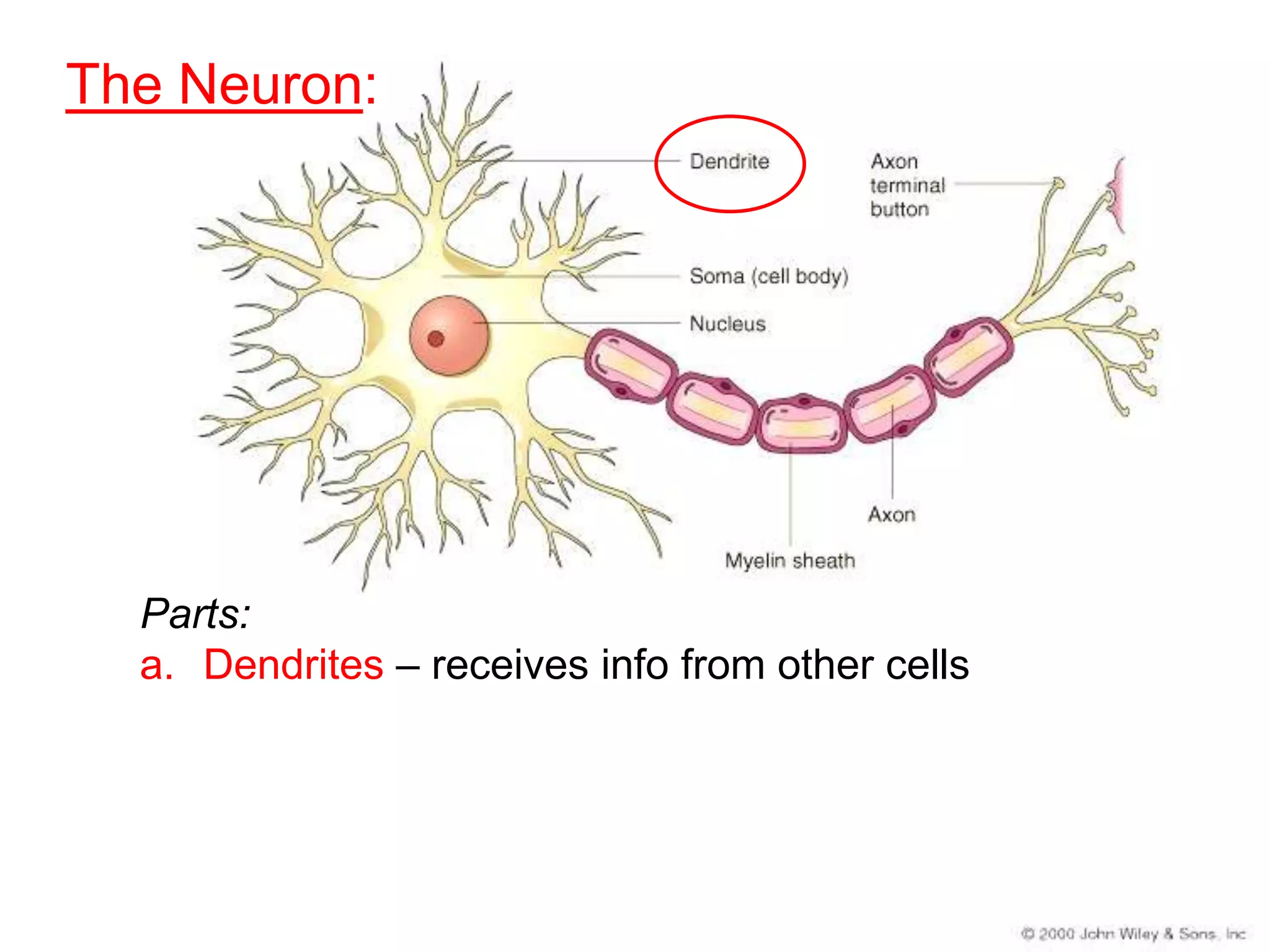
