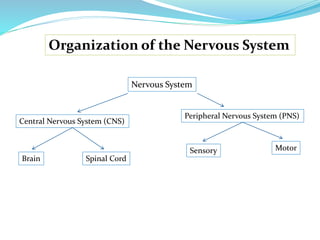
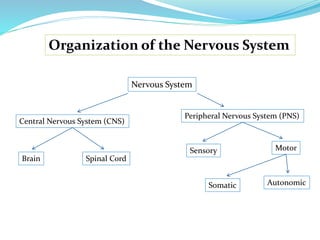
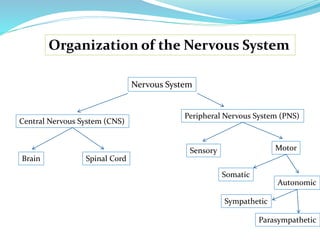
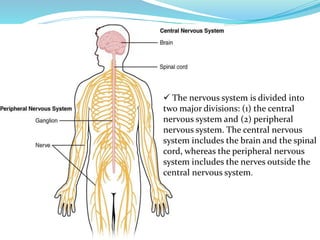
- The nervous system is divided into the central nervous system (CNS), which includes the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), which includes nerves outside the CNS.
- Neurons are the basic functional units of the nervous system and transmit electrochemical signals. A neuron has a cell body, dendrites that receive signals, and an axon that transmits signals to other neurons or effector cells.
- The PNS is further divided into the somatic and autonomic systems. The somatic system controls skeletal muscles and senses the external environment. The autonomic system regulates involuntary functions through the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions.