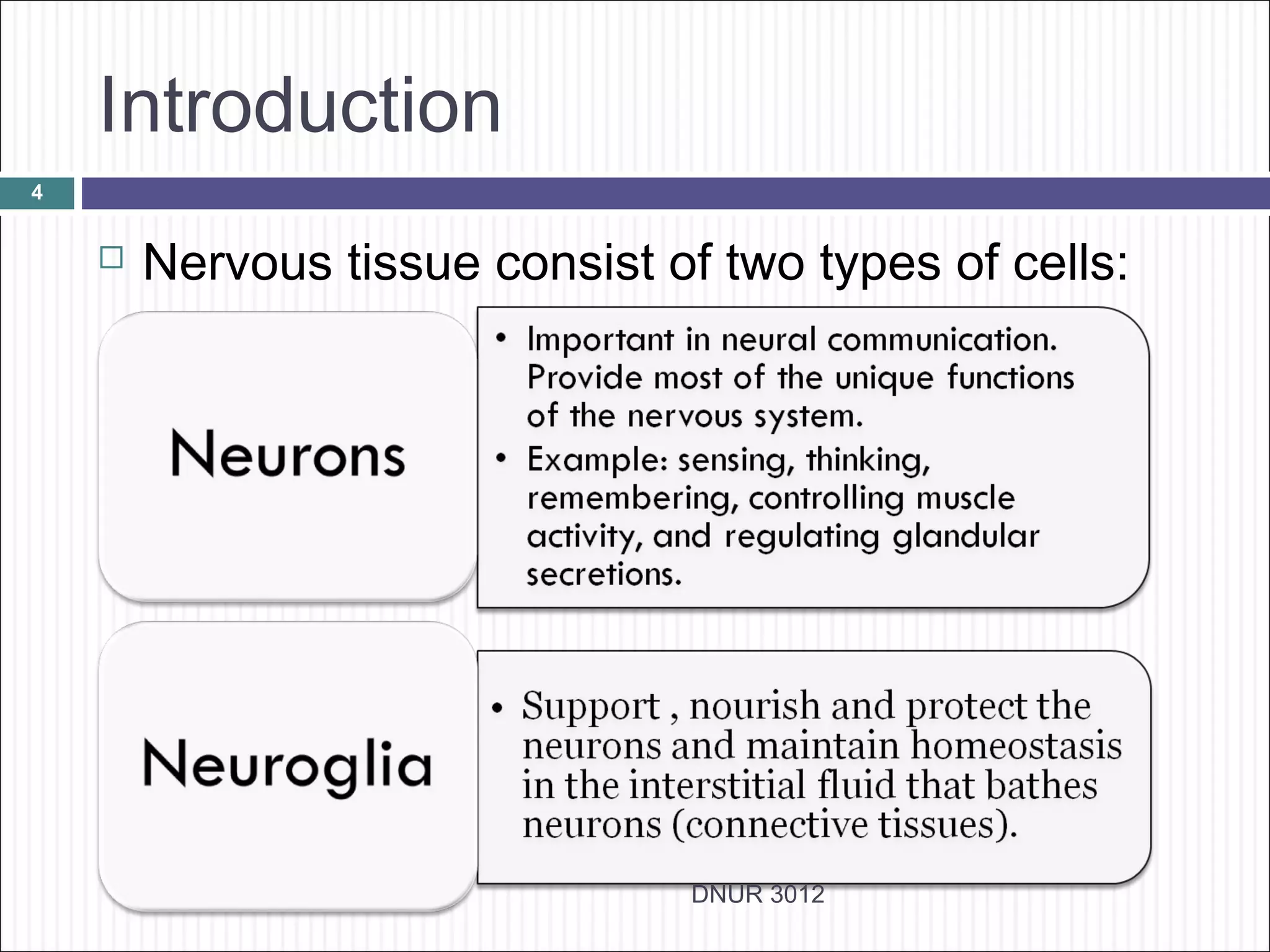
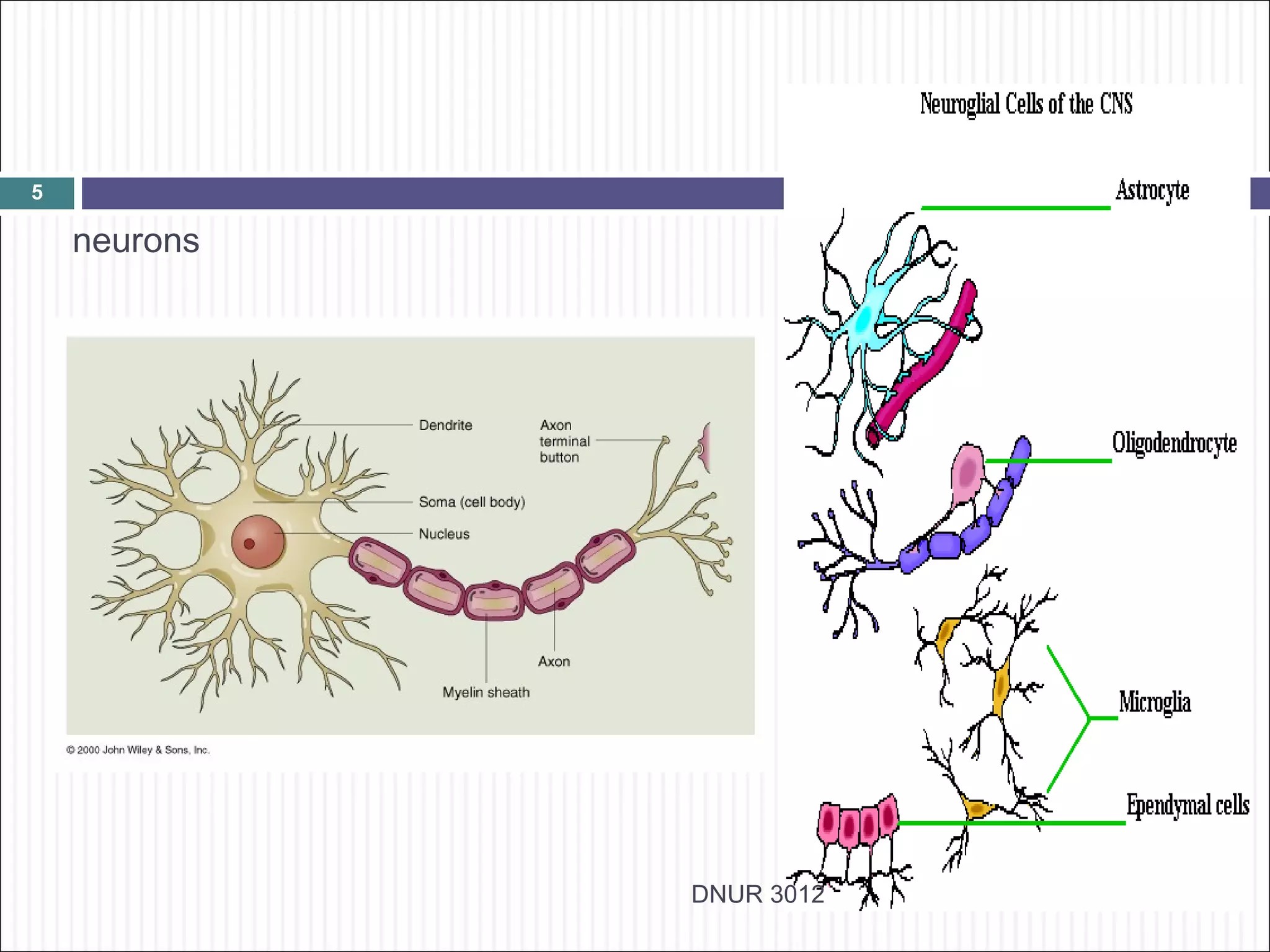
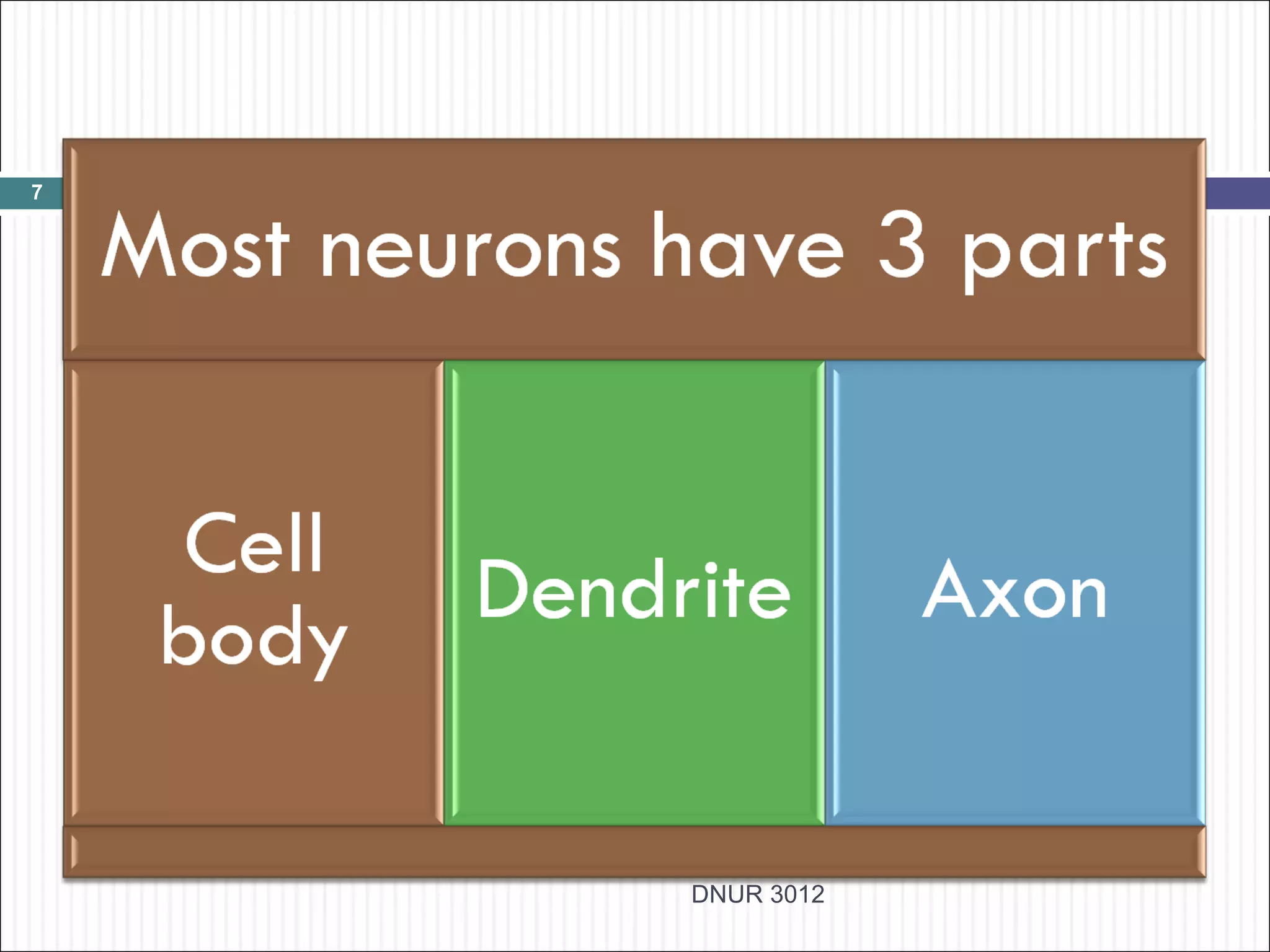
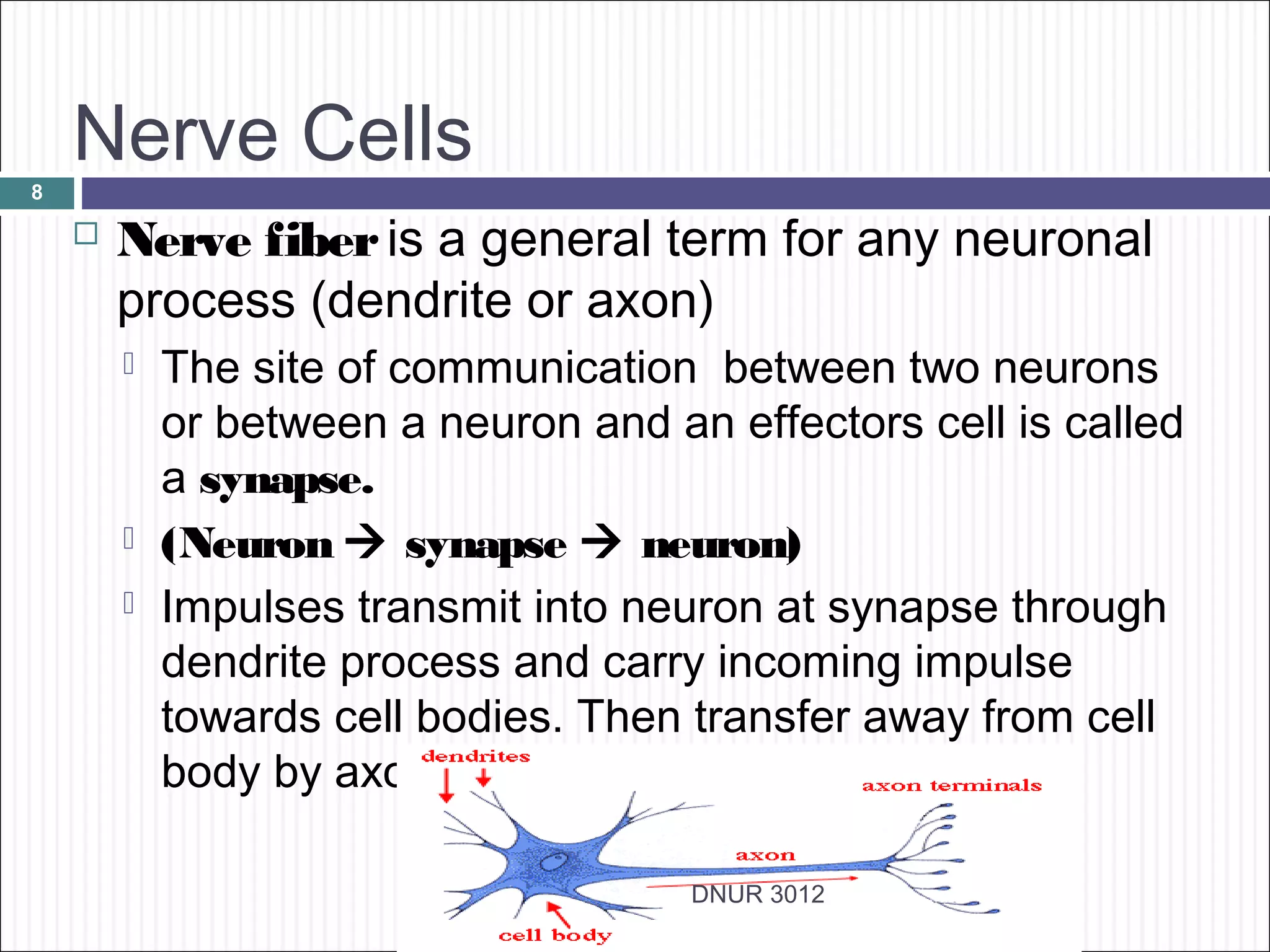
