Embed presentation



This document provides an overview of molecular genetics content including: (1) The structure of DNA and how it is organized in cells, with DNA made up of nucleotides containing bases, sugar, and phosphate that form two parallel strands twisted into a double helix. (2) How genes and DNA are related, with each gene made up of a sequence of nucleotides that can vary, leading to different genes, and DNA containing the genetic information for cellular functions. (3) The rules of complementary base pairing between nucleotides, with adenine binding thymine and cytosine binding guanine.
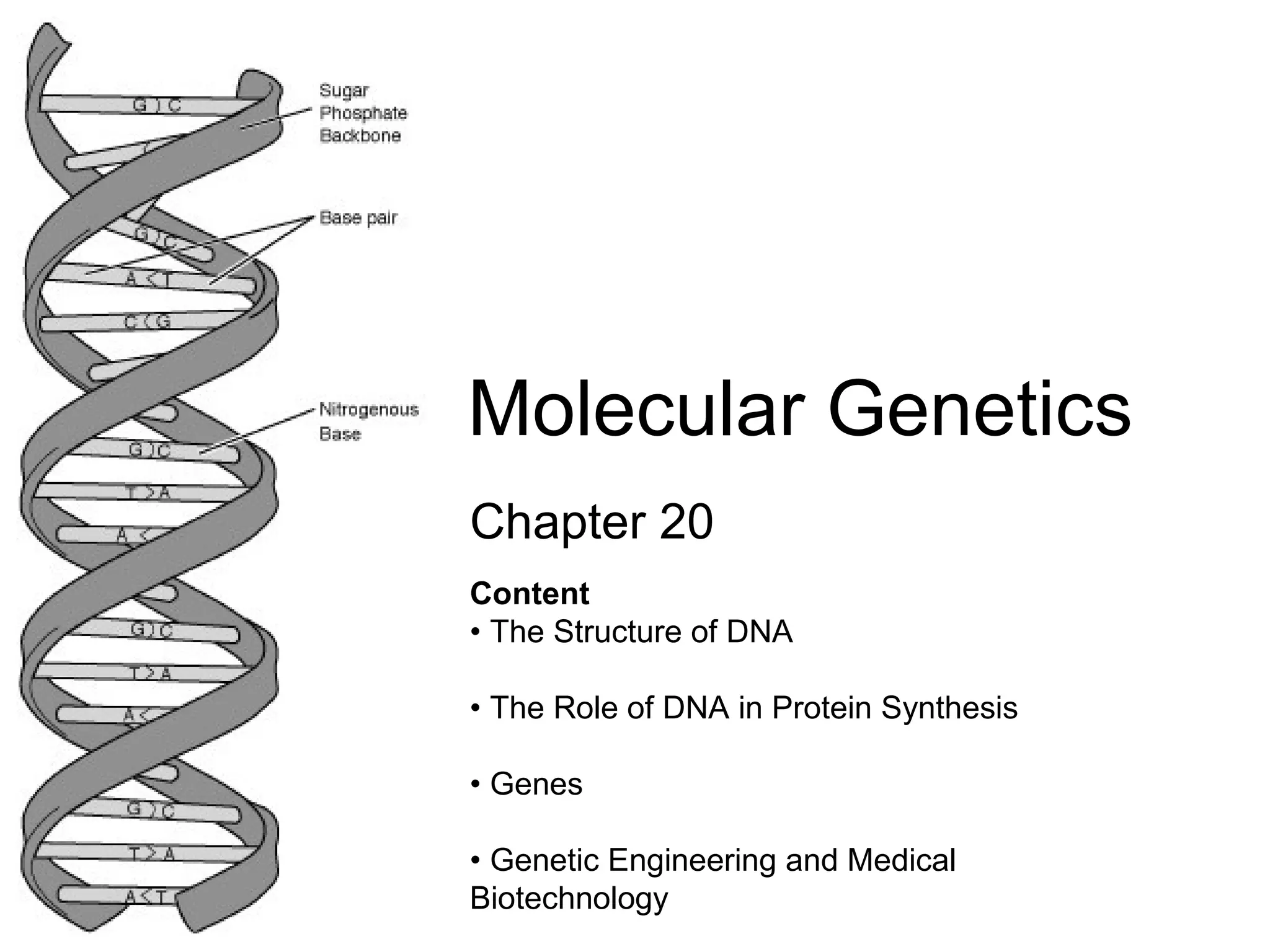
Introduces Chapter 20 on Molecular Genetics focusing on DNA structure, protein synthesis, genes, and genetic engineering.
Outlines the aims of the lesson including understanding DNA, gene relationships, and base pairing rules.
