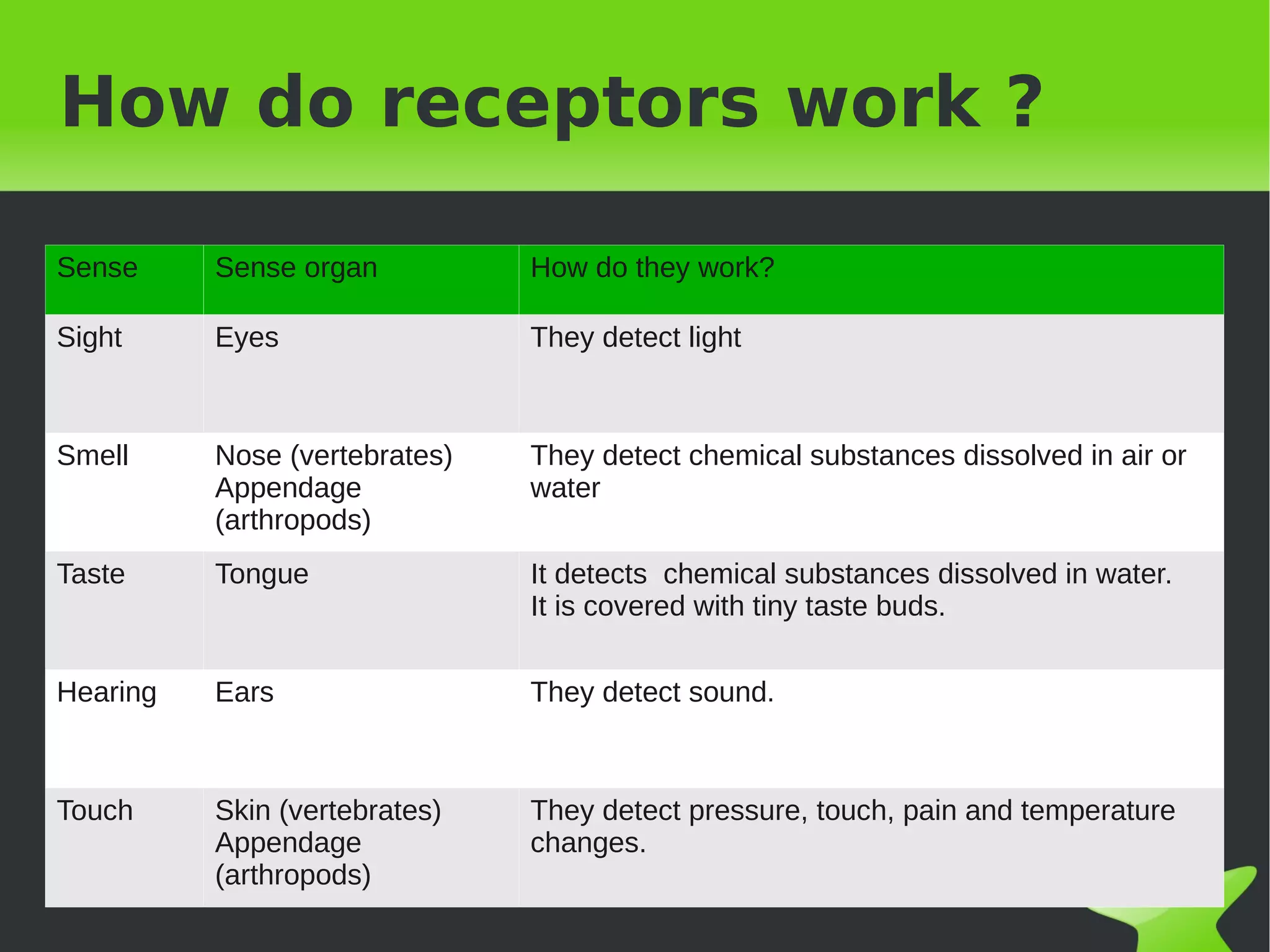
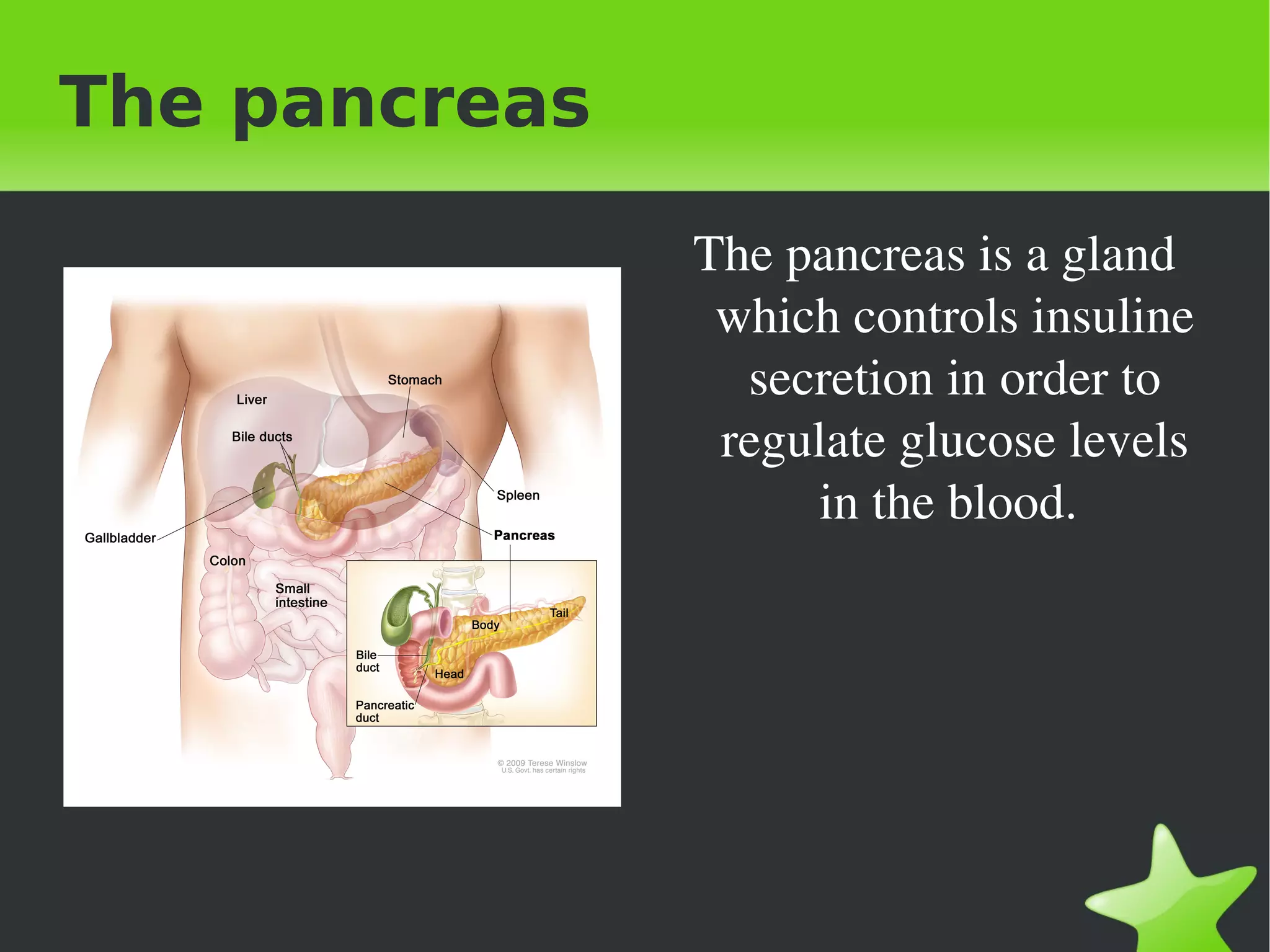
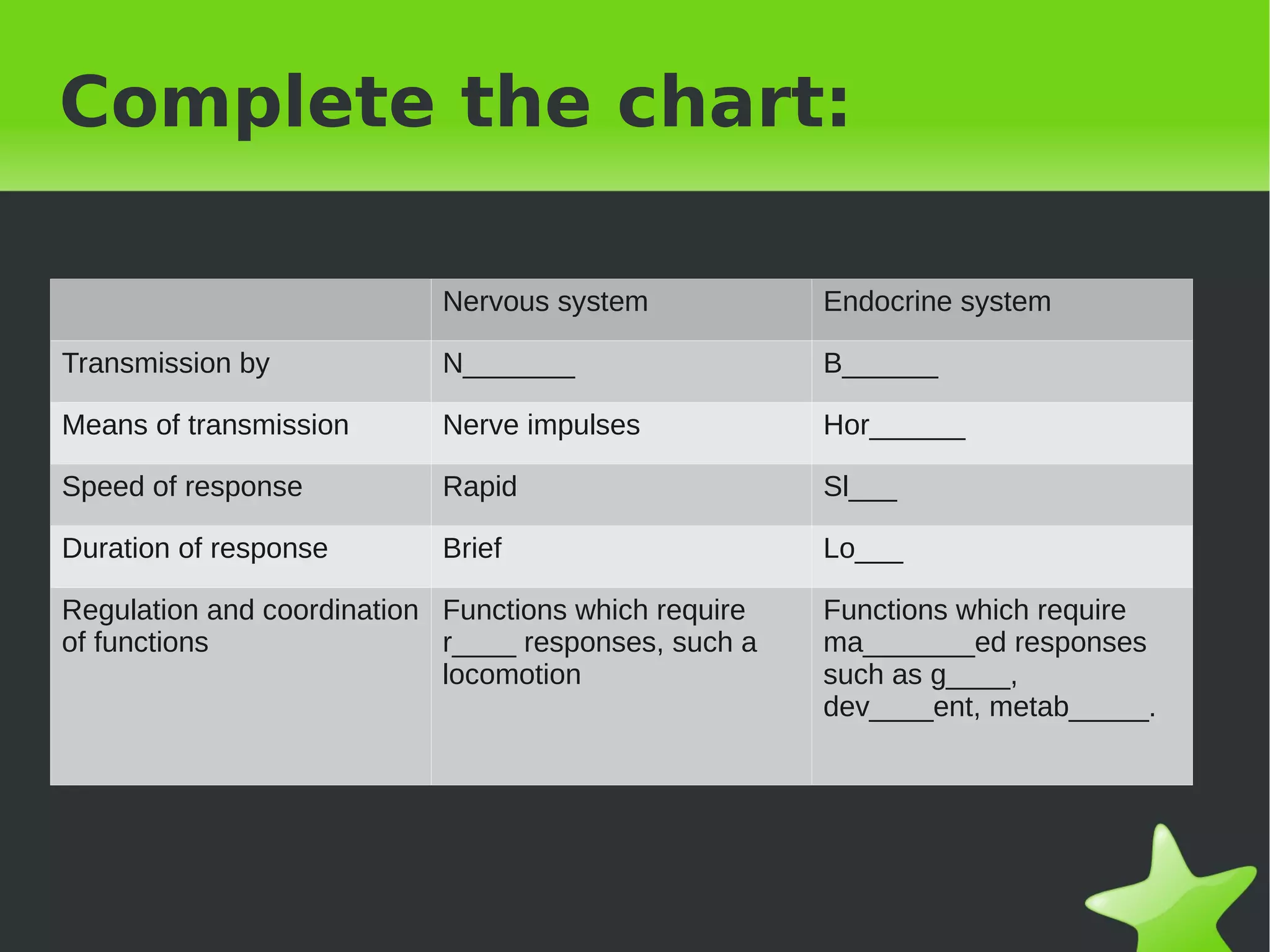