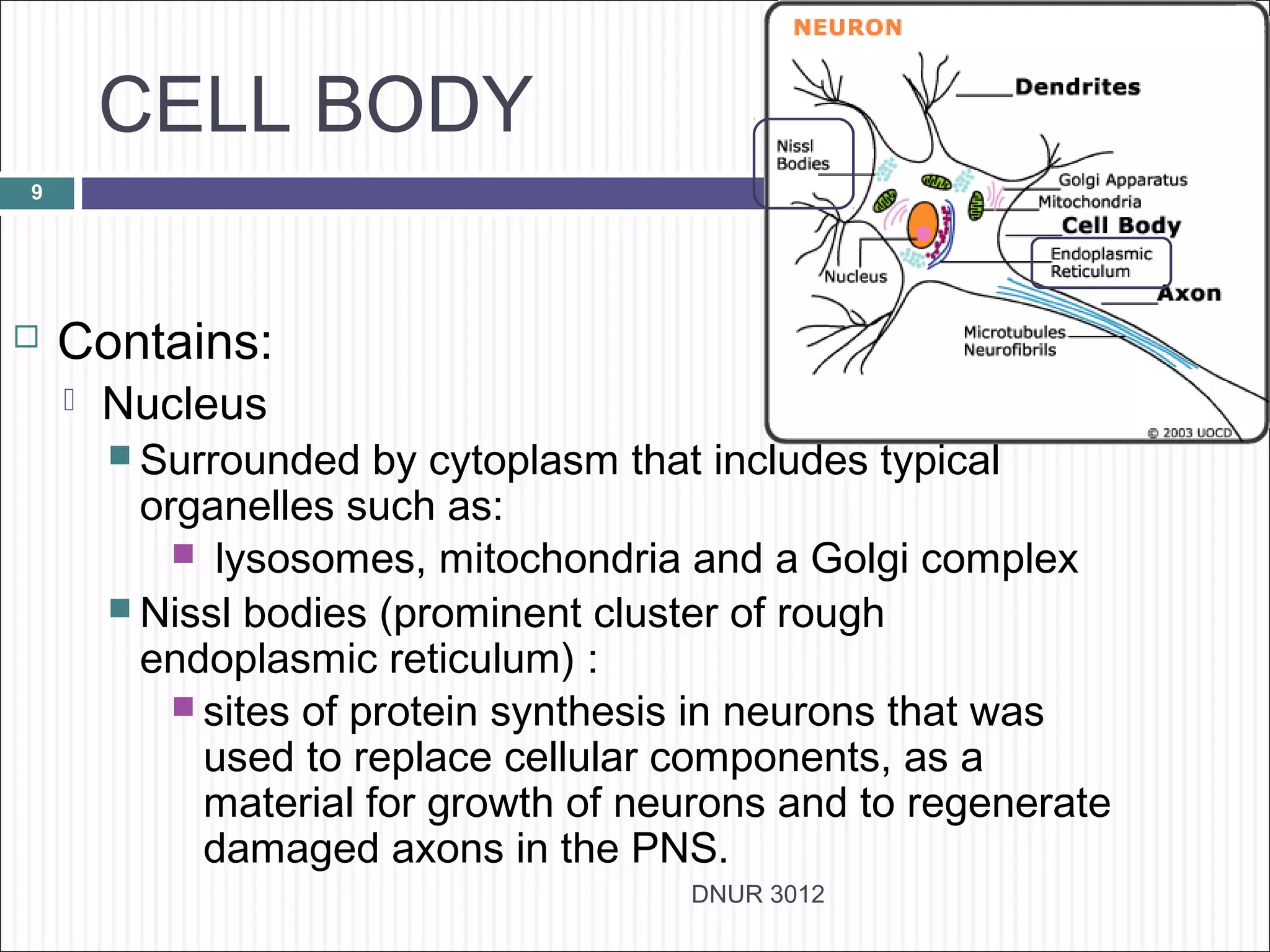
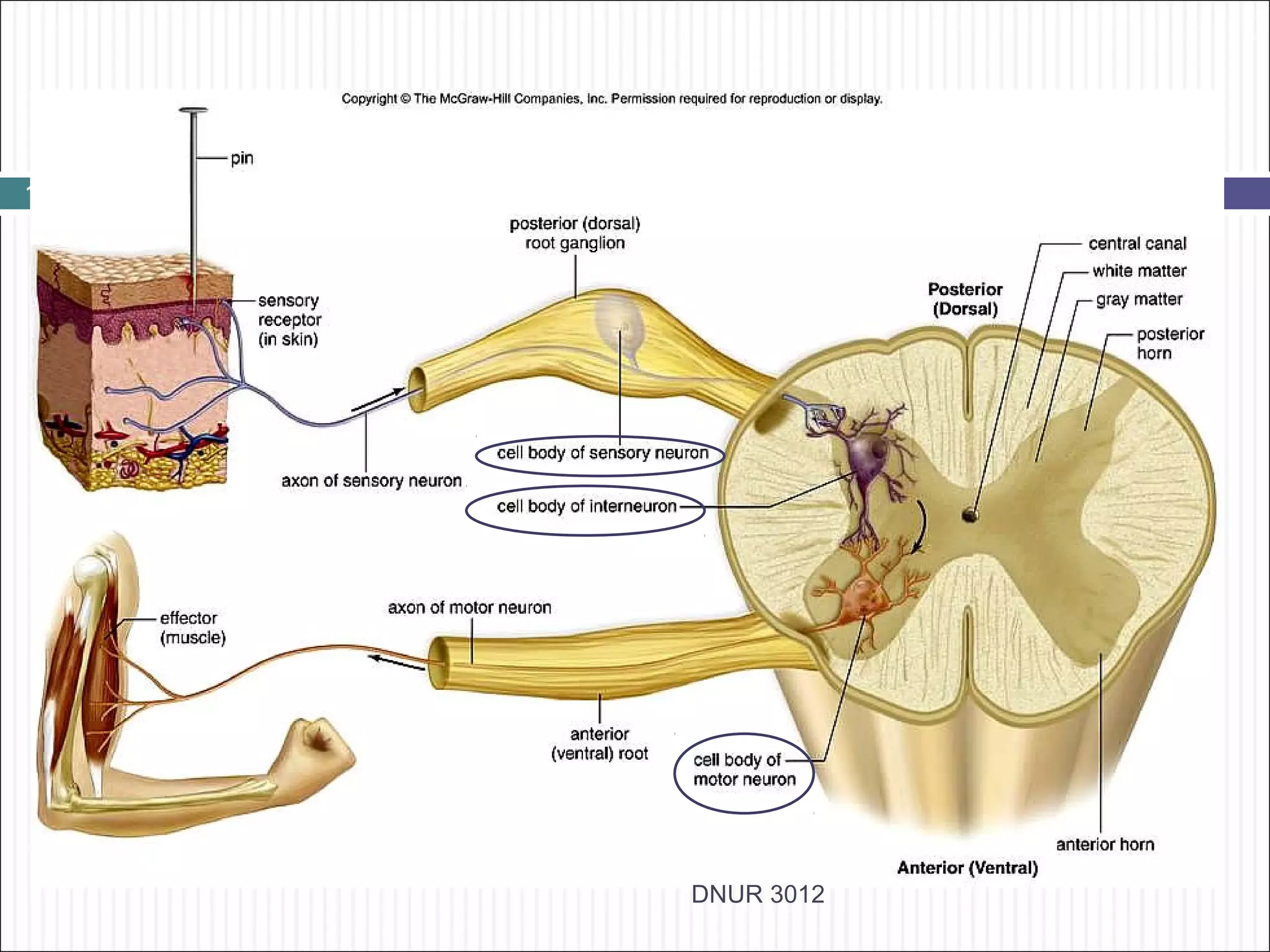
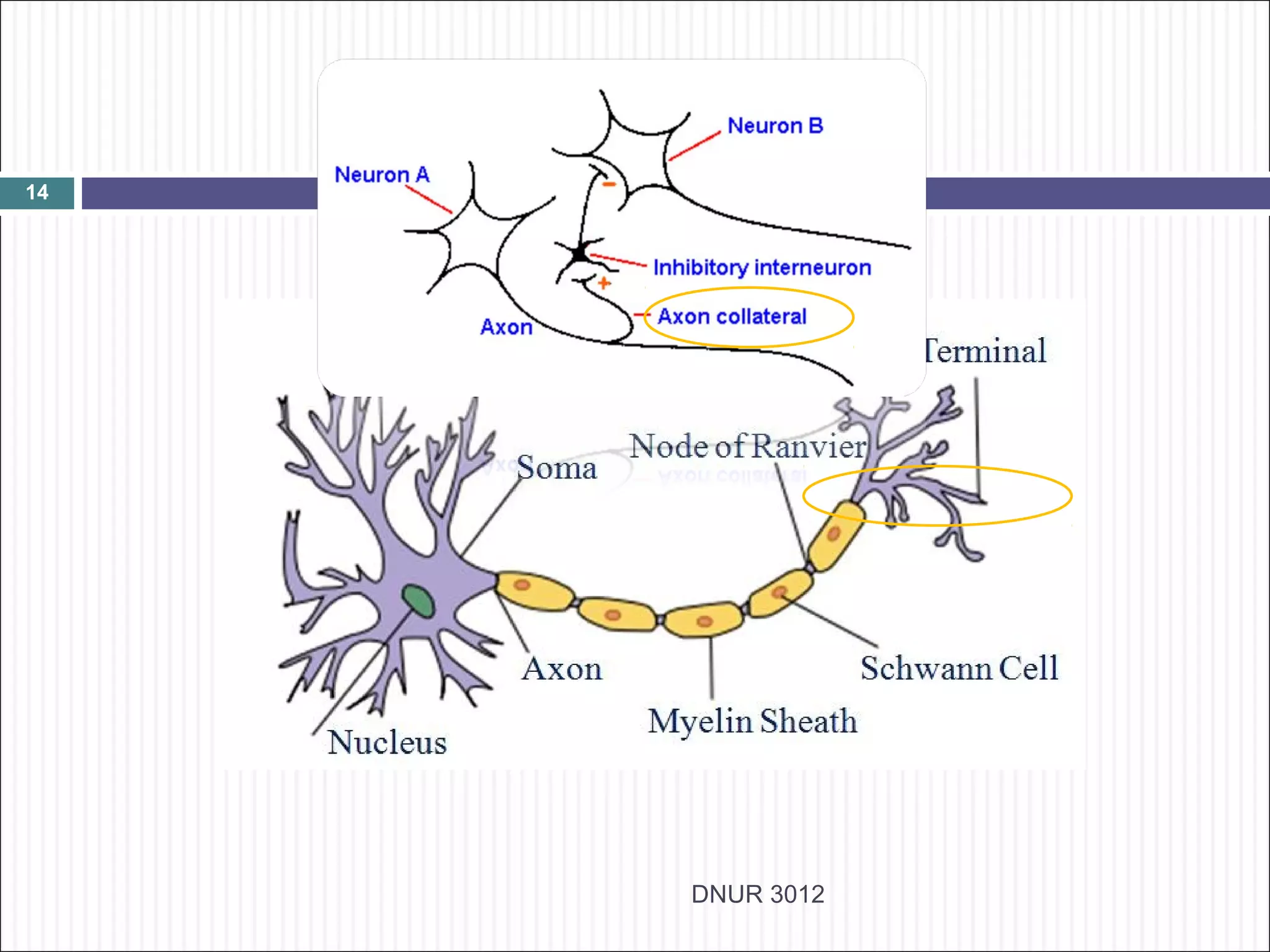