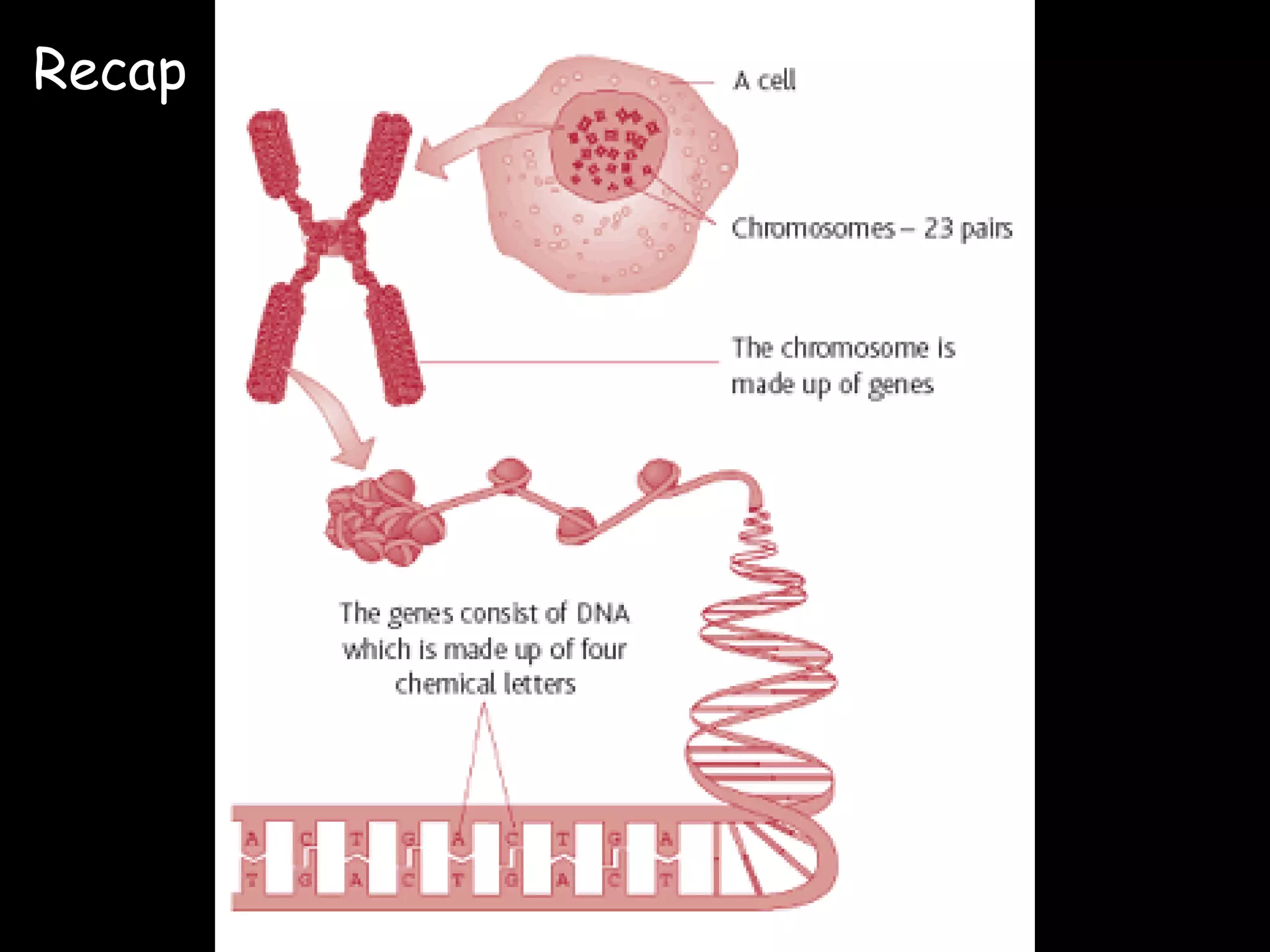
Provides a brief recap of previous material related to DNA and molecular genetics.
Explains DNA's role in carrying genetic information necessary for cellular