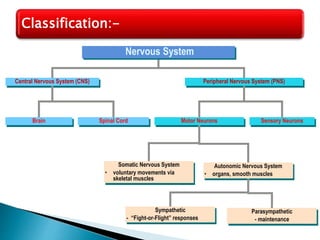
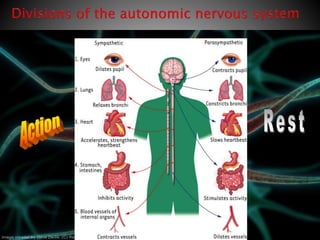
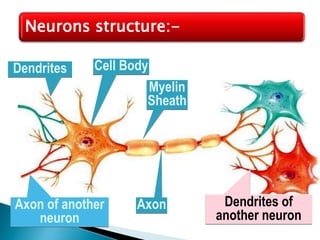
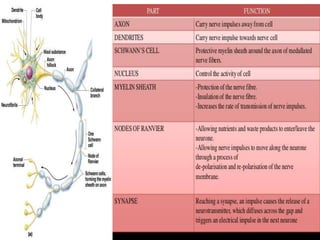
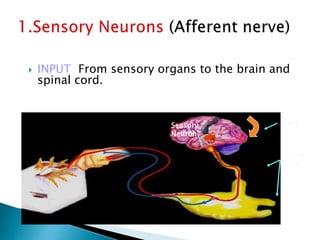
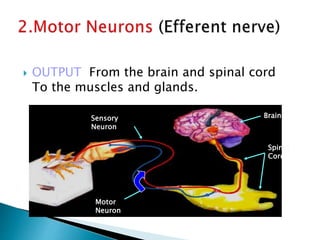
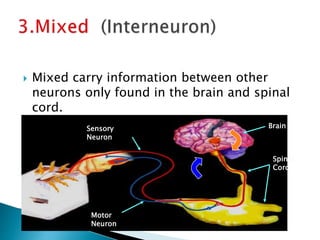
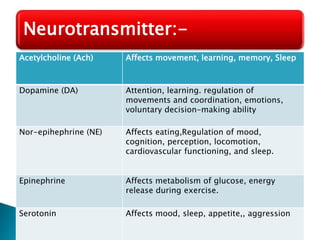
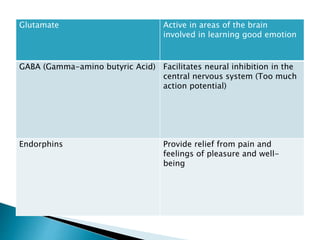
The document discusses the nervous system, which controls and coordinates the body. It describes the central nervous system, made up of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system. The nervous system is classified into the somatic system for voluntary movement, and the autonomic system with the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions for involuntary functions like digestion. Neurons are the basic functional units that receive, integrate, and transmit information via chemical signals. There are sensory neurons, motor neurons, and mixed neurons. Neurotransmitters are the chemical signals that convey information between neurons in the brain and spinal cord.