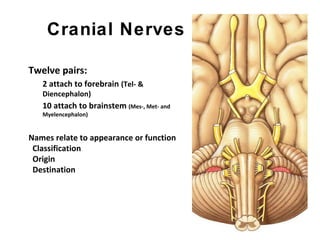
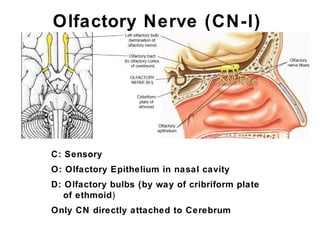
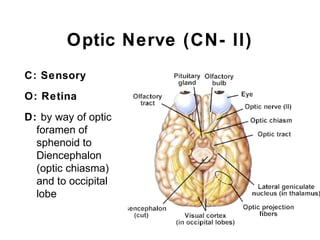
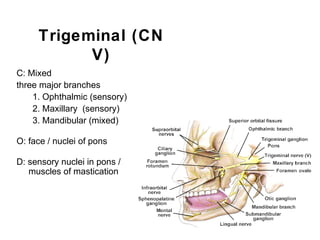
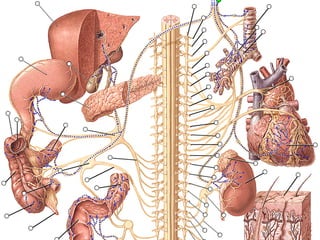
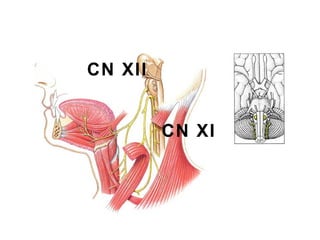
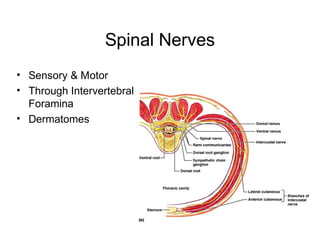
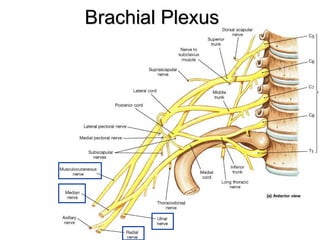
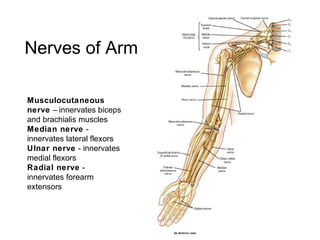
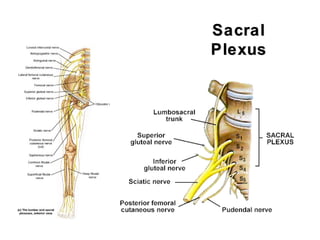
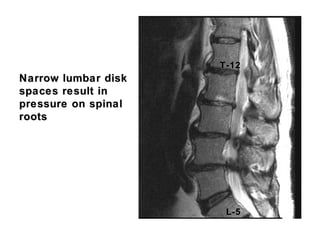
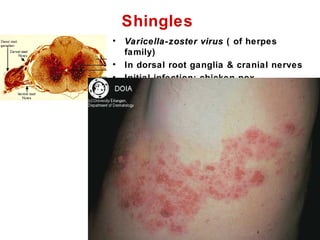
This document summarizes the cranial and spinal nerves. It describes the 12 pairs of cranial nerves including their classification, origin, and destination. It also discusses the four principal plexuses where spinal nerves merge - the cervical, brachial, lumbar, and sacral plexuses. Finally, it outlines the major nerves of the extremities including the nerves of the arm and leg.