functions like division and differentiation.
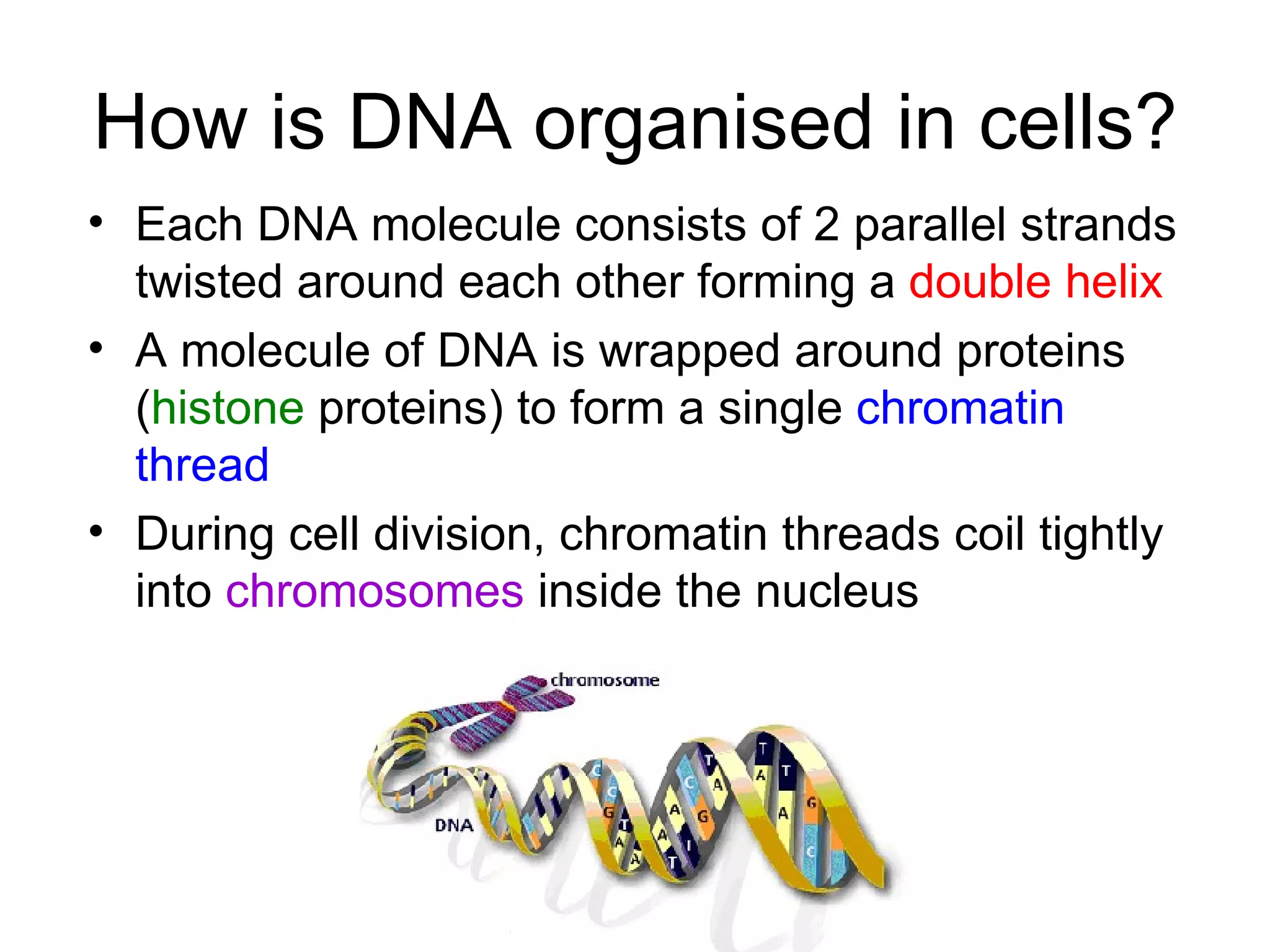
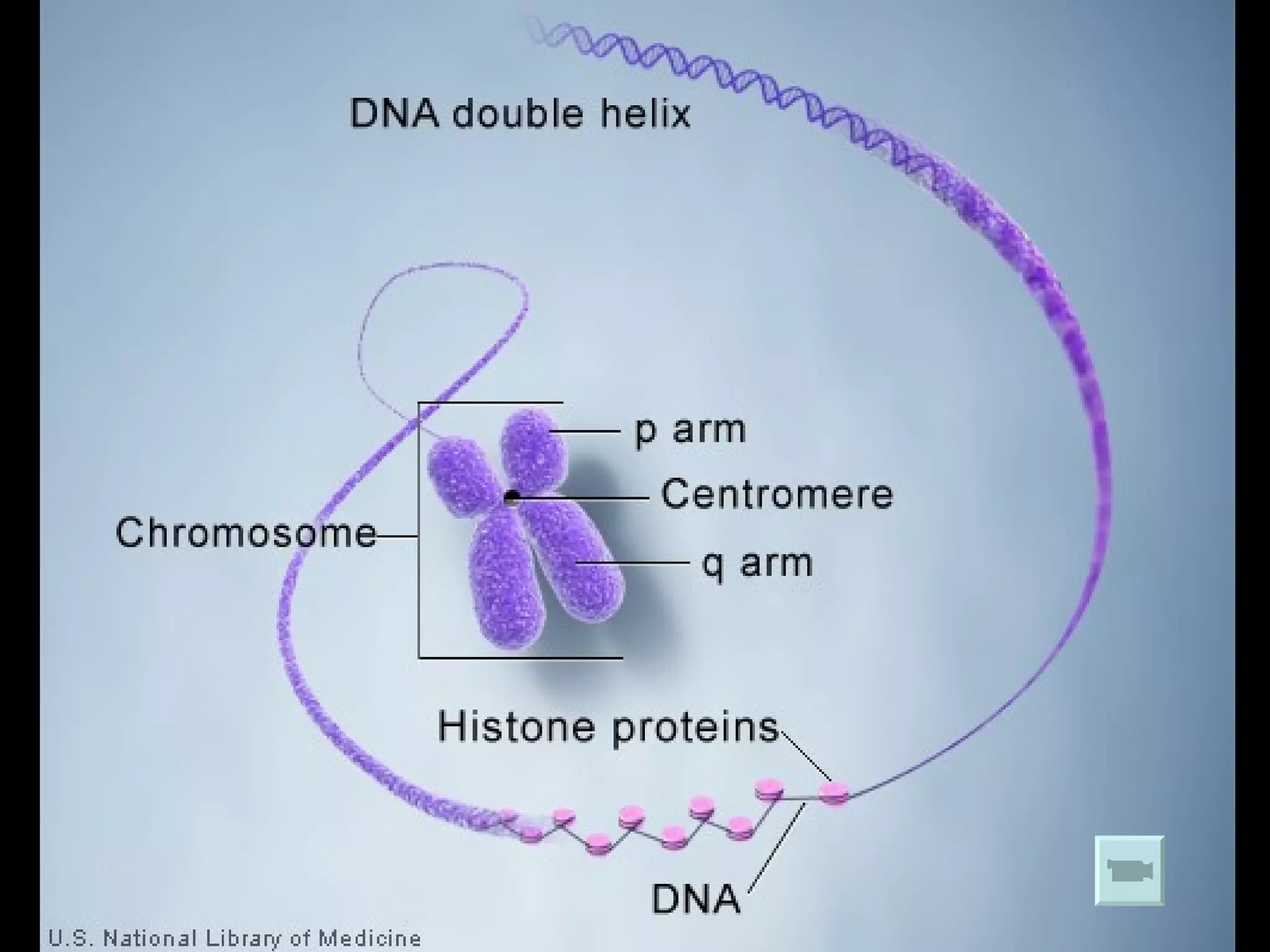
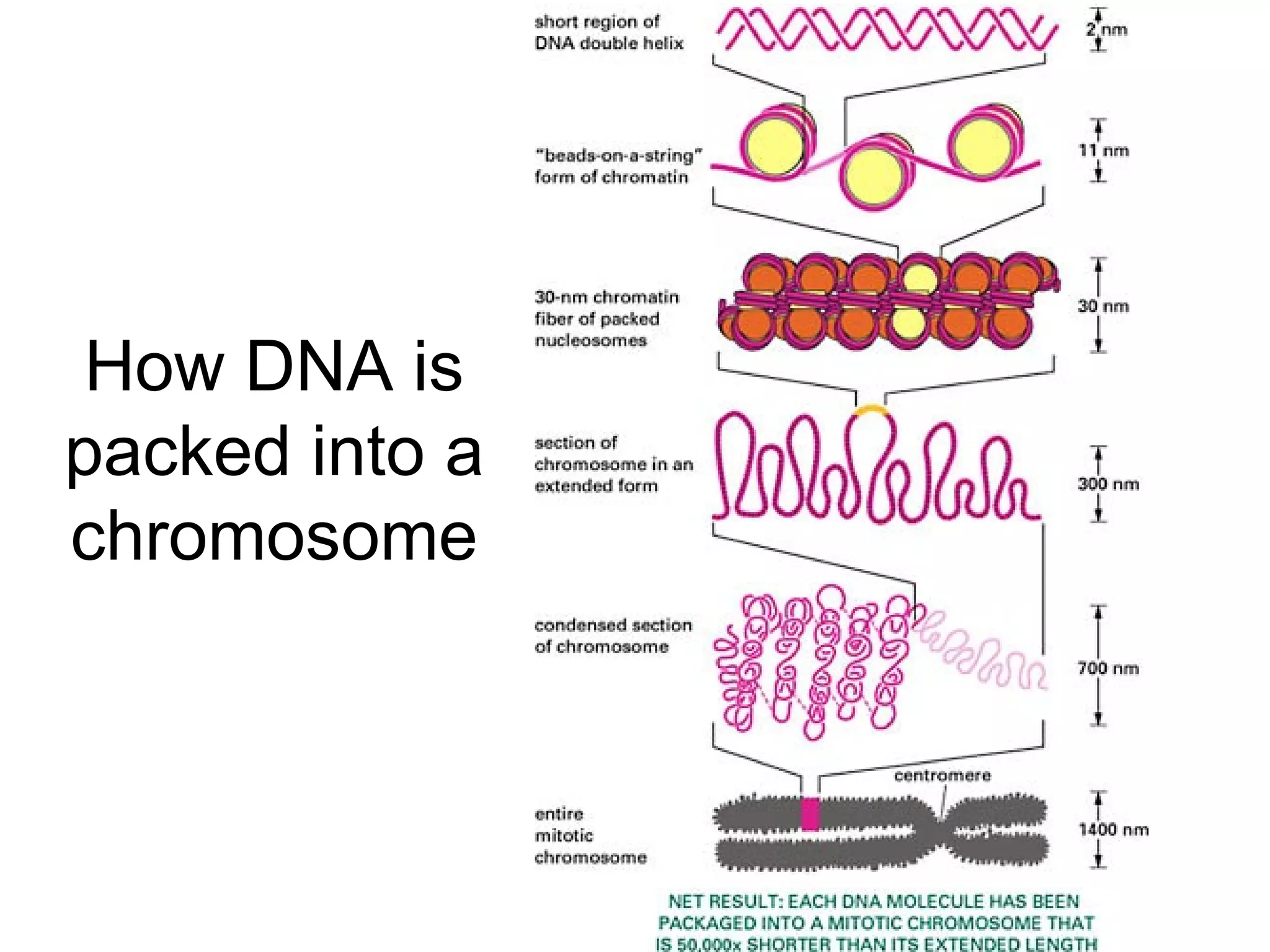
Describes how DNA is organized as a double helix, associated with histones to form chromatin and chromosomes.
Describes how DNA is organized as a double helix, associated with histones to form chromatin and chromosomes.
