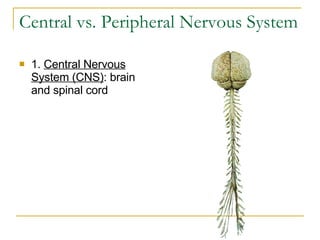
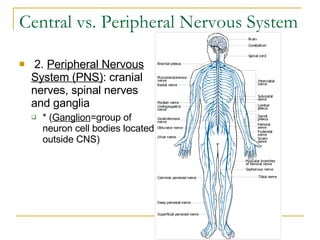
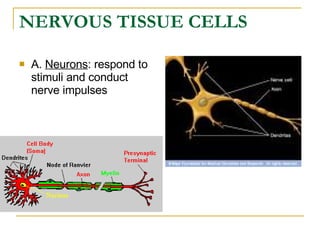
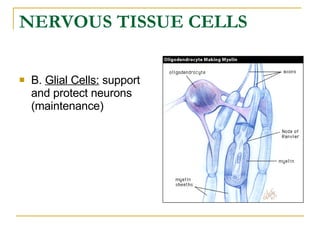
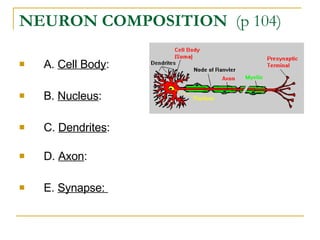
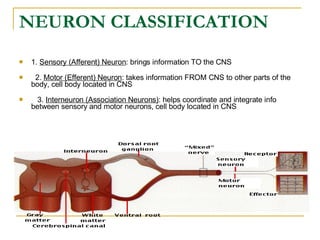
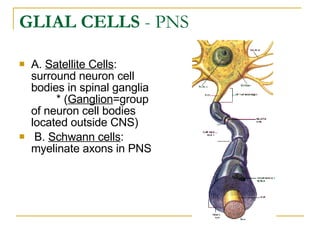
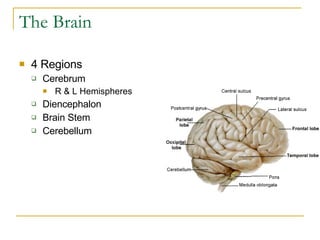
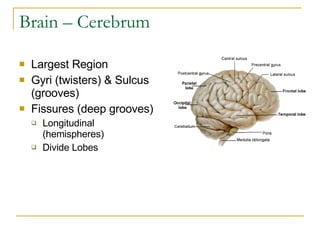
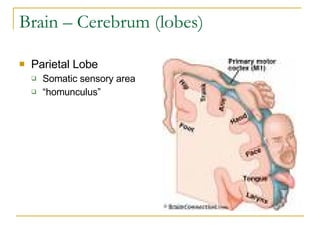
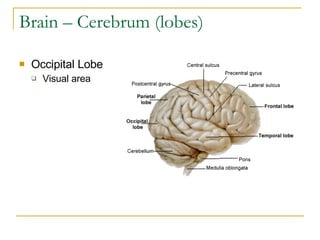
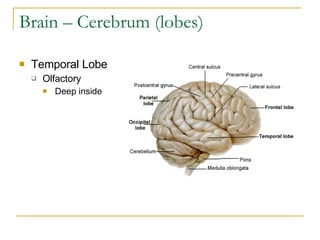
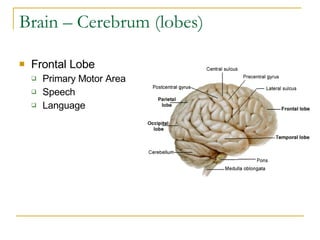
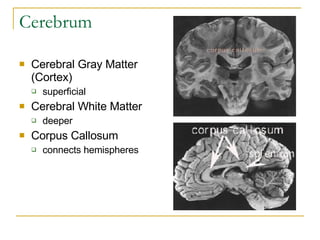
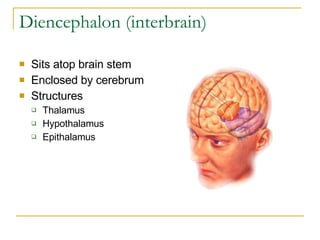
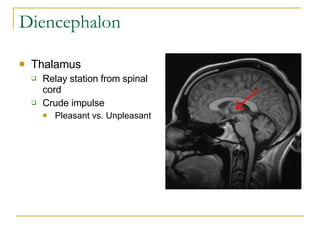
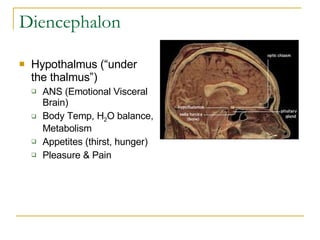
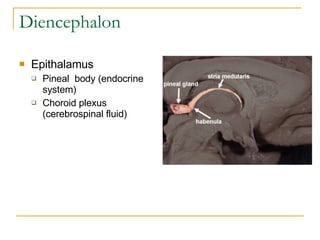
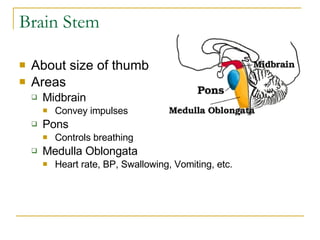
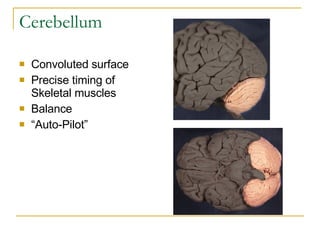
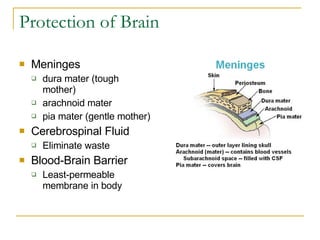