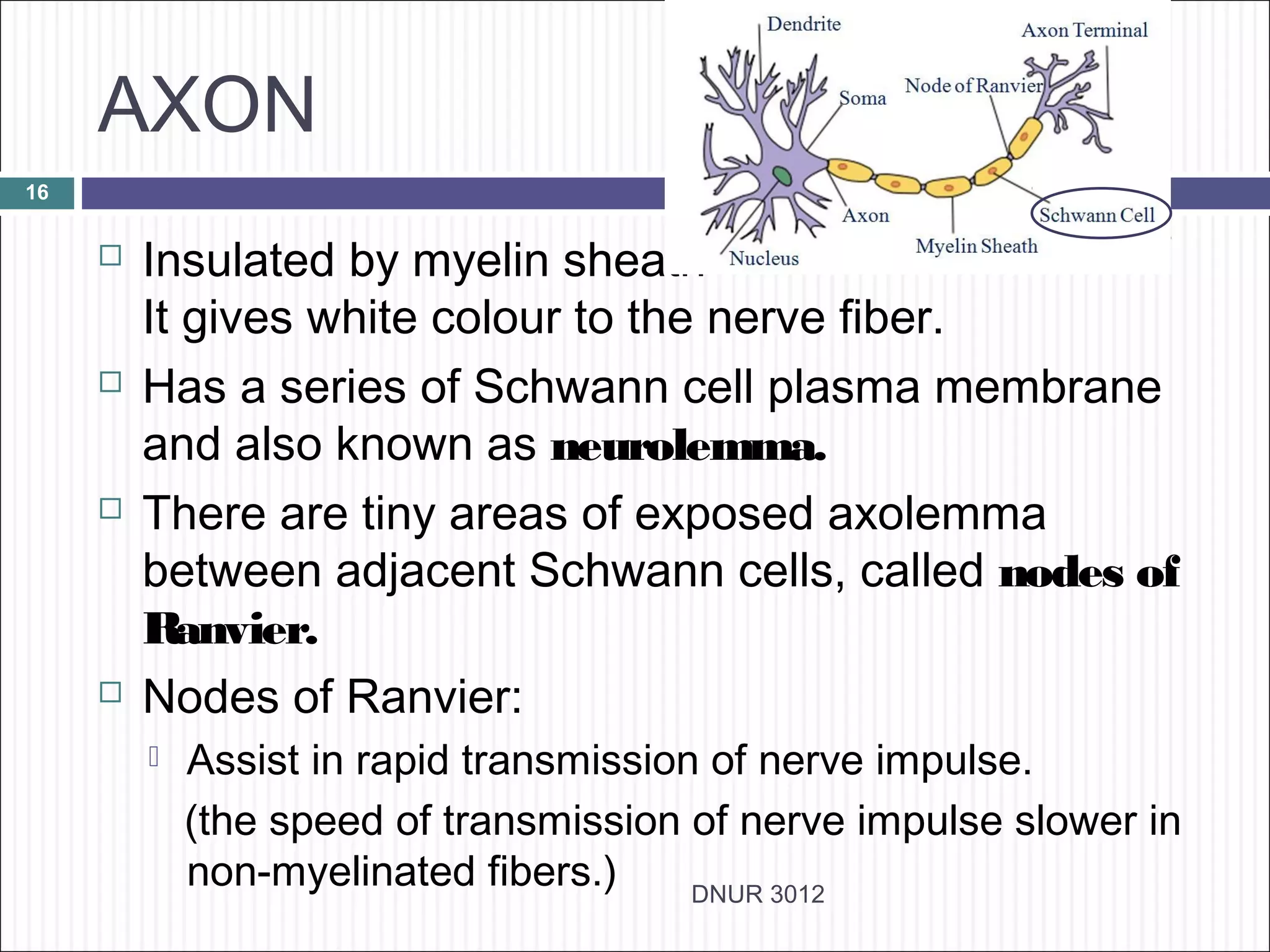
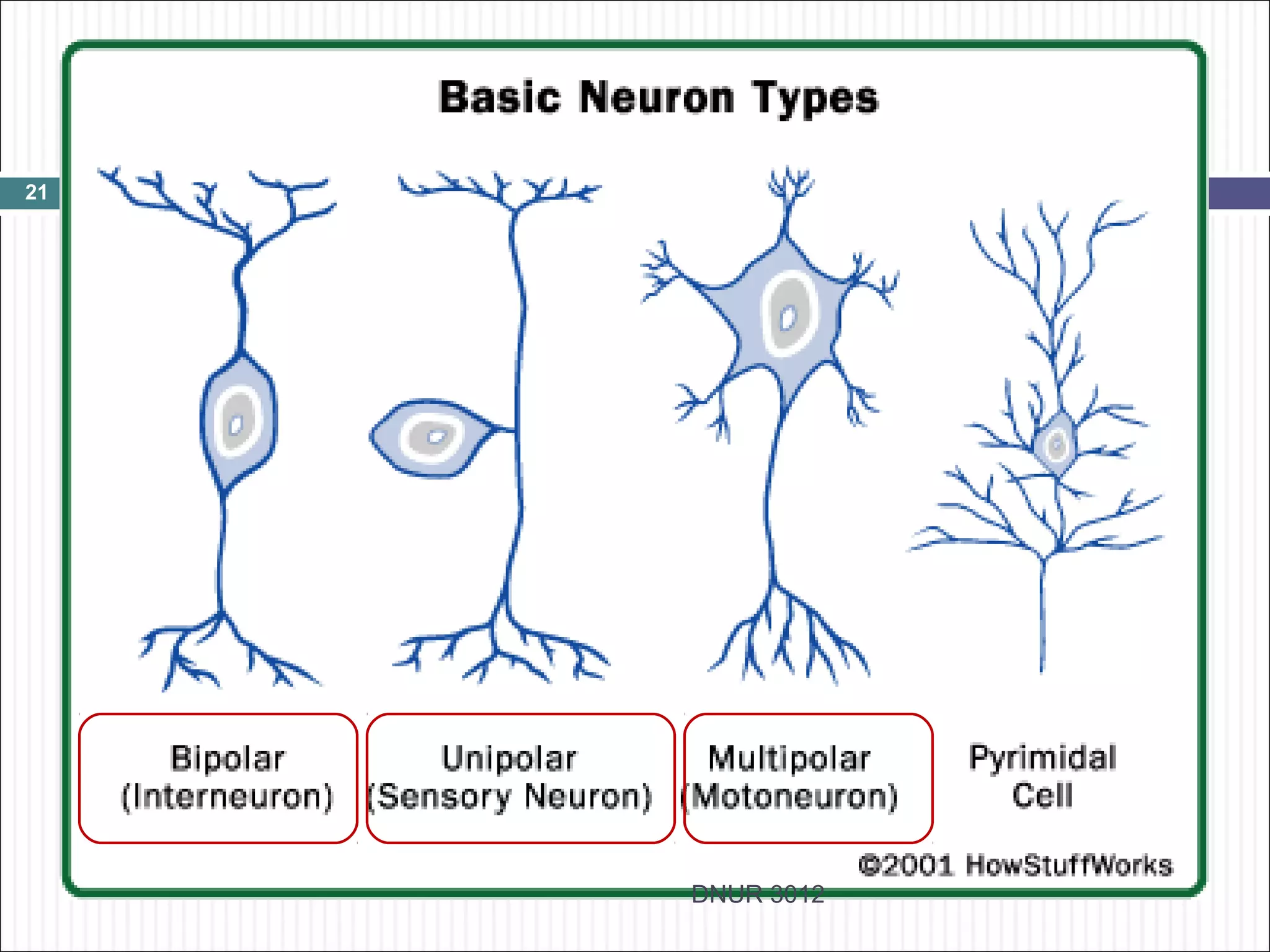
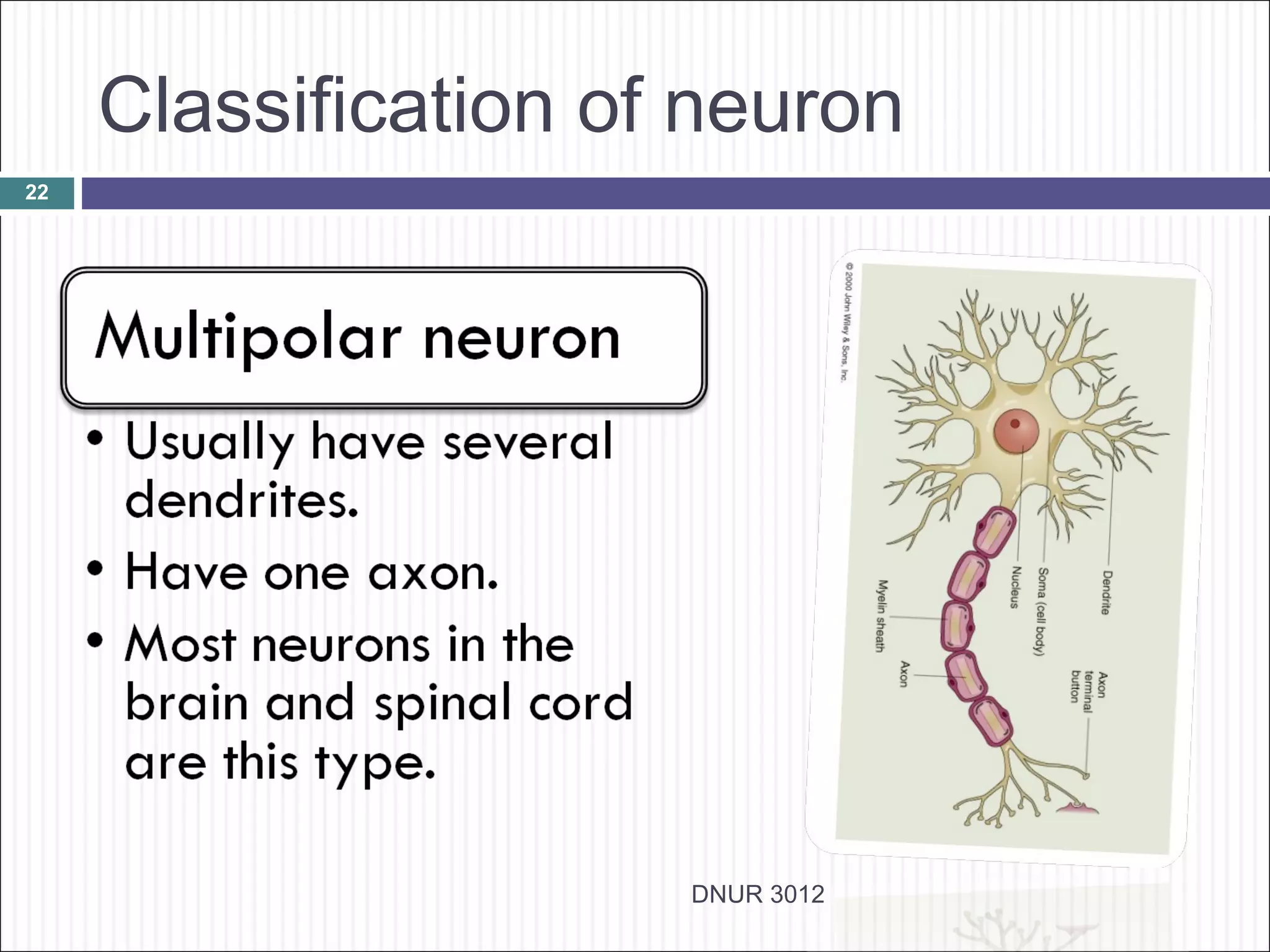
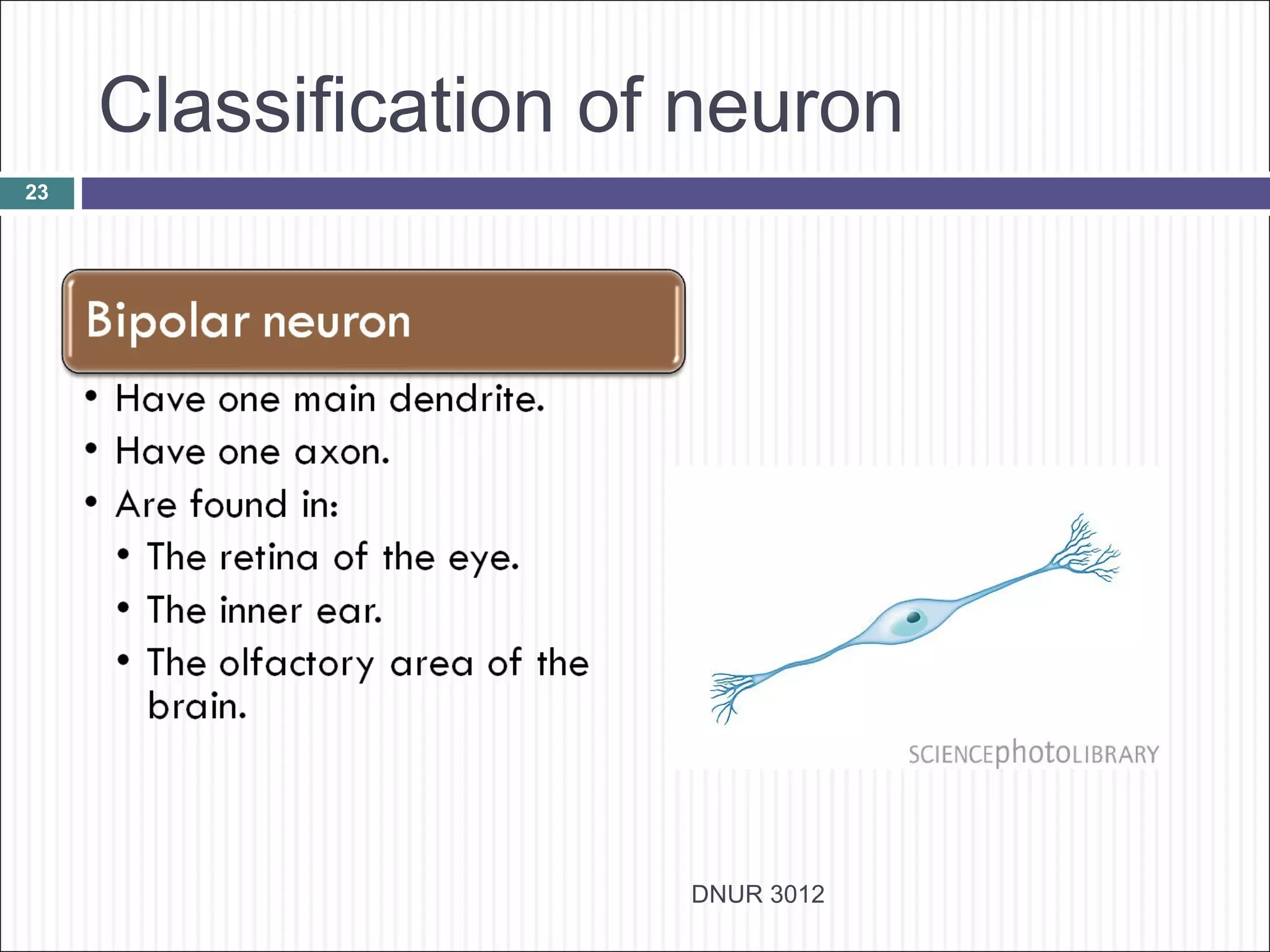