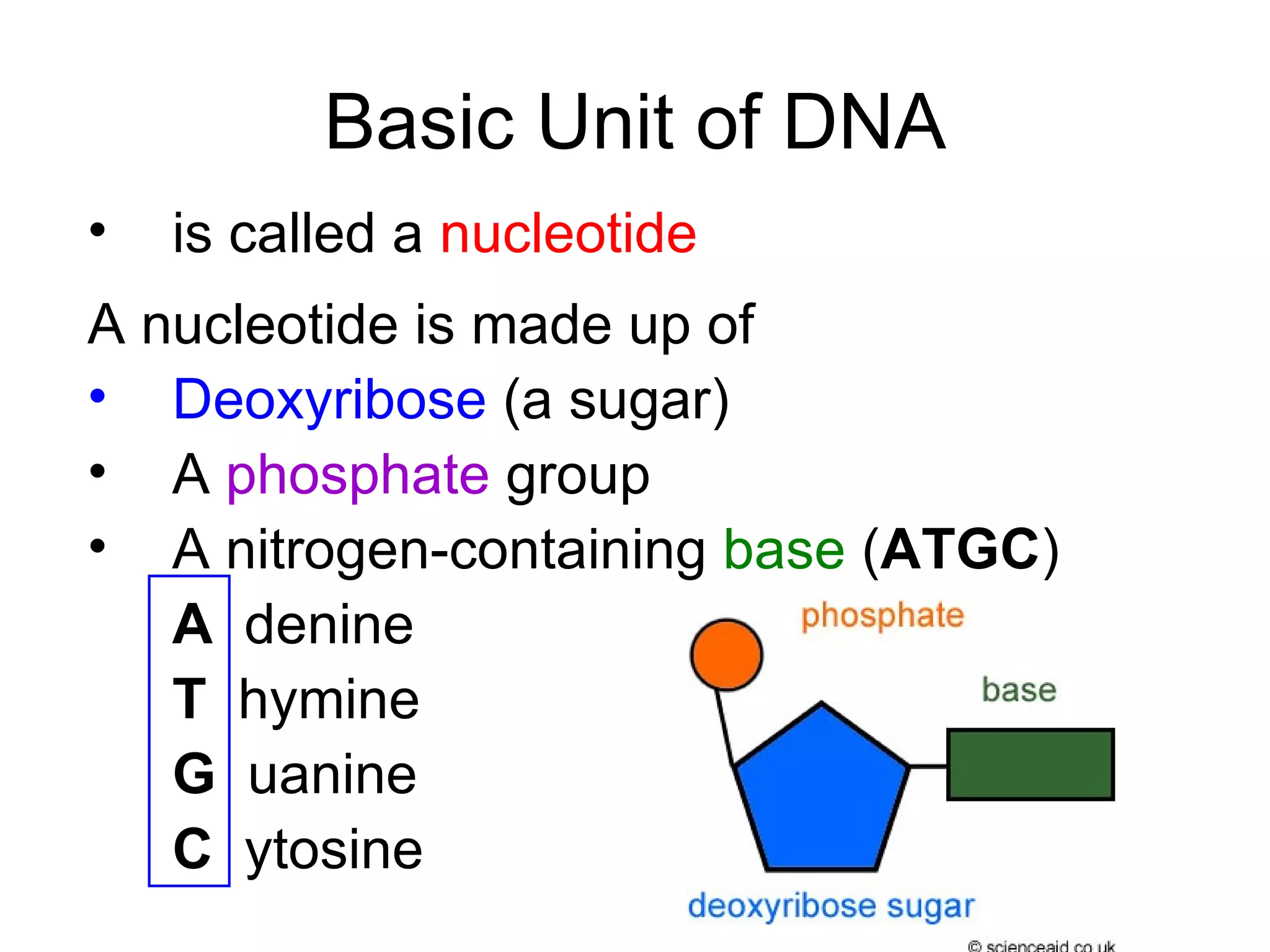
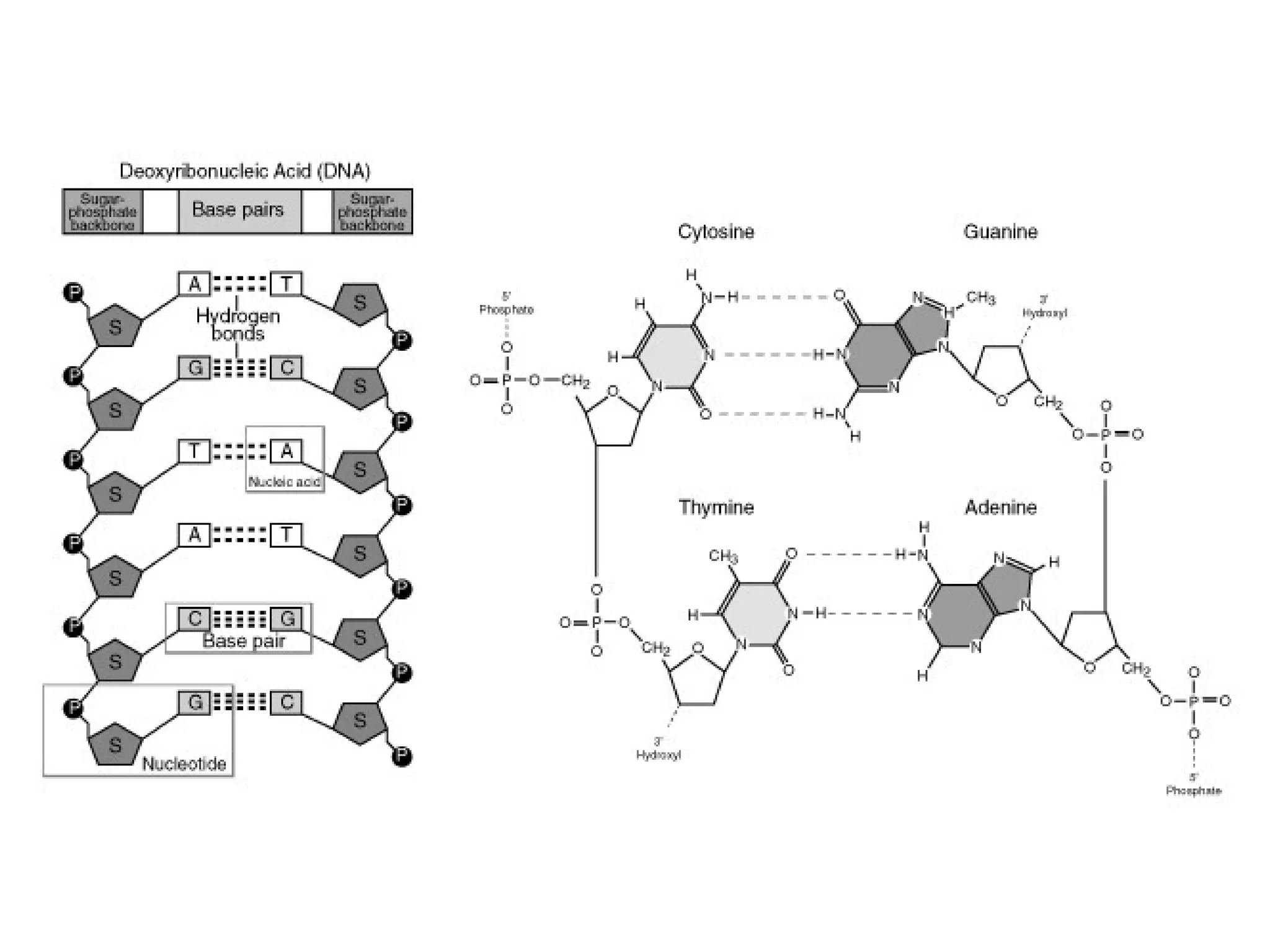
Details the makeup of nucleotides, including sugar, phosphate, and nitrogenous bases (A, T, G, C).
