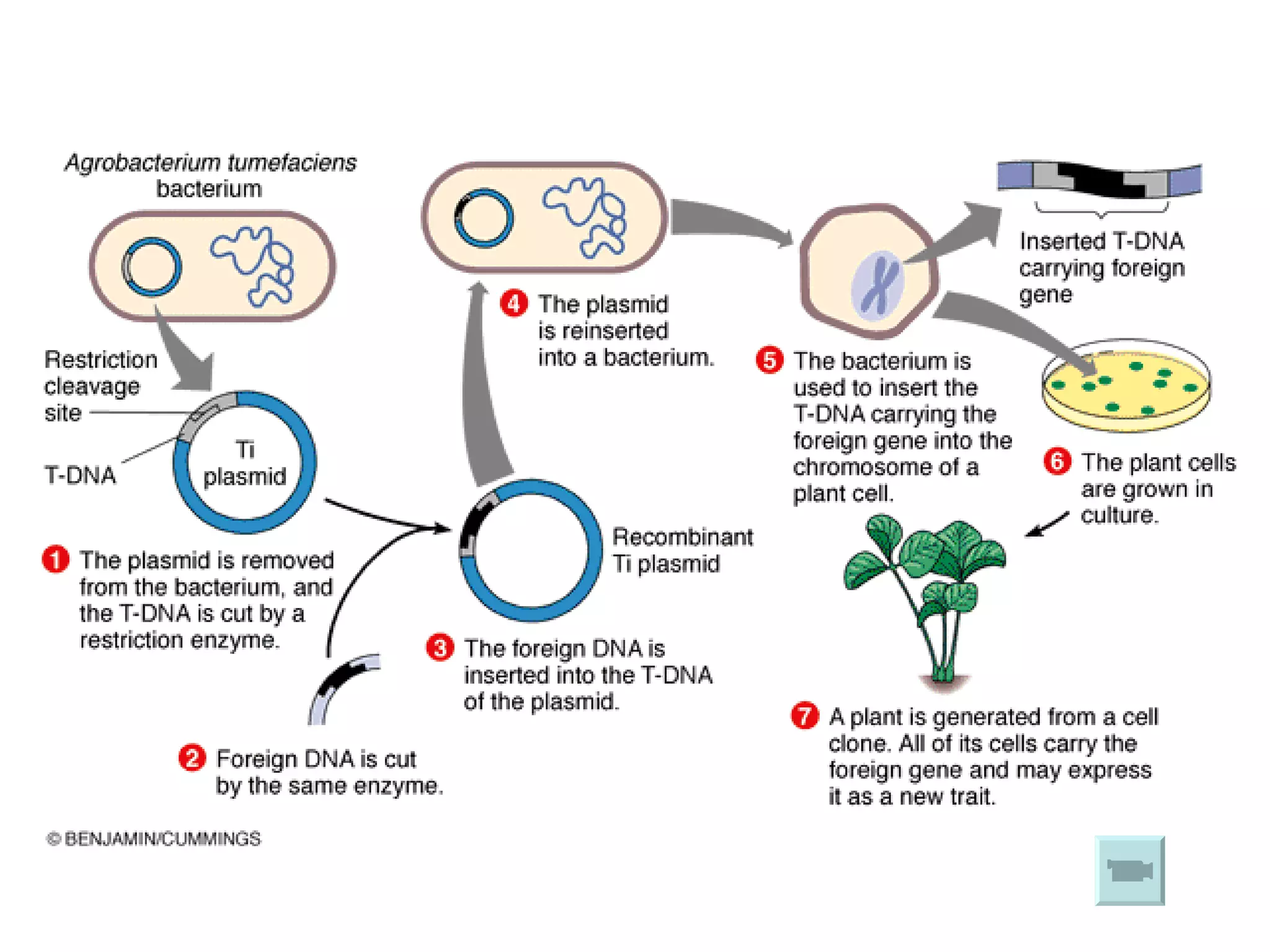
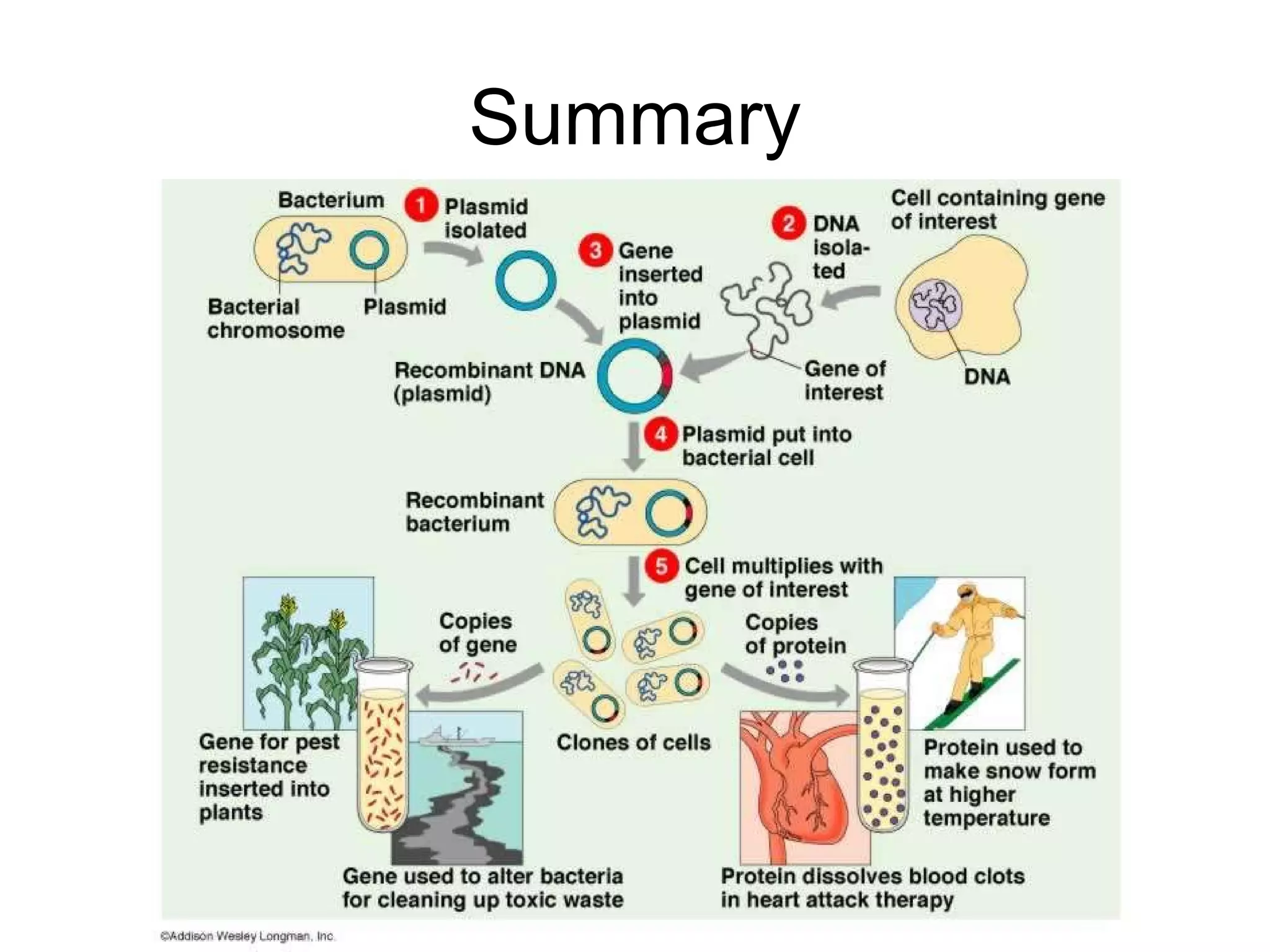
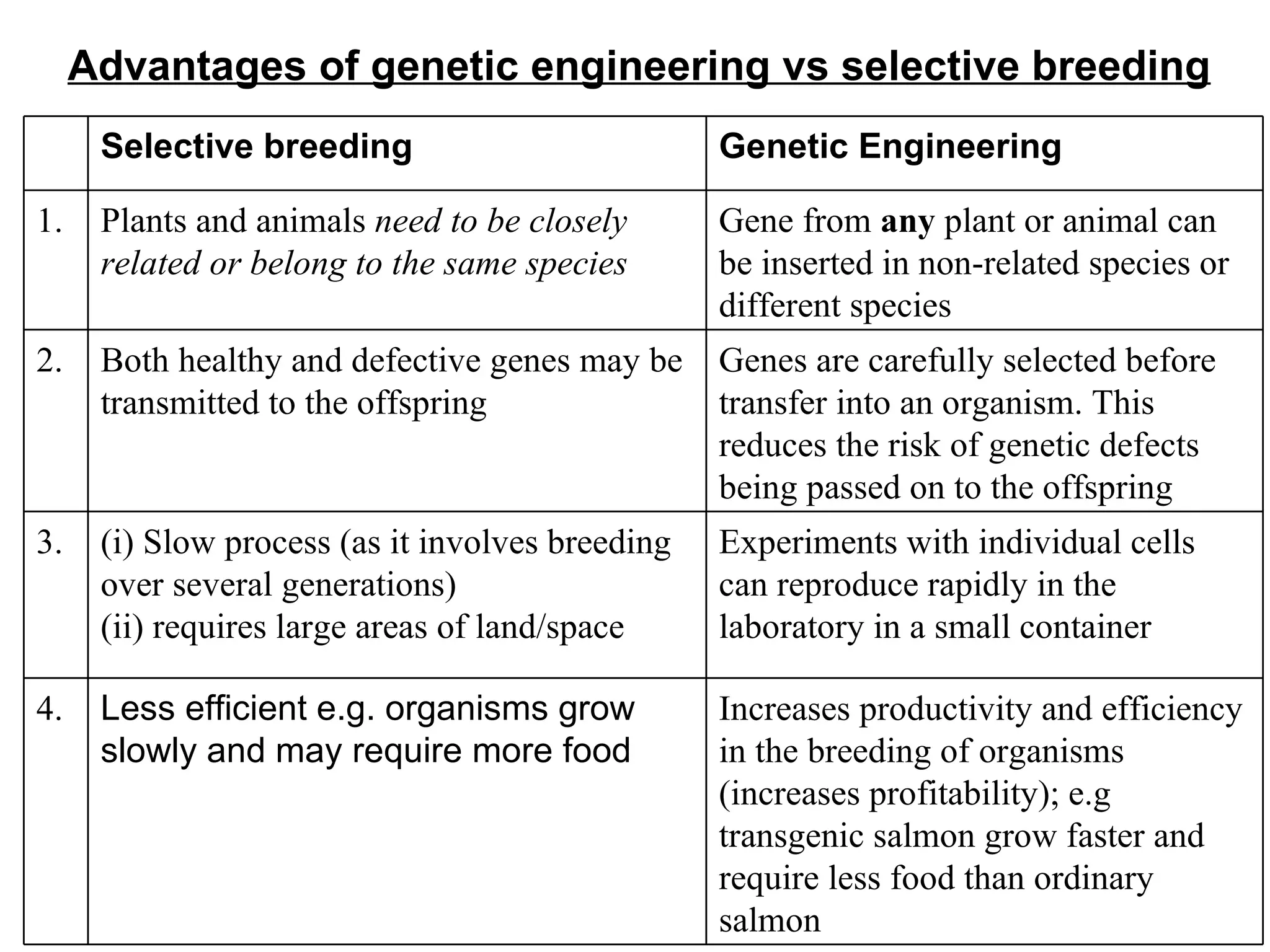
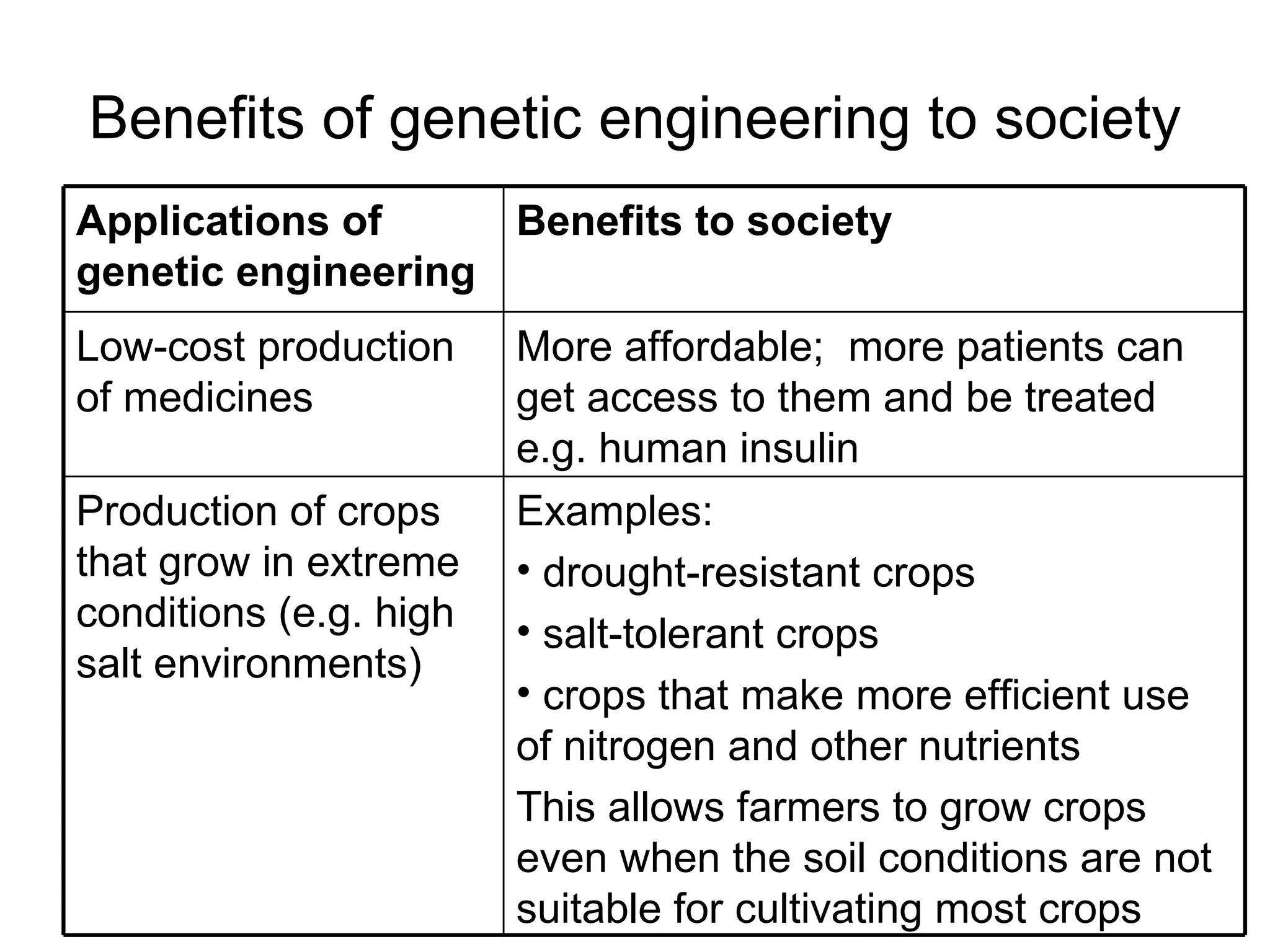
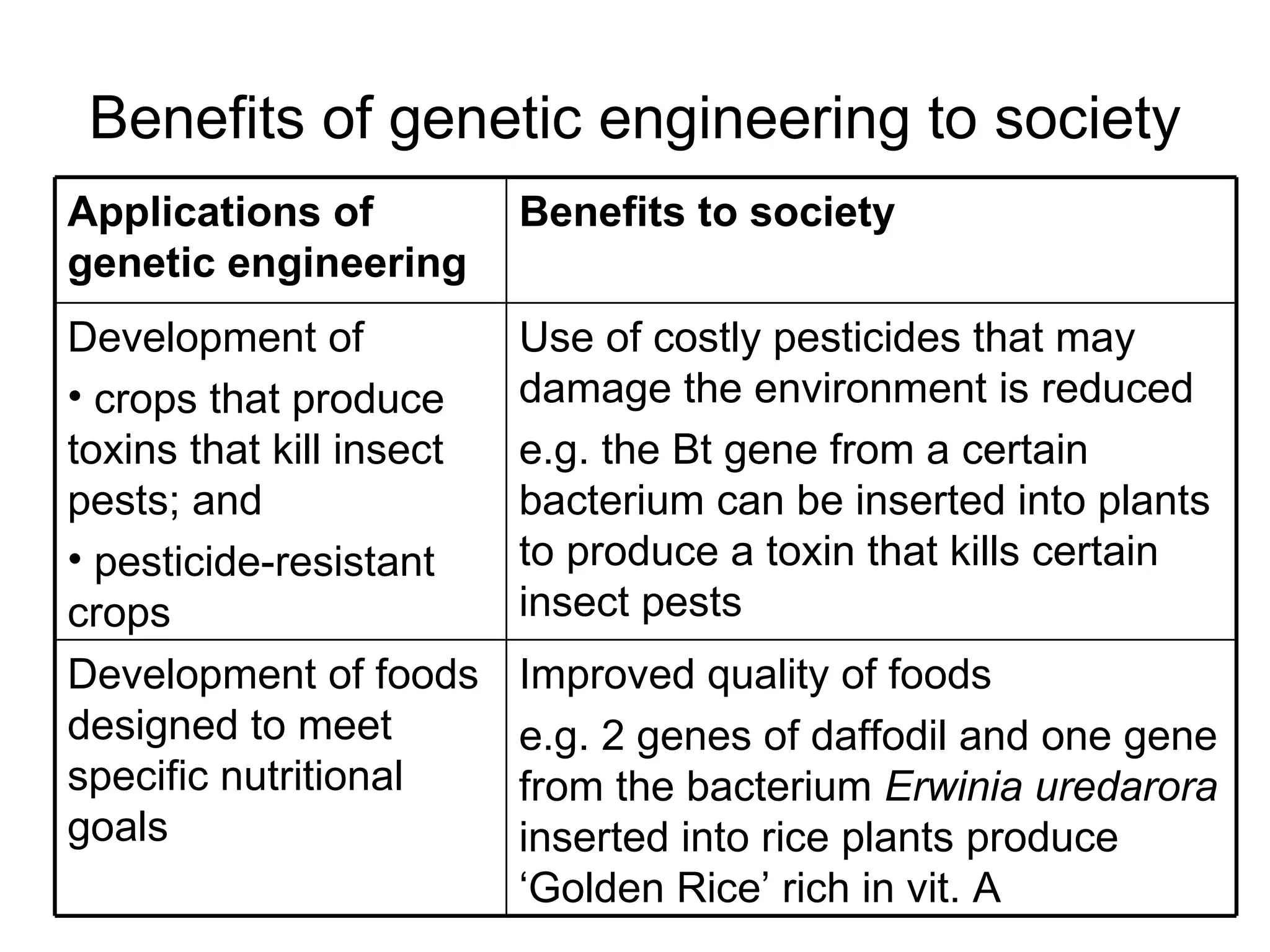
Genetic engineering is a technique used to transfer genes between organisms. It involves identifying the desired gene, using restriction enzymes to cut it from donor DNA, and inserting it into a vector like a plasmid. This vector is then inserted into a host cell like E. coli bacteria. For insulin production, the human insulin gene is inserted into bacterial DNA. The engineered bacteria are grown in large fermenters under controlled conditions to produce large quantities of human insulin. While genetic engineering has benefits like producing affordable insulin, it also raises social and ethical concerns regarding environmental impacts, economic issues, and potential health risks.
























![TYS Questions Describe the process of large-scale production of insulin through medical biotechnology. [5] With reference to named examples, explain the social and ethical implications of genetic engineering? [5]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3geneticengineering-101019040958-phpapp01/75/Chapter-20-Molecular-Genetics-Lesson-3-Genetic-Engineering-43-2048.jpg)