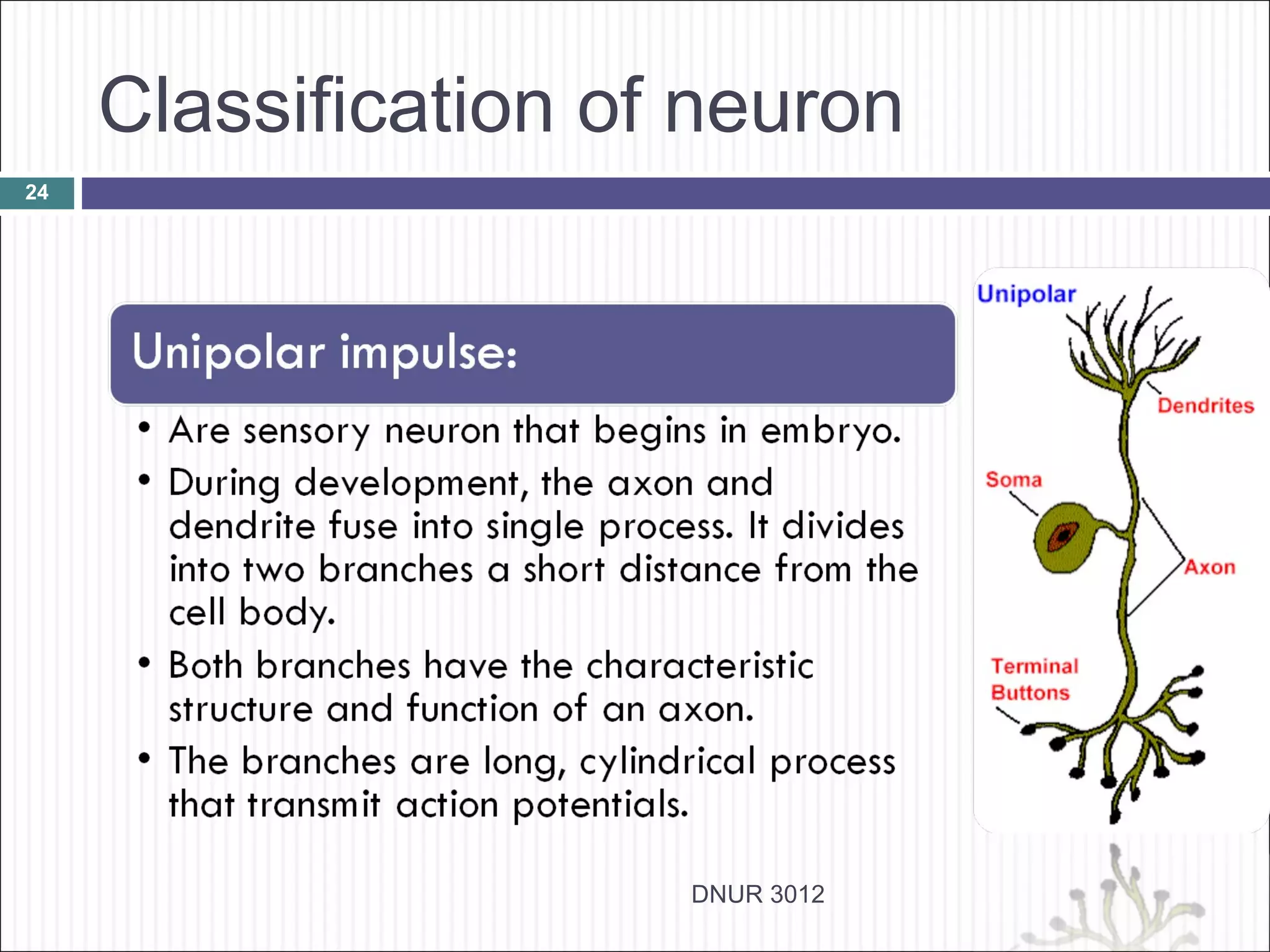
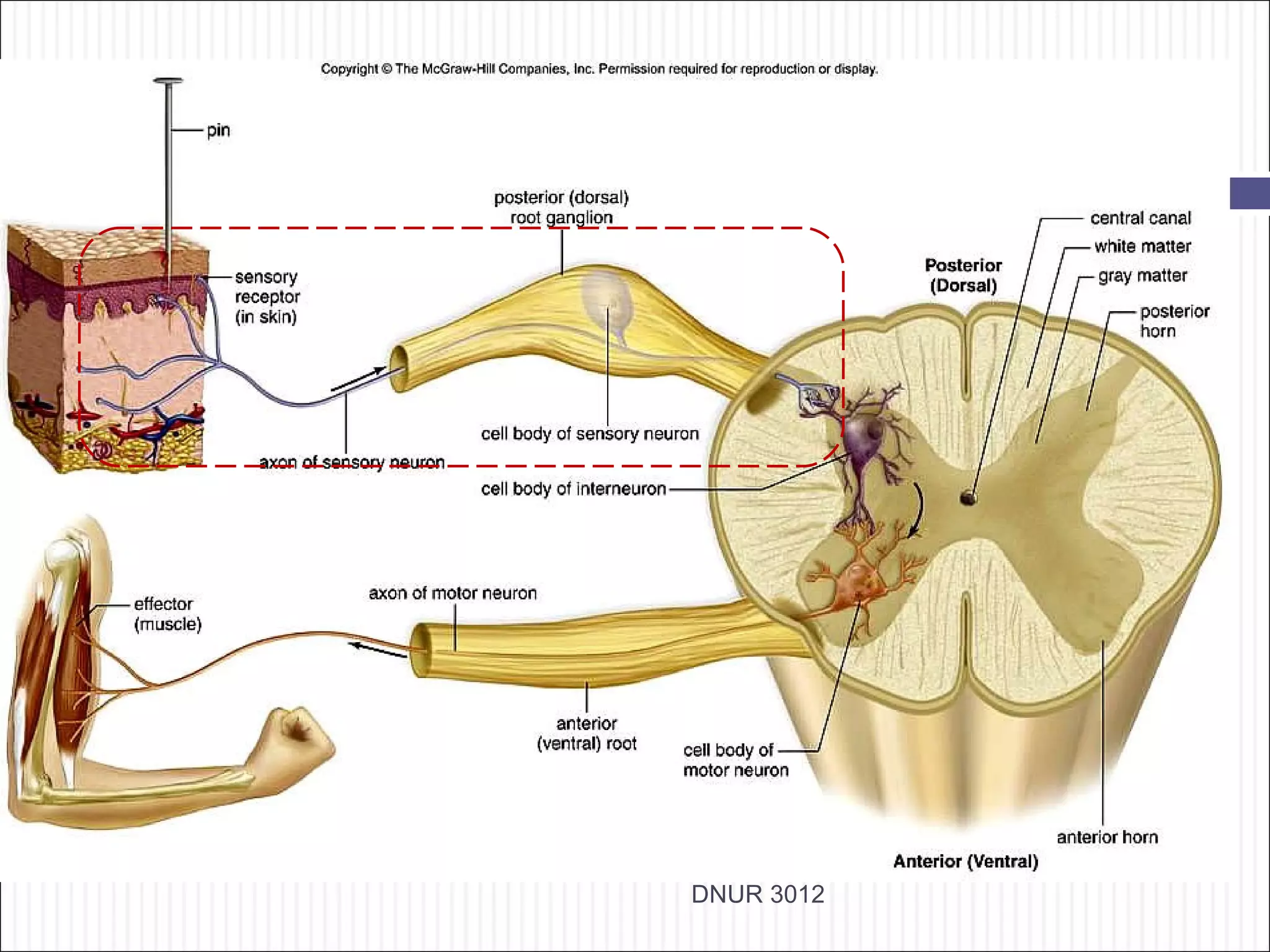
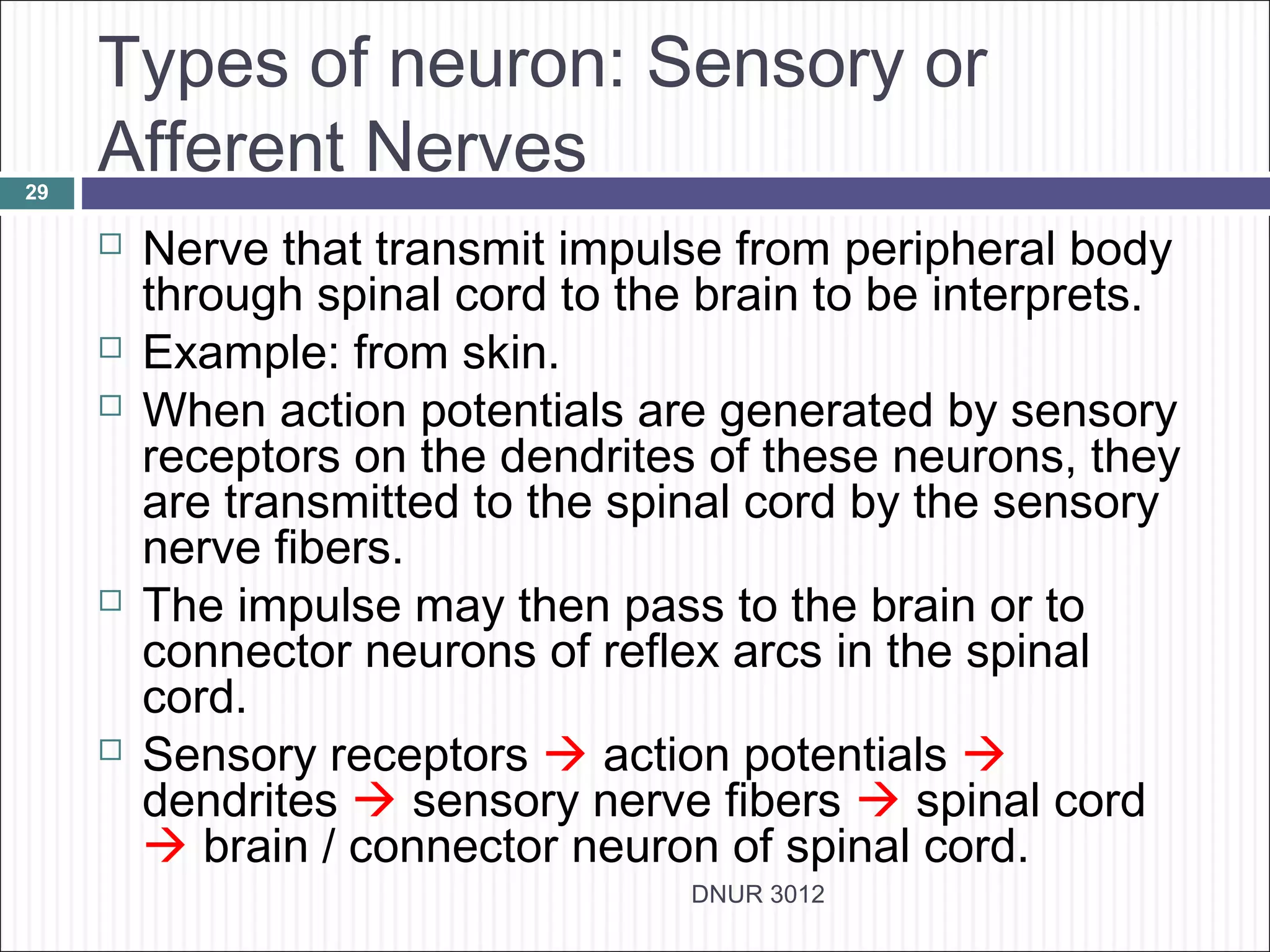