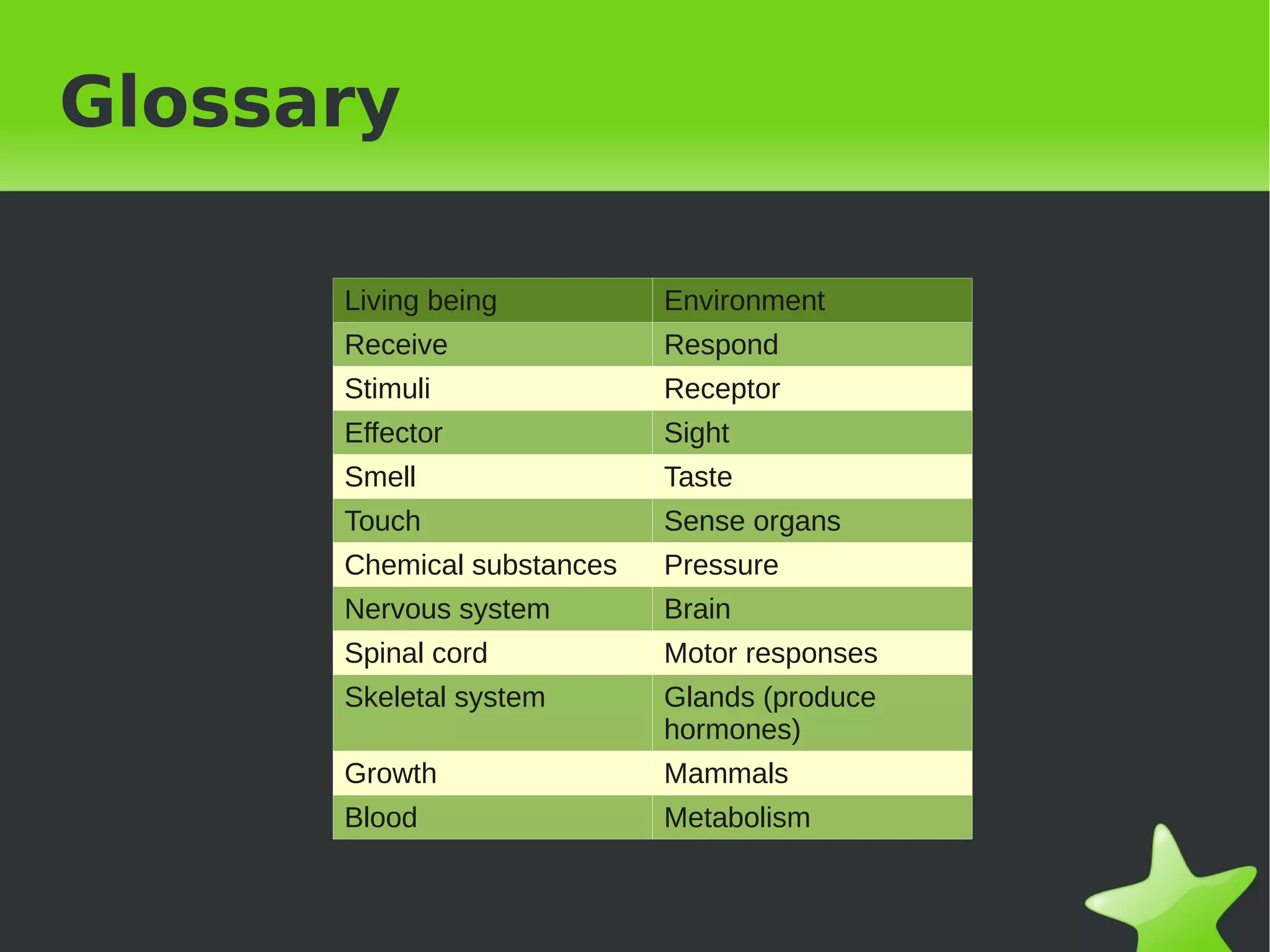
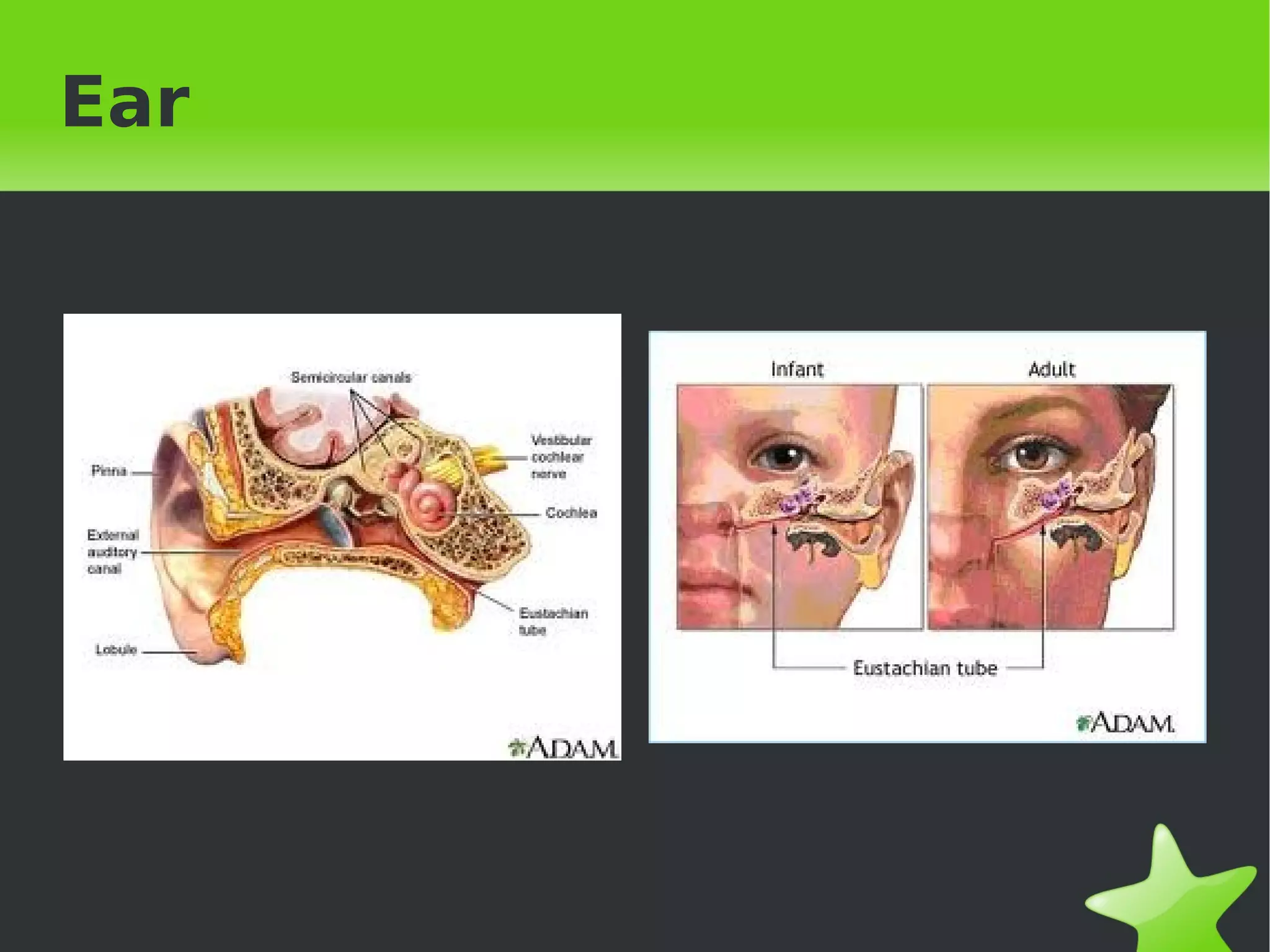
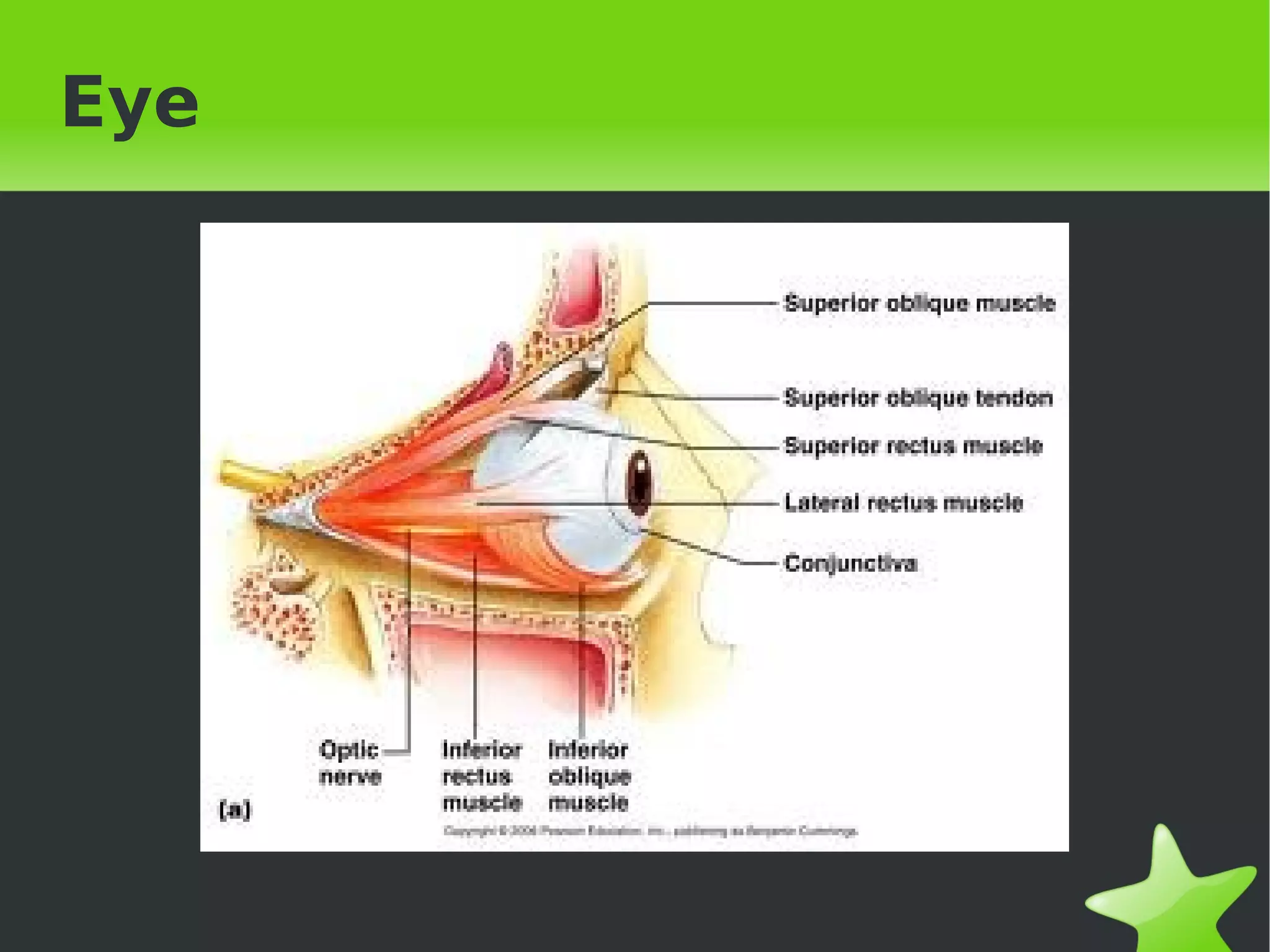