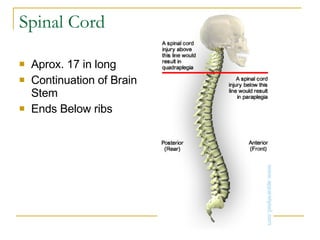
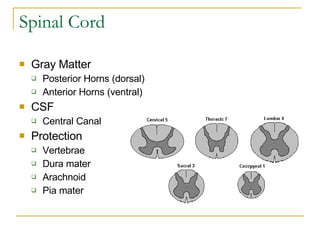
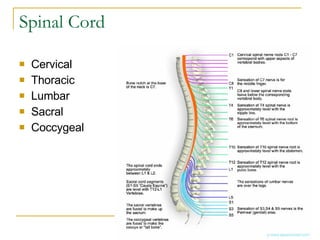
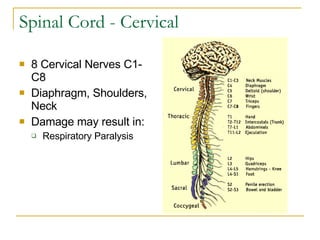
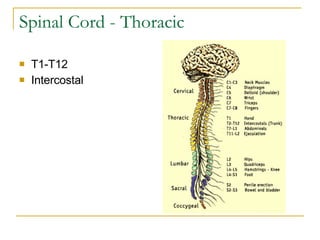
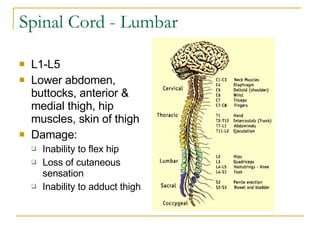
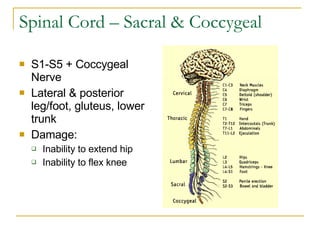
The document describes the structure and function of the nervous system. It discusses the central nervous system (CNS), which includes the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), which includes nerves and ganglia outside the CNS. The nervous system has sensory and motor divisions, with sensory receiving information and motor transmitting it. Neurons conduct nerve impulses while glial cells support neurons. The brain regions include the cerebrum, diencephalon, brain stem, and cerebellum. The spinal cord extends from the brain stem and is divided into sections.