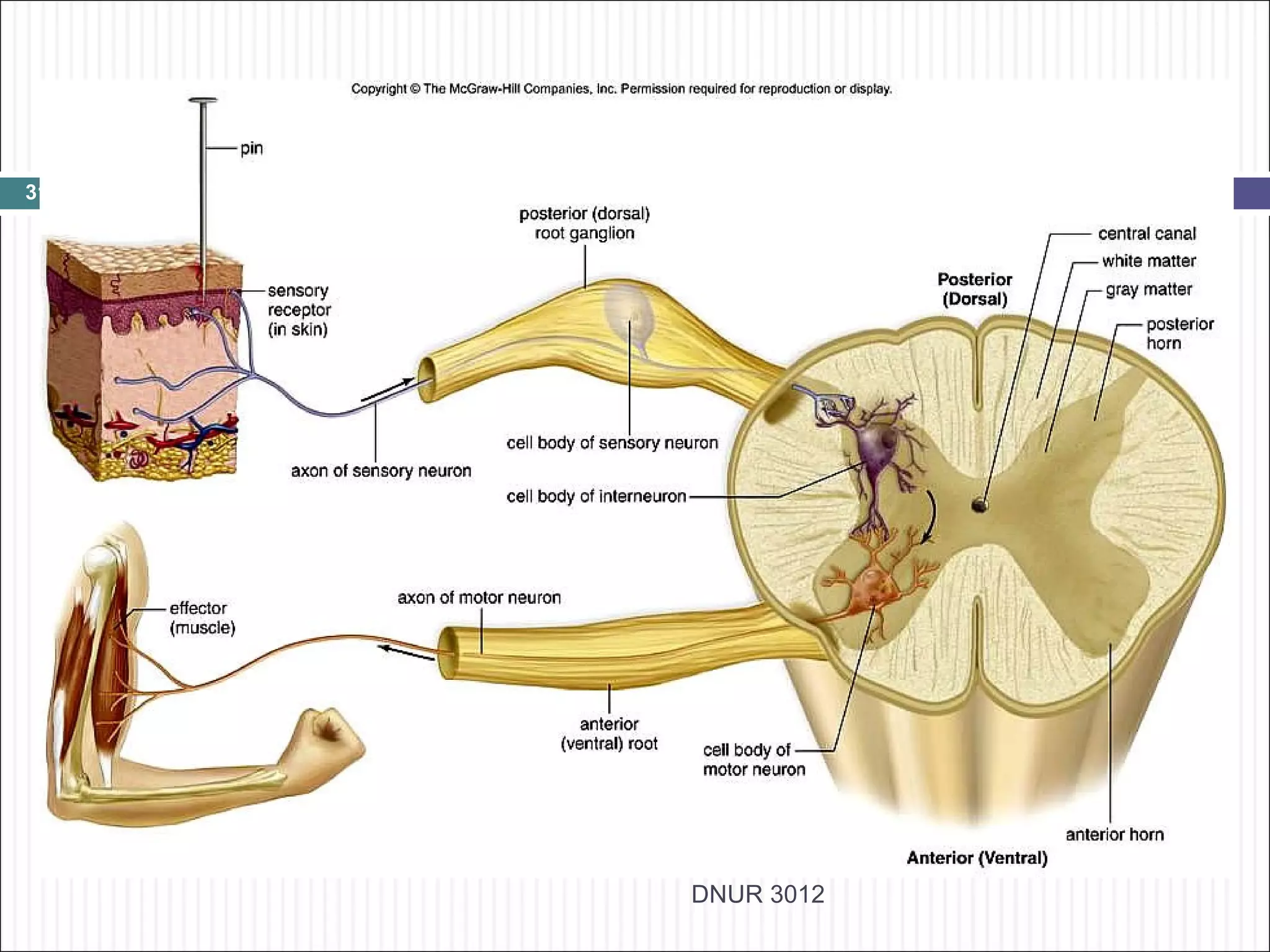
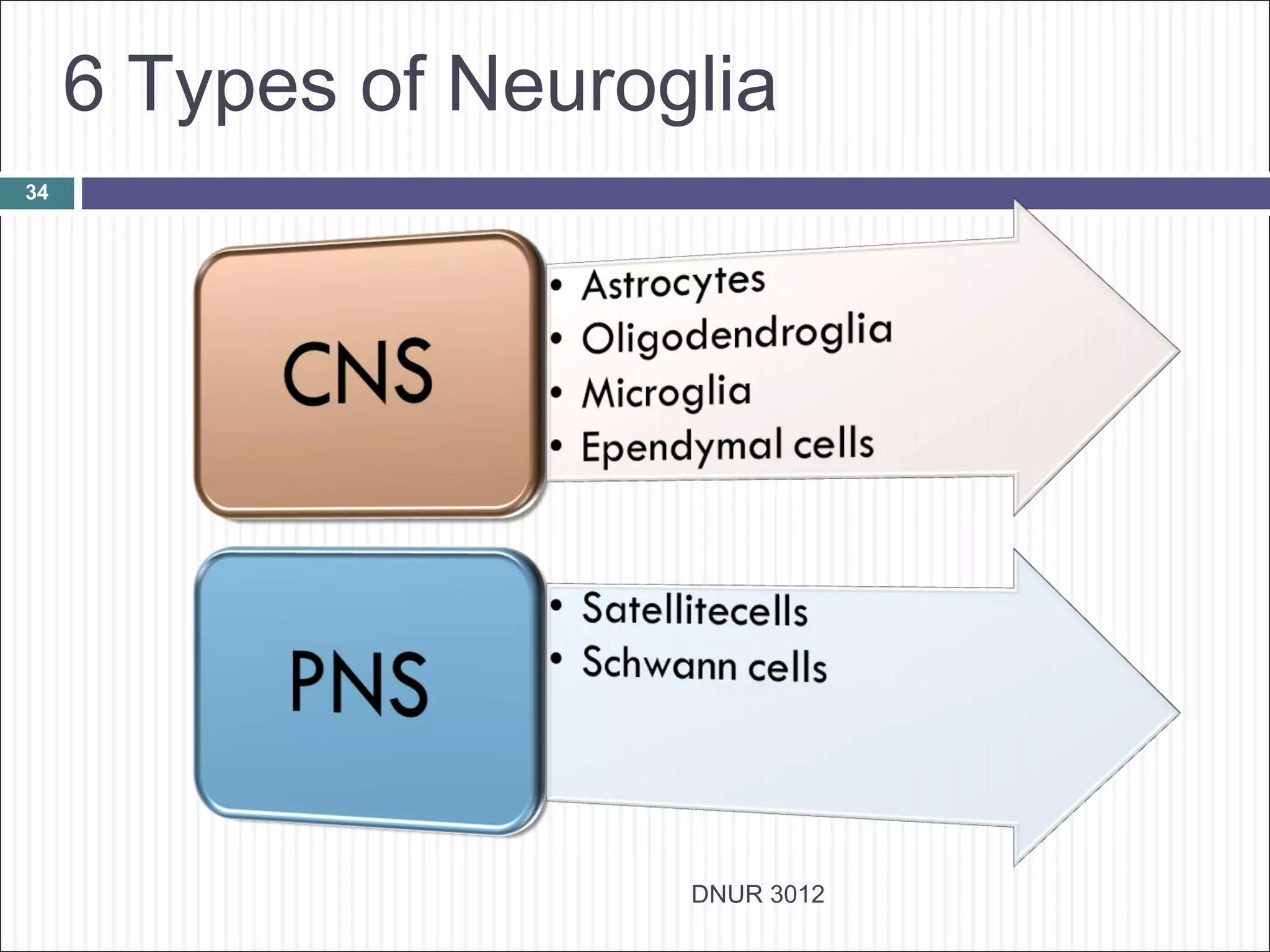
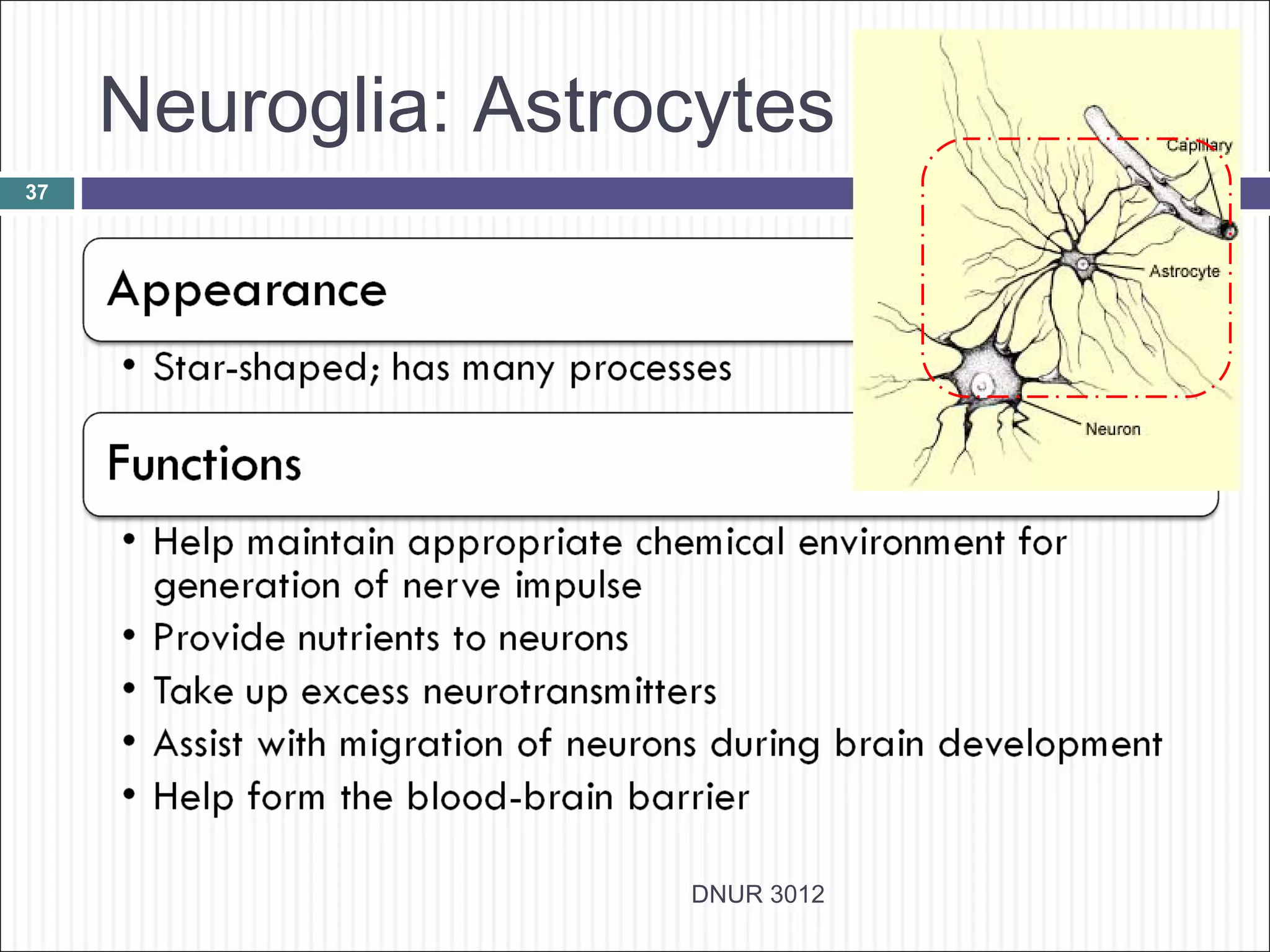
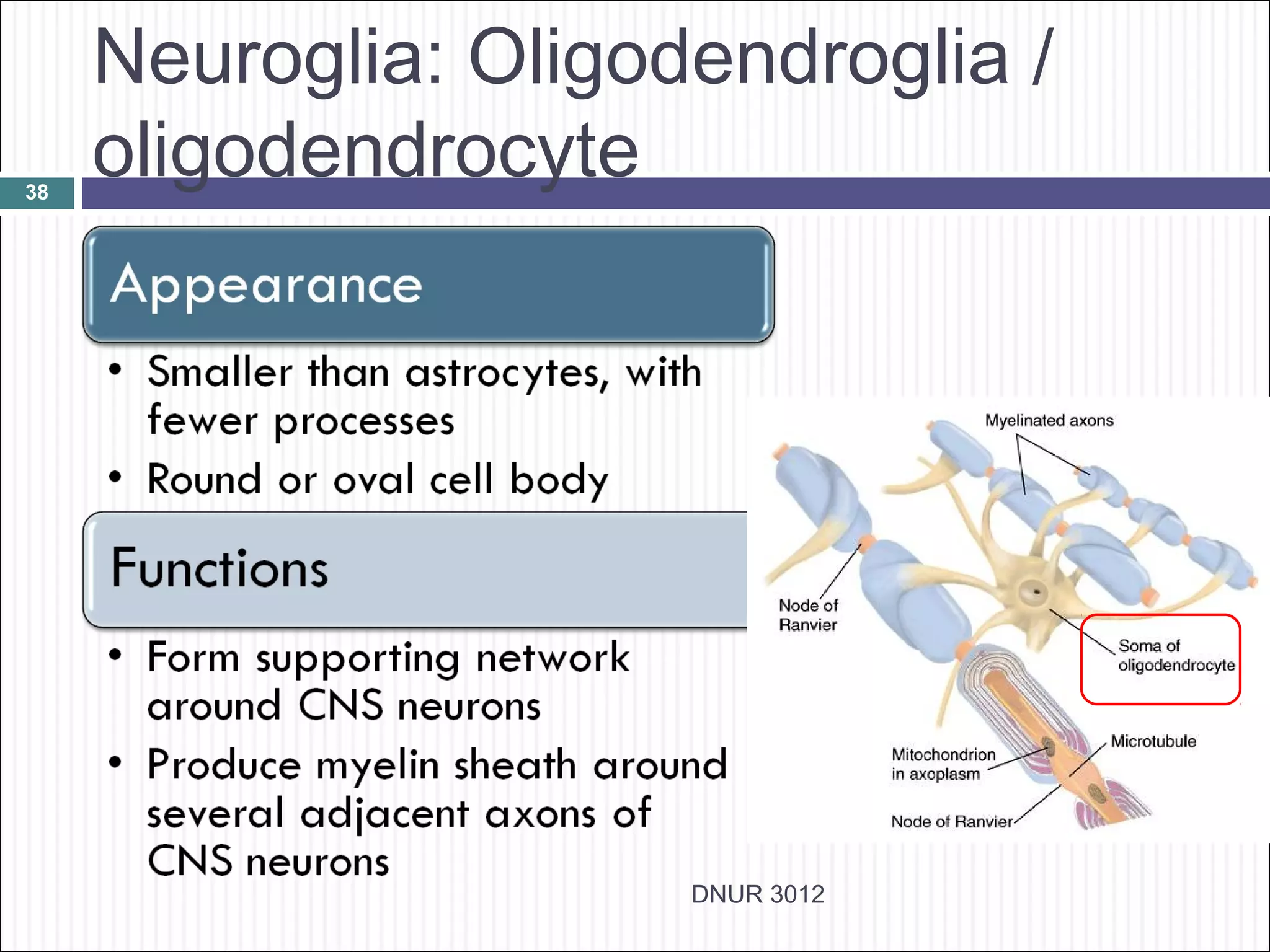
