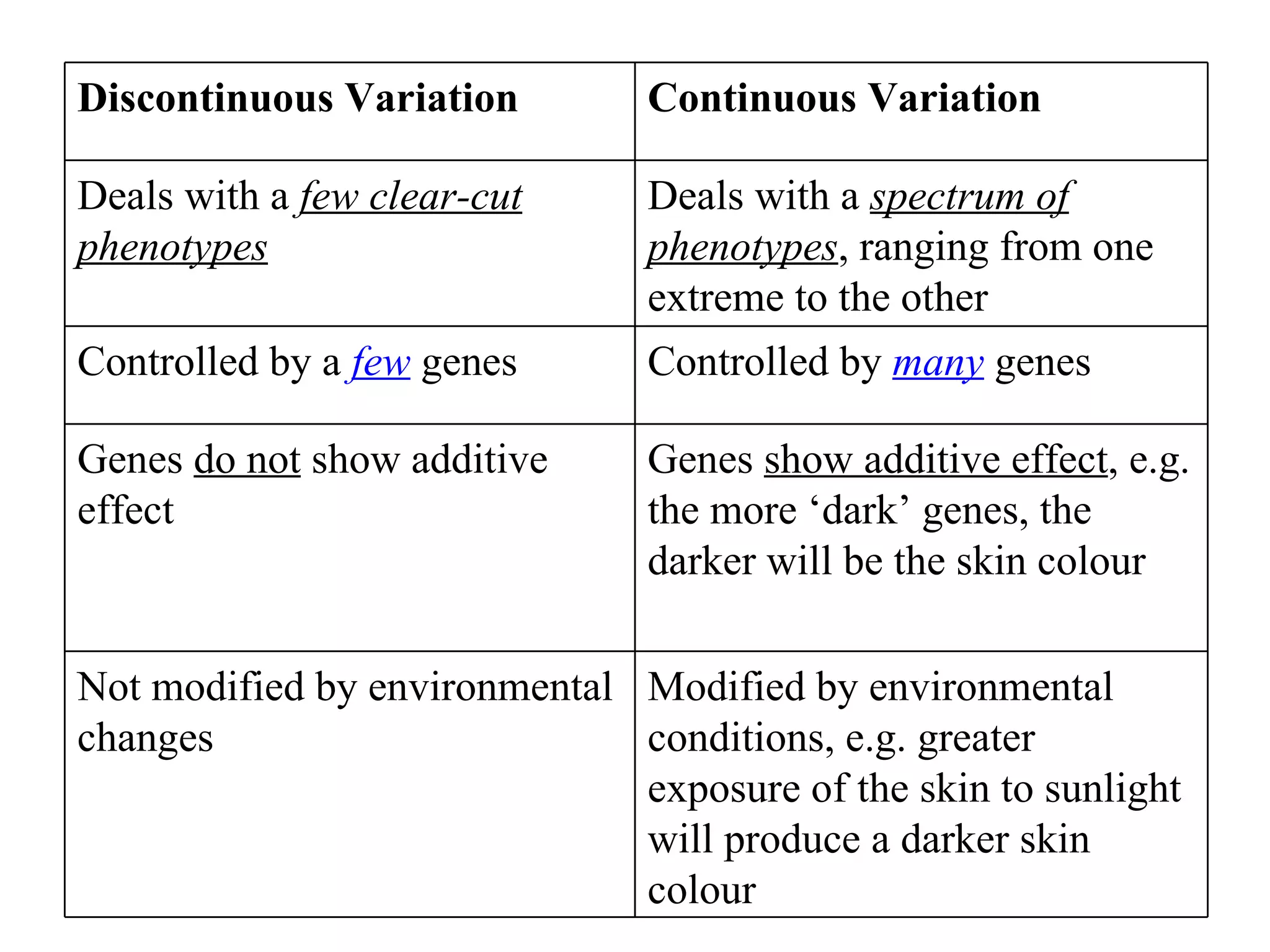
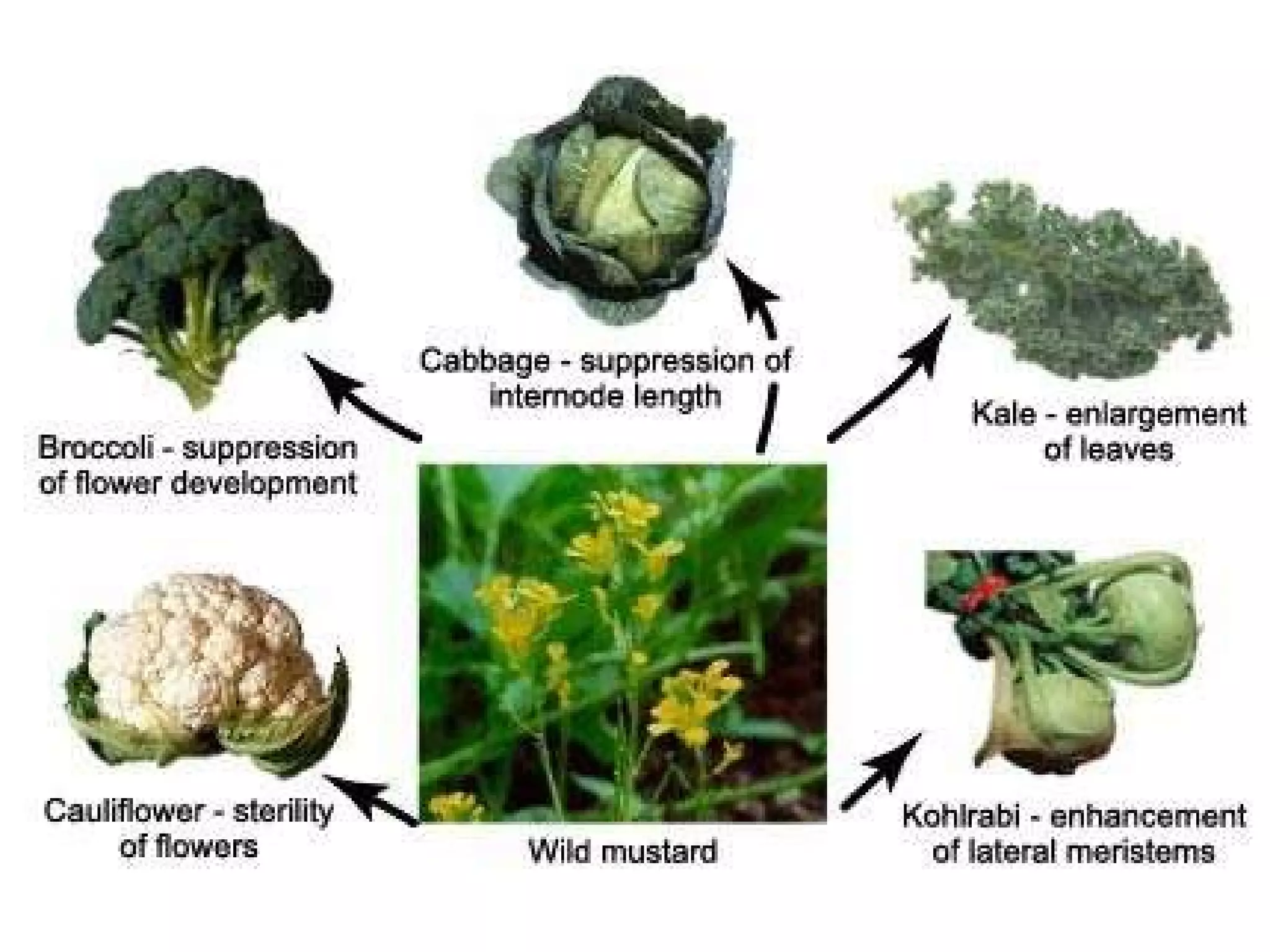
There are two types of variation: discontinuous and continuous. Discontinuous variation results in distinct phenotypes controlled by one or a few genes, like pea plant height. Continuous variation produces a spectrum of intermediate phenotypes controlled additively by many genes, such as human skin color. Continuous traits can also be influenced by the environment, unlike discontinuous traits. Both natural and artificial selection can act on variations to influence evolution over generations.