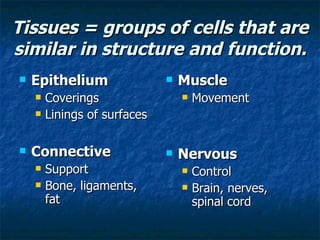
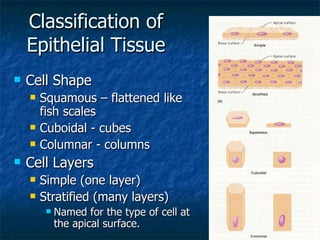
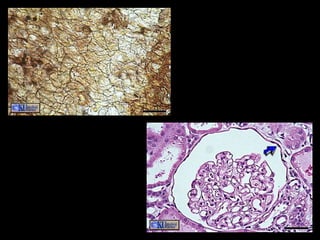
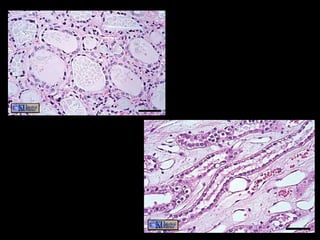
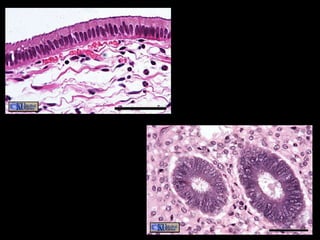
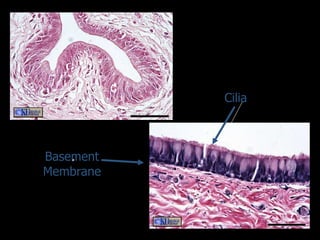
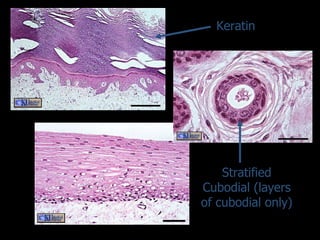
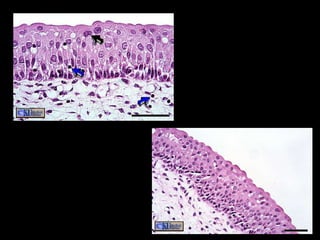
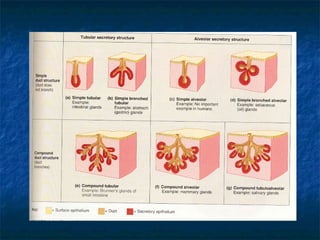
There are four main types of tissues in the human body: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous tissue. Epithelial tissue forms protective coverings and linings throughout the body, including the skin, digestive tract, and respiratory tract. It has several key characteristics, such as being avascular and forming sheets of cells. Epithelial tissue is classified based on cell shape and number of cell layers into simple and stratified types, including squamous, cuboidal, columnar, pseudostratified, and transitional epithelium. Glands are specialized clusters of epithelial cells that secrete substances like hormones, acids, and oils.