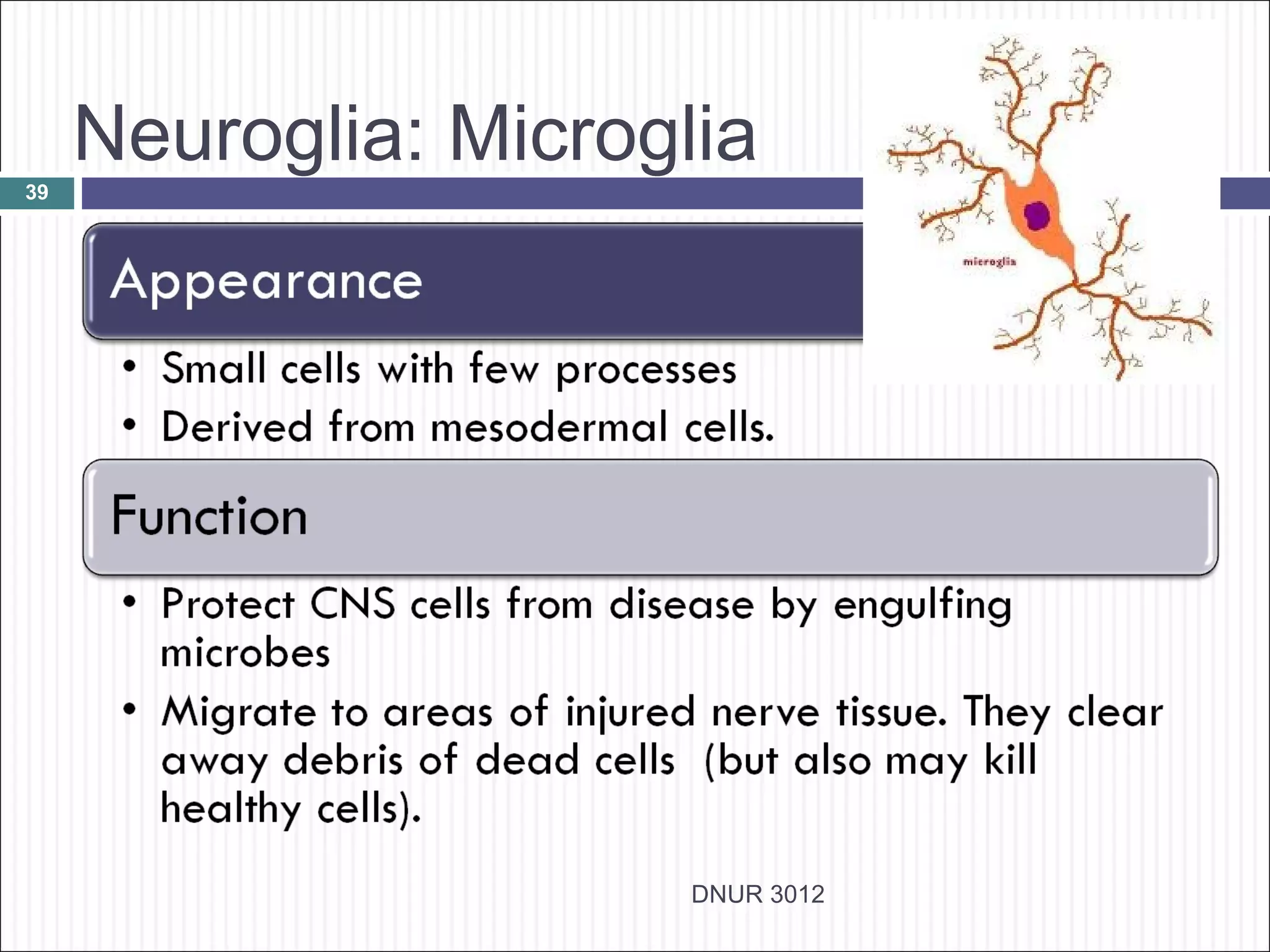
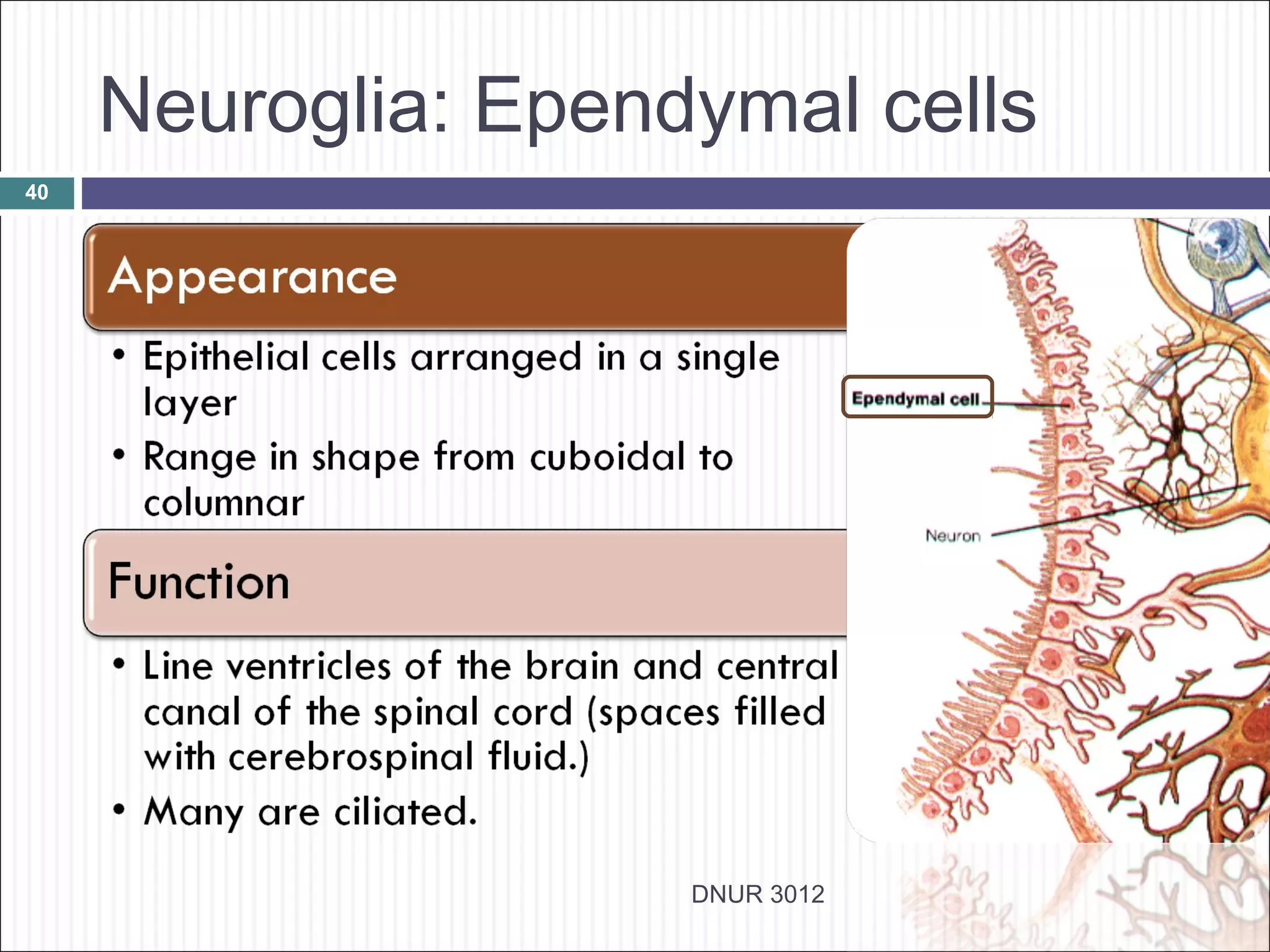
The document describes the anatomy and physiology of the nervous system. It discusses the key cell types - neurons and neuroglia. Neurons include the cell body, dendrites, axon and myelin sheath. The document classifies neurons as sensory, motor or interneurons. It also describes the 6 types of neuroglia and their functions in supporting neurons.