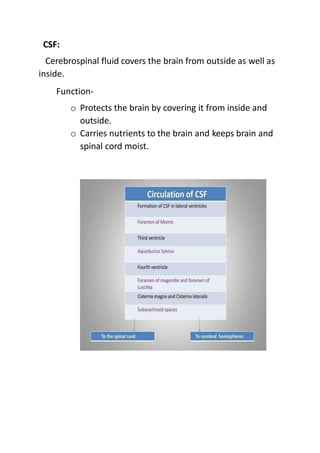
The nervous system consists of the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system receives and integrates sensory information and coordinates voluntary and involuntary motor activity. It is protected by three layers of meninges and nourished by a network of blood vessels. The peripheral nervous system comprises the cranial and spinal nerves along with their ganglia and sensory receptors throughout the body. It is divided into the somatic and autonomic nervous systems.





![Hypothalamus –
A bilateral structure below the thalamus.
Acts as biological gland.
Weight—7g
Position –in front of the thalamus immediately above
the pituitary gland.
Function—
1.vegetative and endocrine function:
o Regulation of body temperature 37
o Regulation of water balance
o Regulation of feeding
o Regulation of cardiovascular system[increase BP
and HR]
o Endocrine function—controls secretion of pituitary
gland and release hormones of posterior pituitary.
2.Behavioural function:
o Stimulation of certain areas of hypothalamus causes
rage or fighting.
o Sexual drive is stimulated by anterior and posterior
portions of hypothalamus.
o Responsible for pleasant and unpleasant sensation.
Metathalamus—
Consists of medial and lateral geniculate bodies.
Function—
1.Medial geniculate body receives auditory impulses.
2.lateral geniculate body receives visual impulses.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nervoussystem-230522174255-5056048d/85/NERVOUS_SYSTEM-pptx-7-320.jpg)