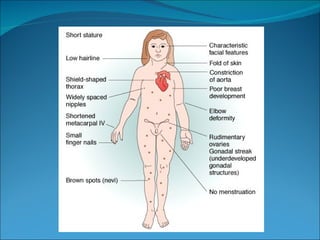
Turner syndrome is a genetic condition that affects development in girls caused by a missing or partial X chromosome. It was first described in 1938 by Dr. Henry Turner. Common characteristics include short stature, ovarian dysfunction leading to infertility, and heart defects. Diagnosis involves chromosome analysis from amniocentesis or blood tests. Treatment may include growth hormone, estrogen therapy, and assisted reproduction. Research continues on treatments and managing associated health problems throughout life.