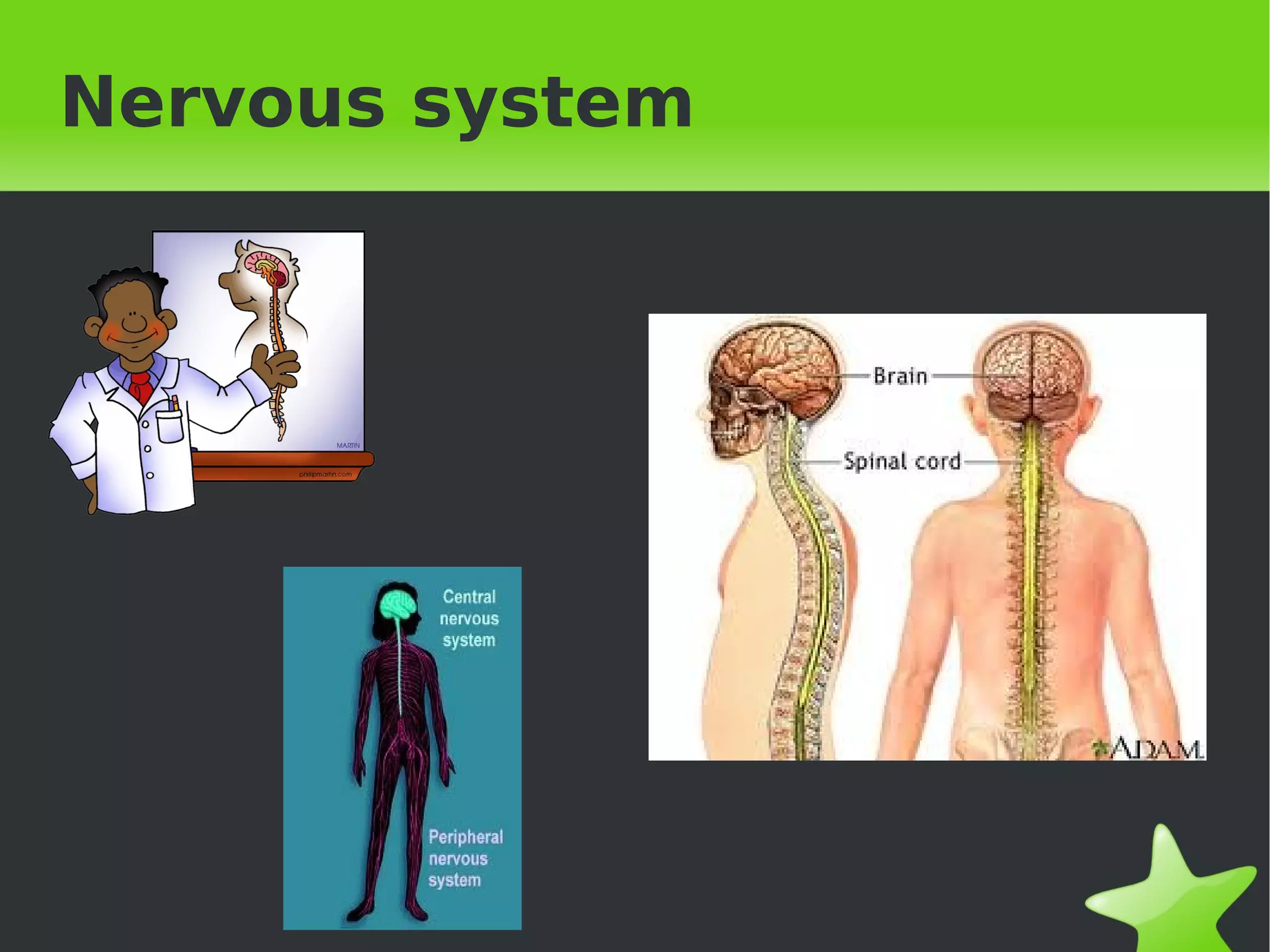
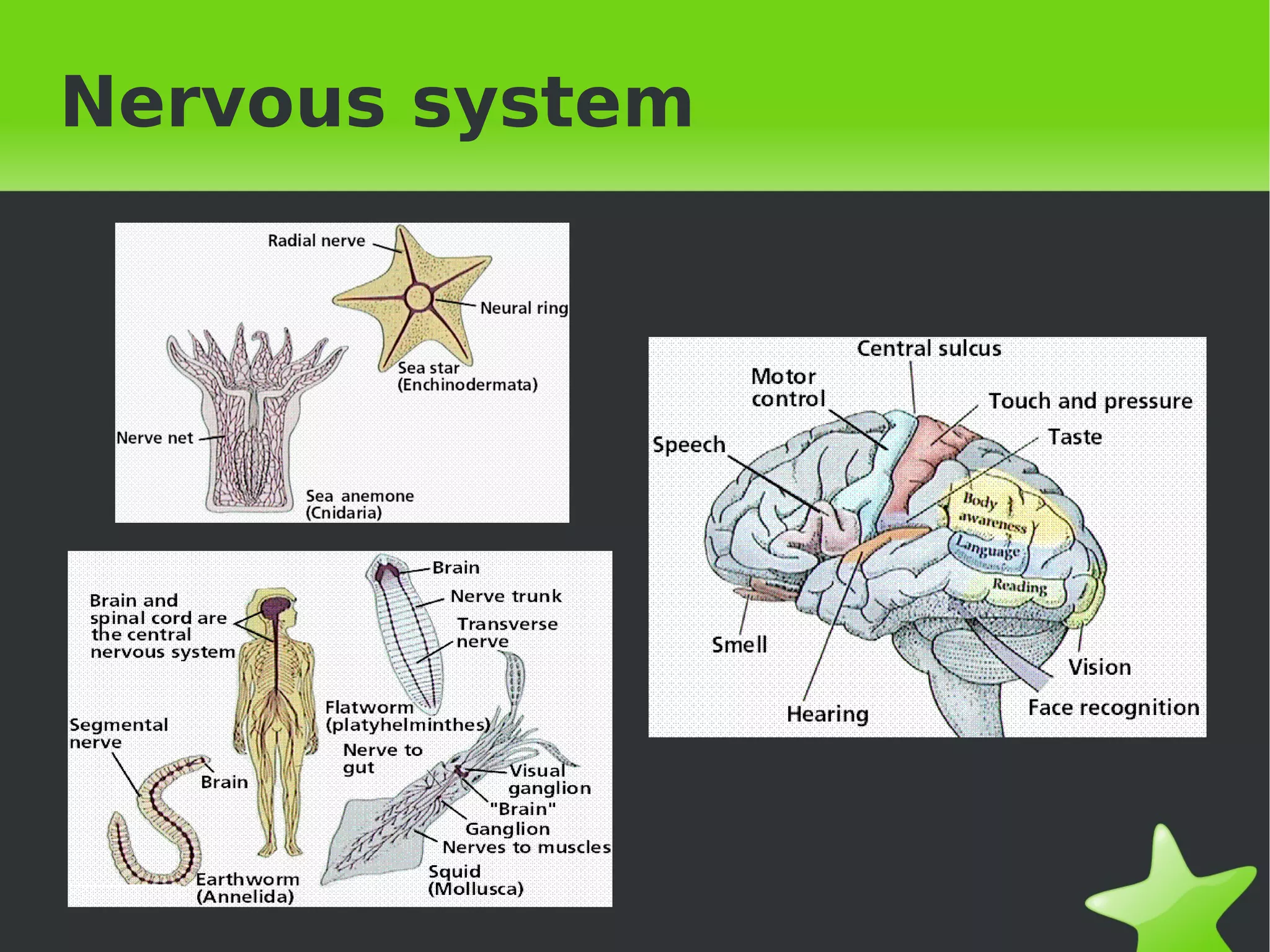
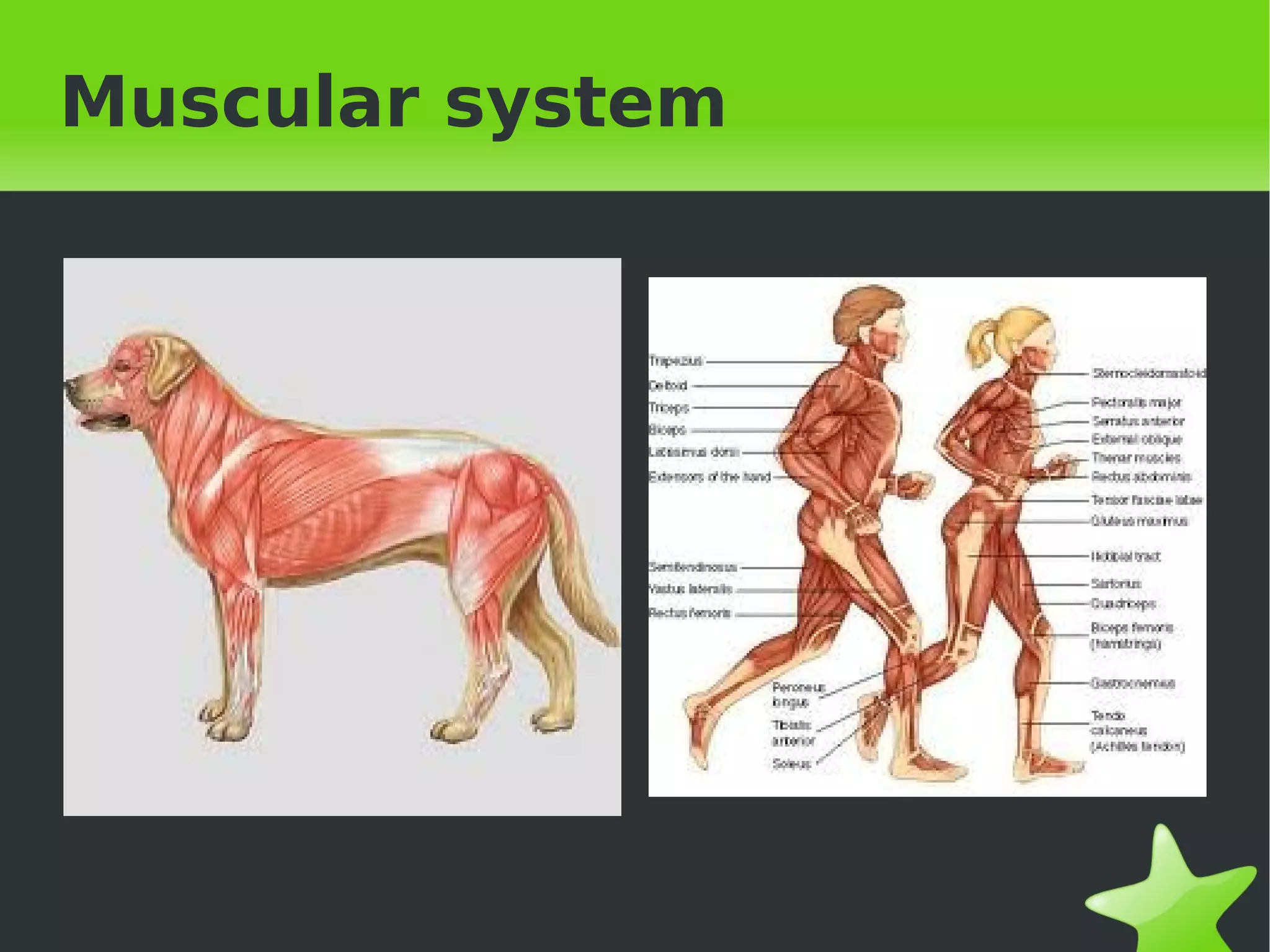
Interaction and coordination in living beings involves stimuli, receptors, coordination systems, and responsive organs. Stimuli are detected changes that provoke responses. Receptors receive stimuli and sense organs like eyes, nose, tongue, and ears function as receptors. Coordination involves the nervous system which receives information and transmits responses, and the endocrine system which regulates functions through hormone release. Responses can be motor movements through muscles and skeletal system or endocrine responses through hormone release from glands.