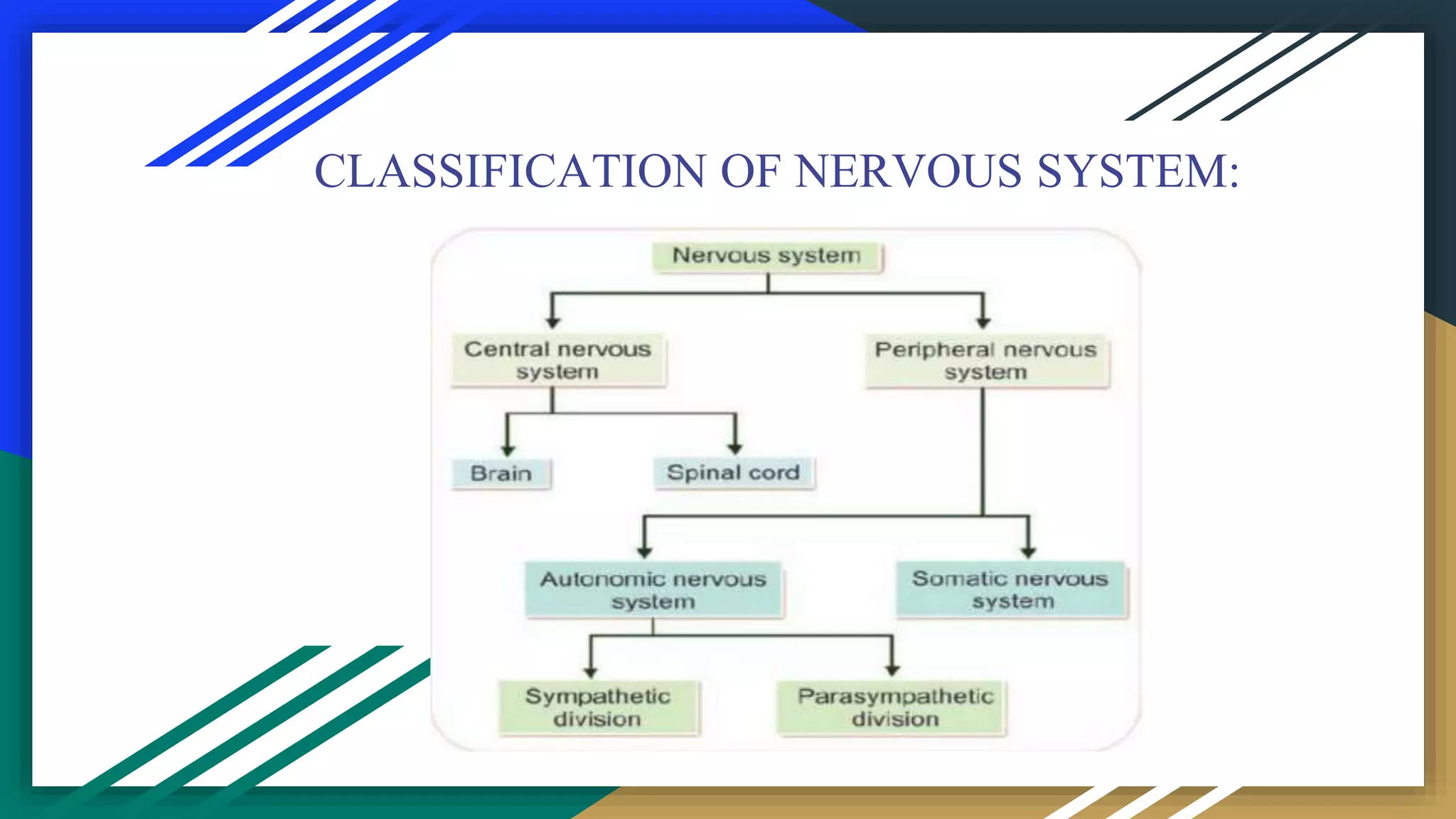
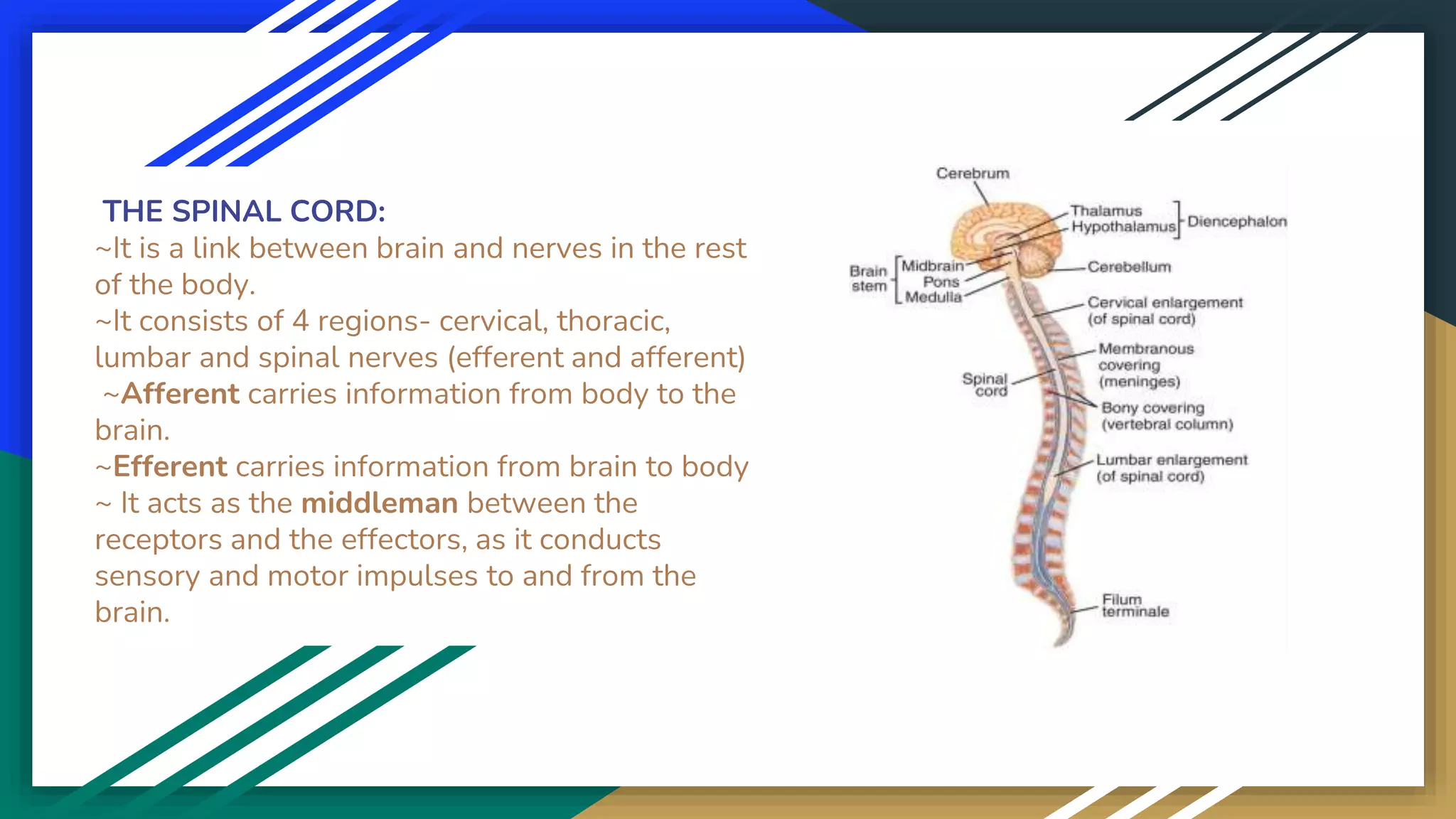
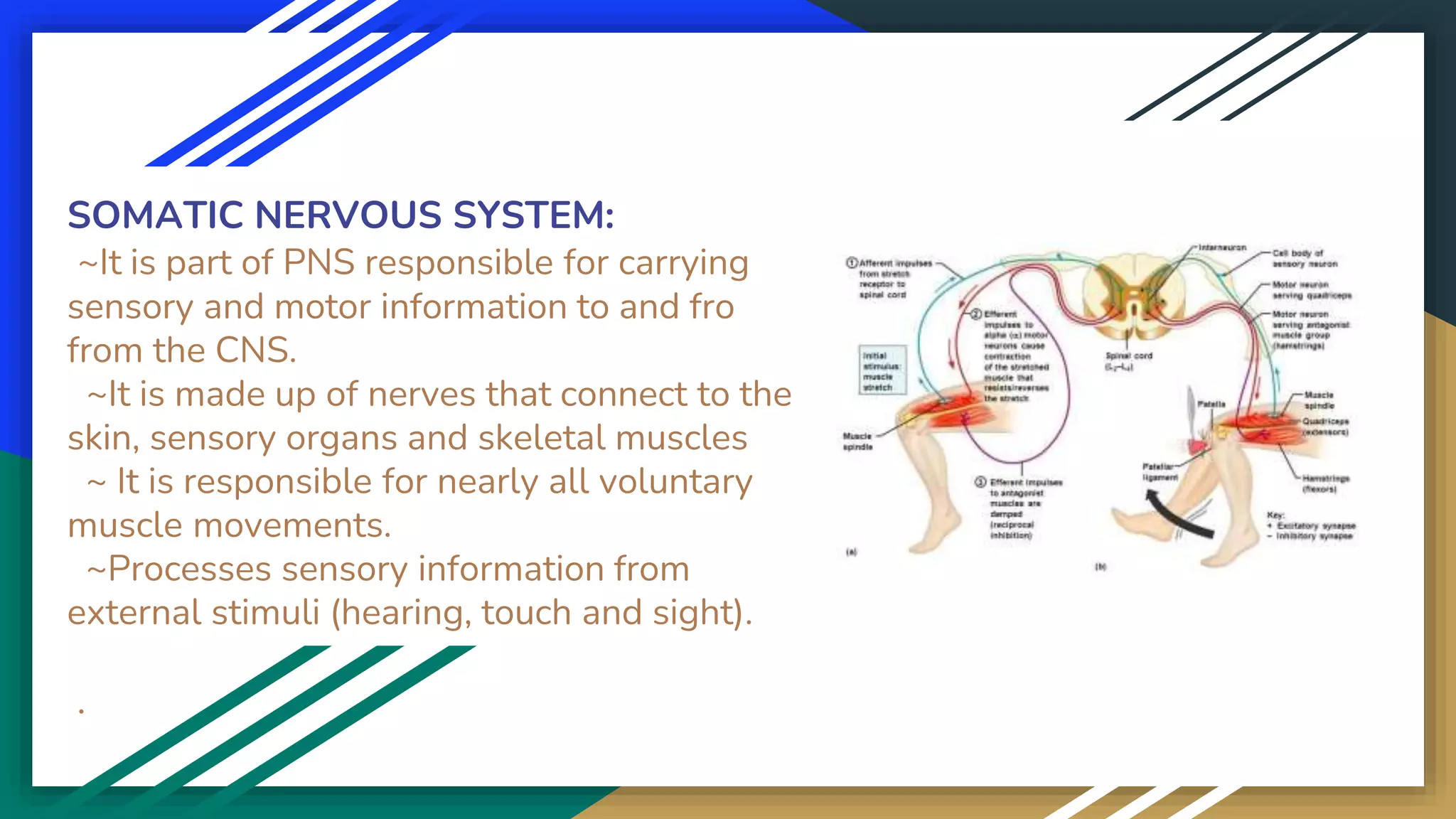
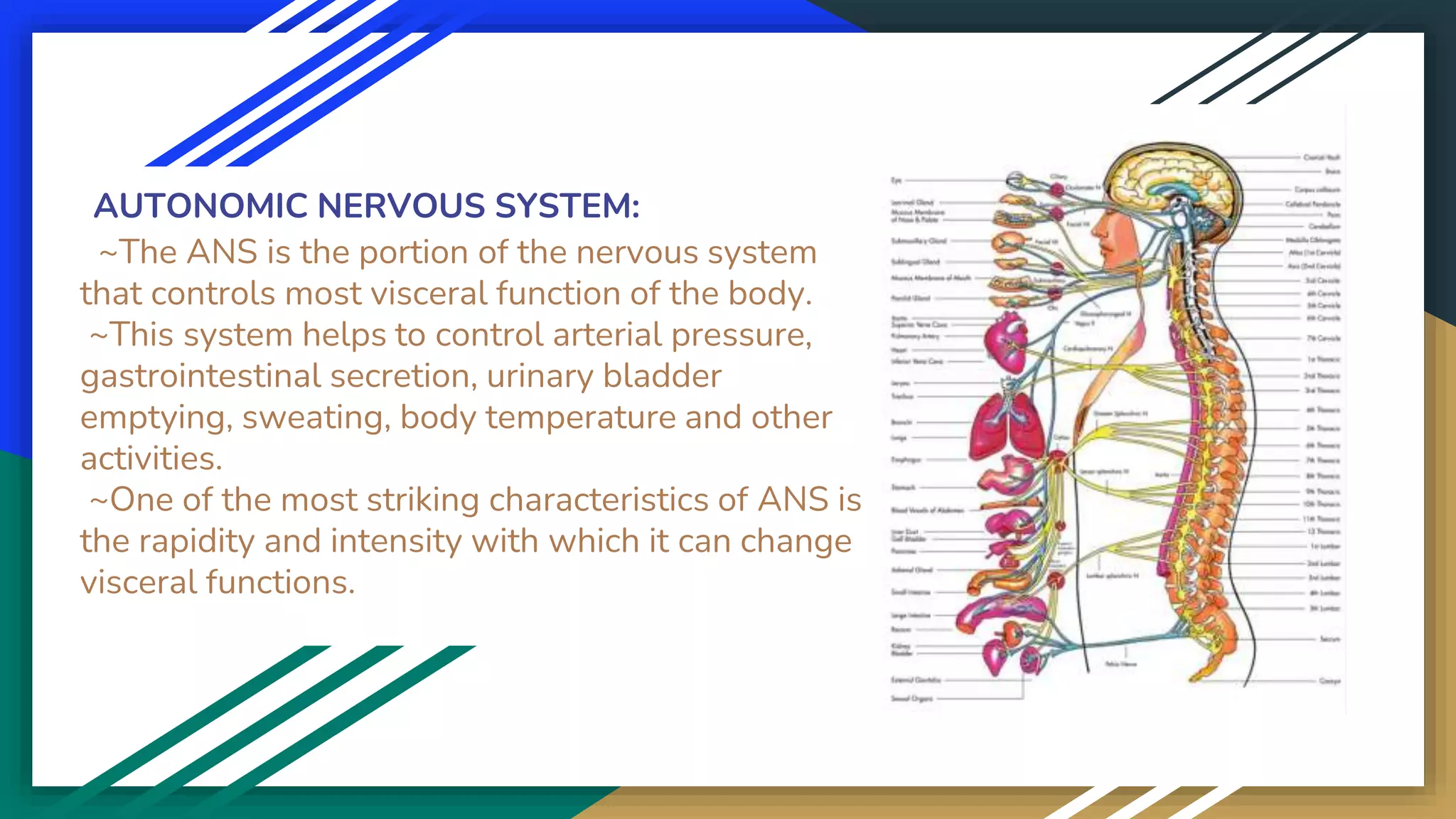
The document outlines the structure and function of the nervous system, highlighting its role as the master control system of the body. It details the central nervous system (CNS), including the brain and spinal cord, and explains the peripheral nervous system (PNS), comprising cranial and spinal nerves. It further distinguishes between the somatic and autonomic nervous systems, describing their specific roles in body functions and responses.