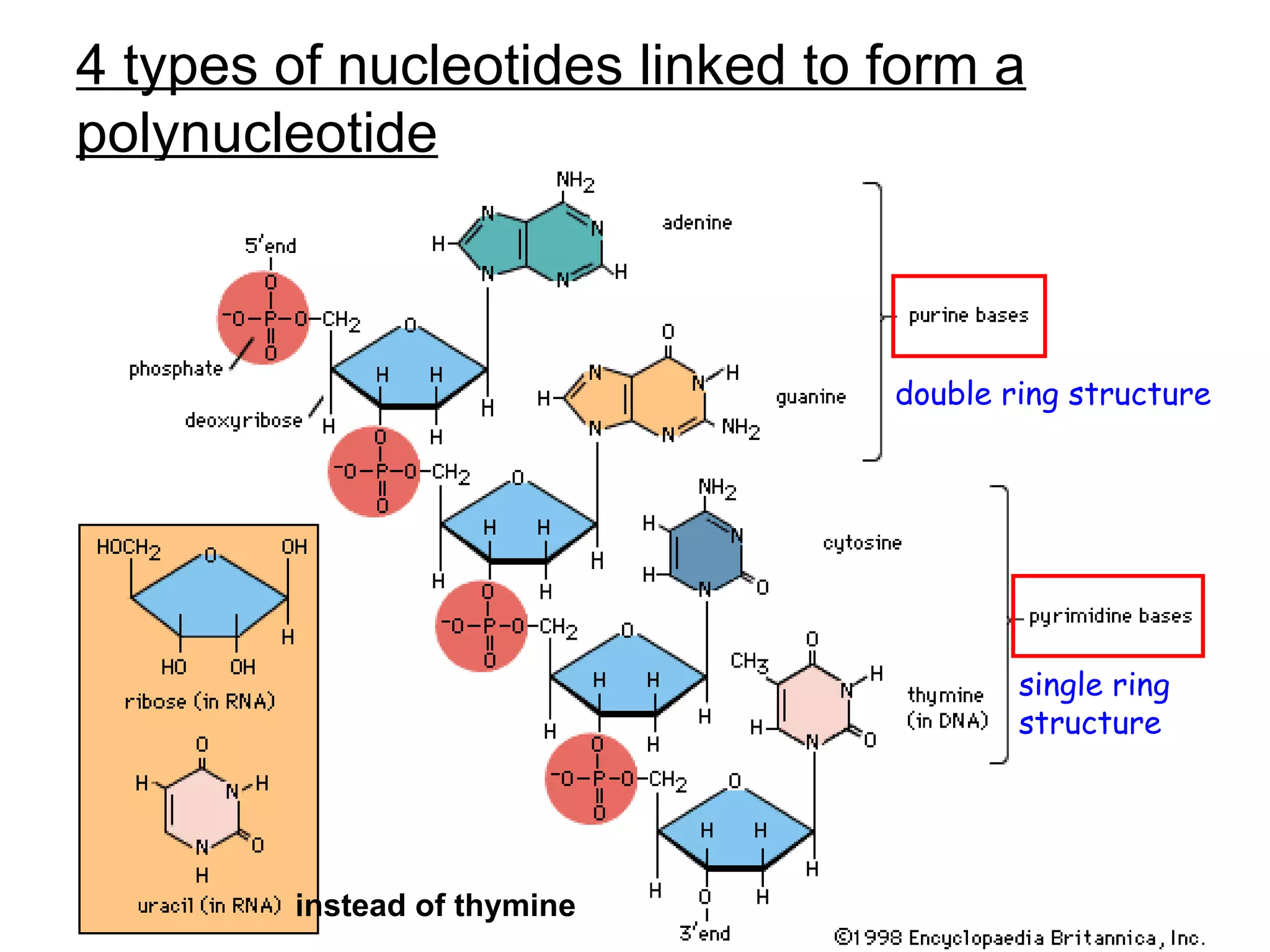
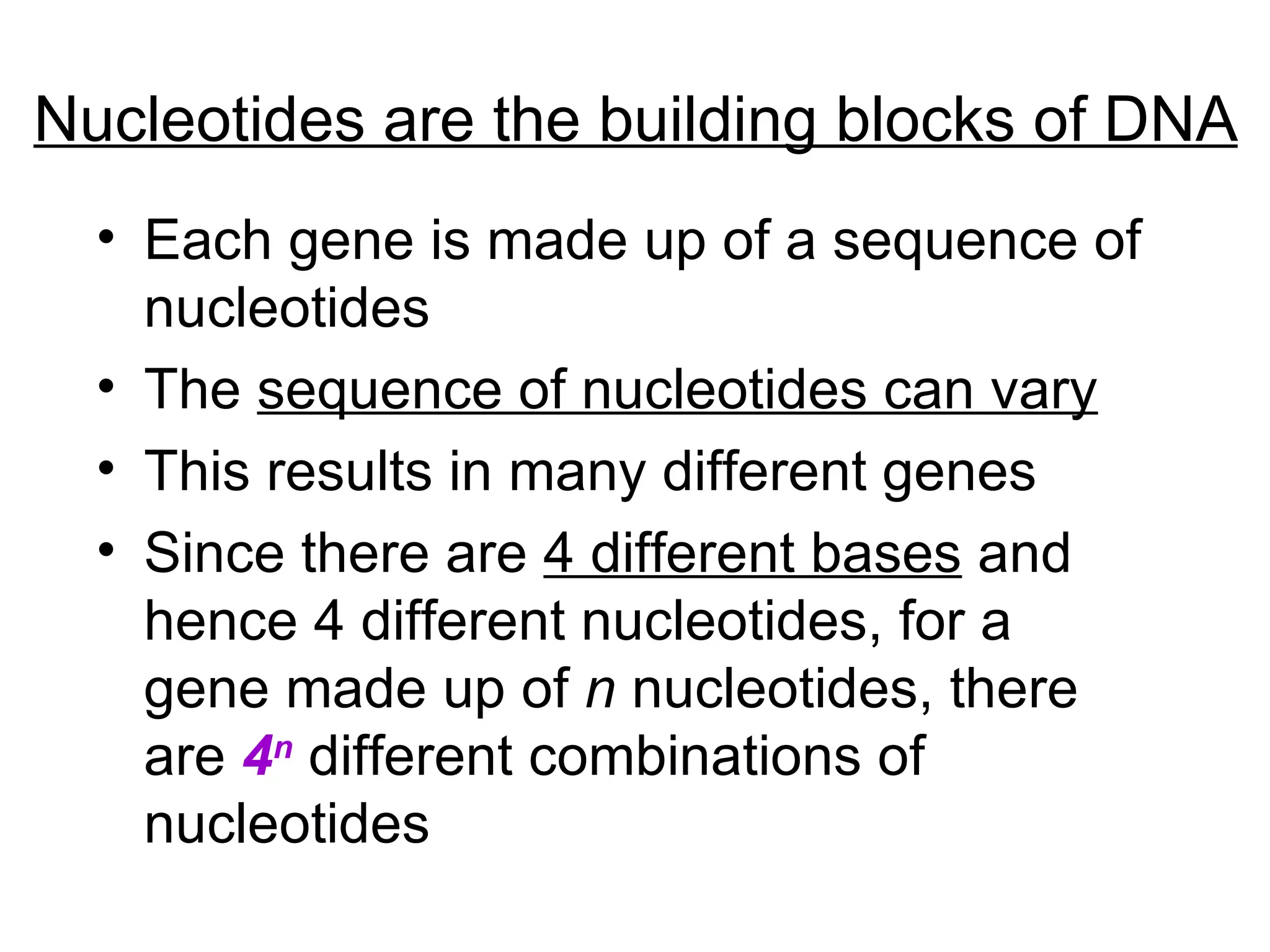
Highlights that genes are sequences of nucleotides with numerous combinations due to four bases.
