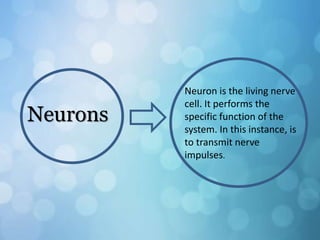
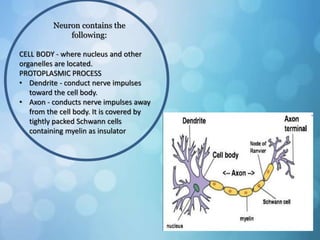
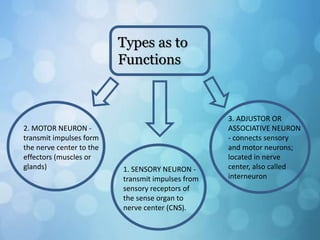
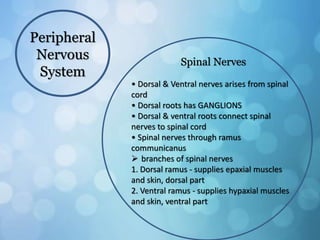
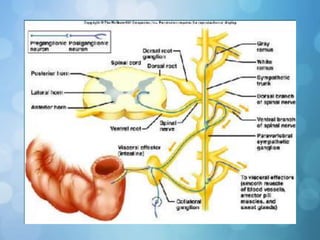
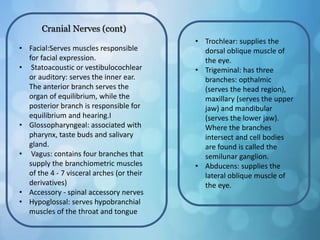
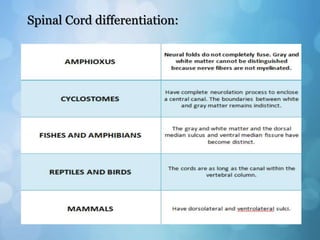
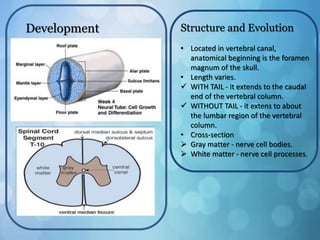
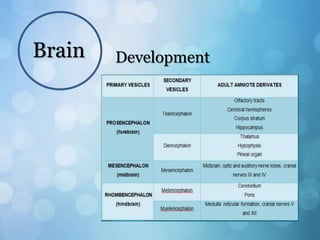
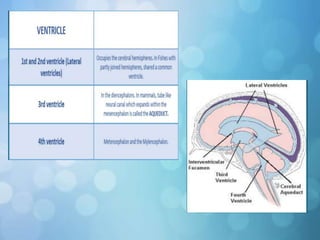
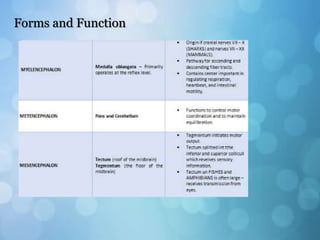
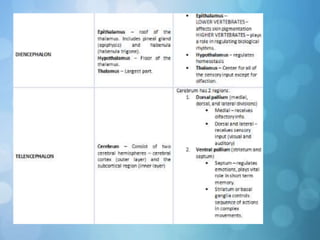
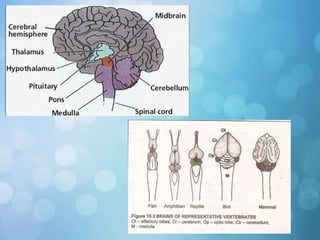
The nervous system is divided into the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS includes the brain and spinal cord, while the PNS includes nerves that connect the CNS to sensory receptors and effectors throughout the body. Neurons are the basic functional units that transmit nerve impulses and include dendrites, a cell body, and an axon. Neuroglia provide support to neurons. The PNS includes spinal and cranial nerves, with different types serving sensory, motor, or integrative functions.