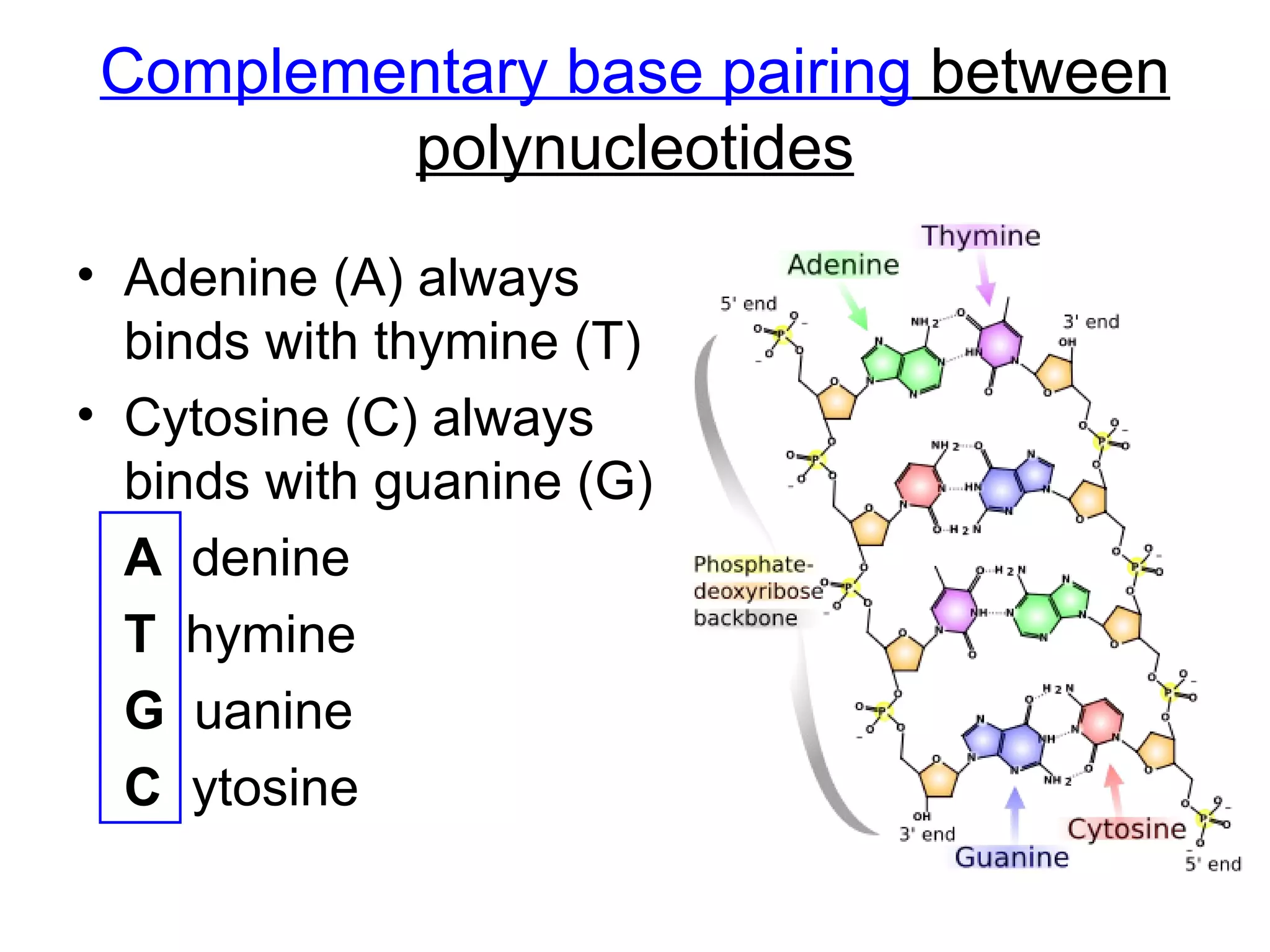
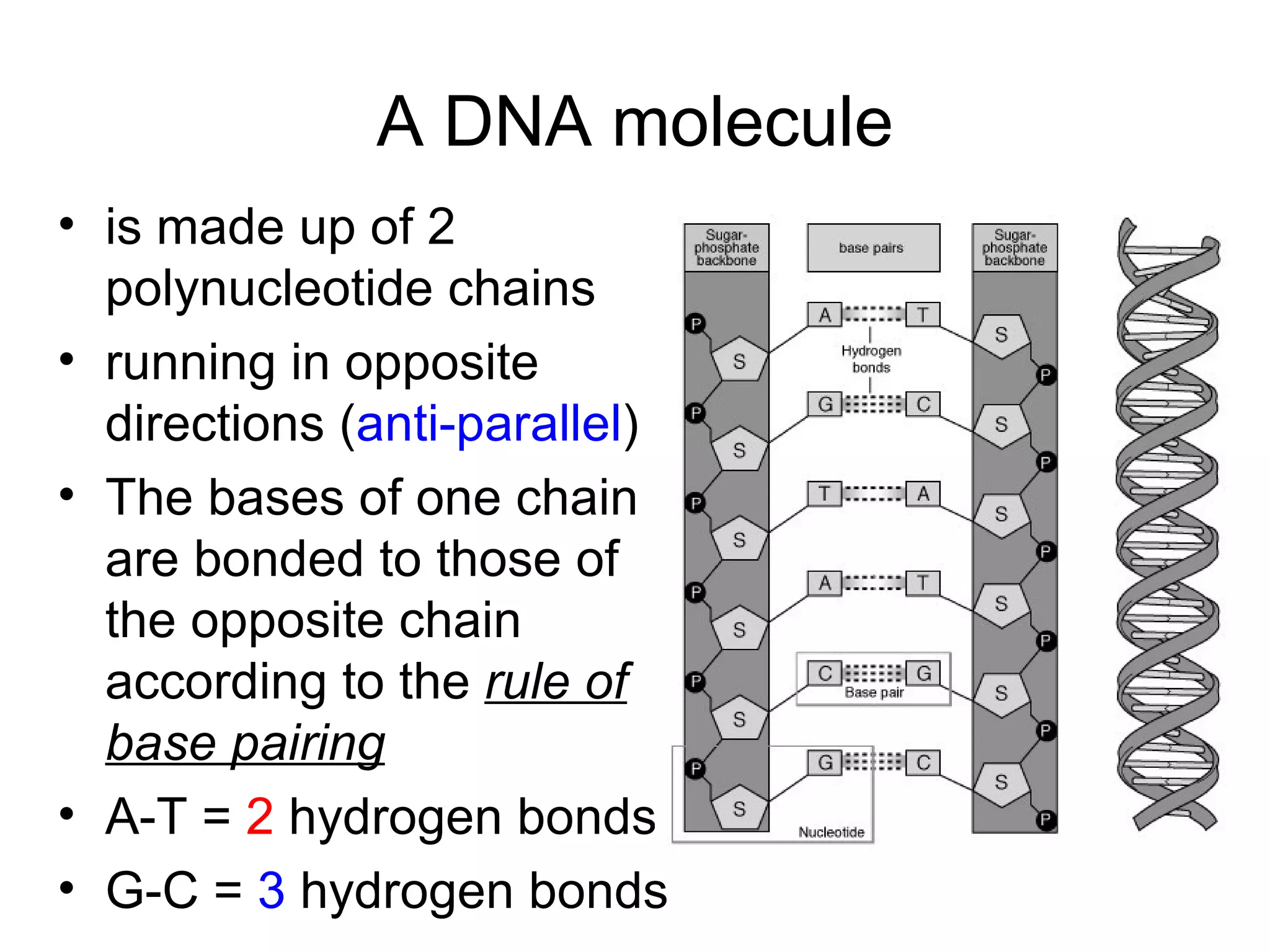
Discusses the complementary base pairing of nucleotides (A-T, C-G) and the anti-parallel structure of DNA.
References a worksheet activity for creating a DNA model, reinforcing concepts learned in the presentation.