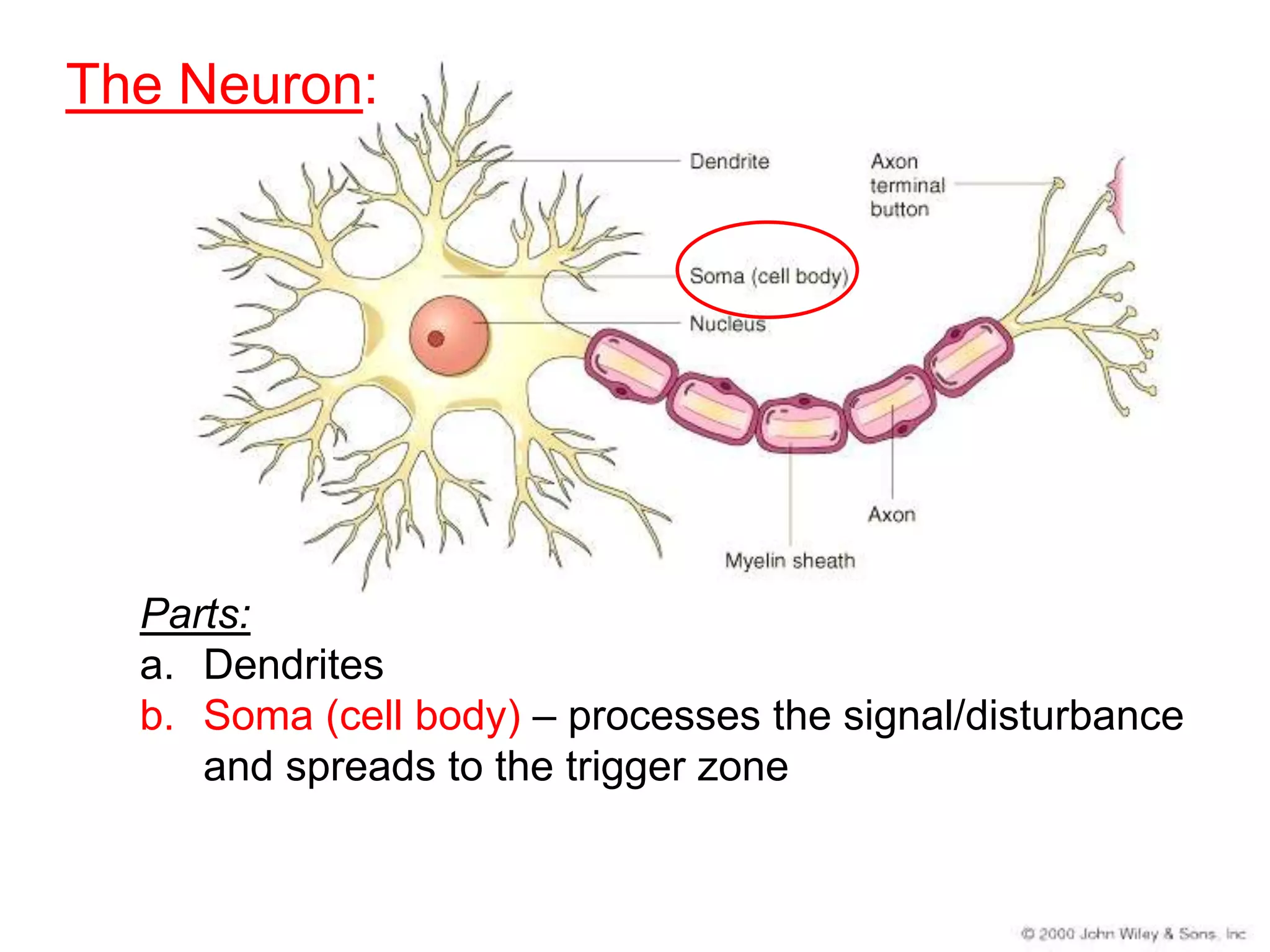
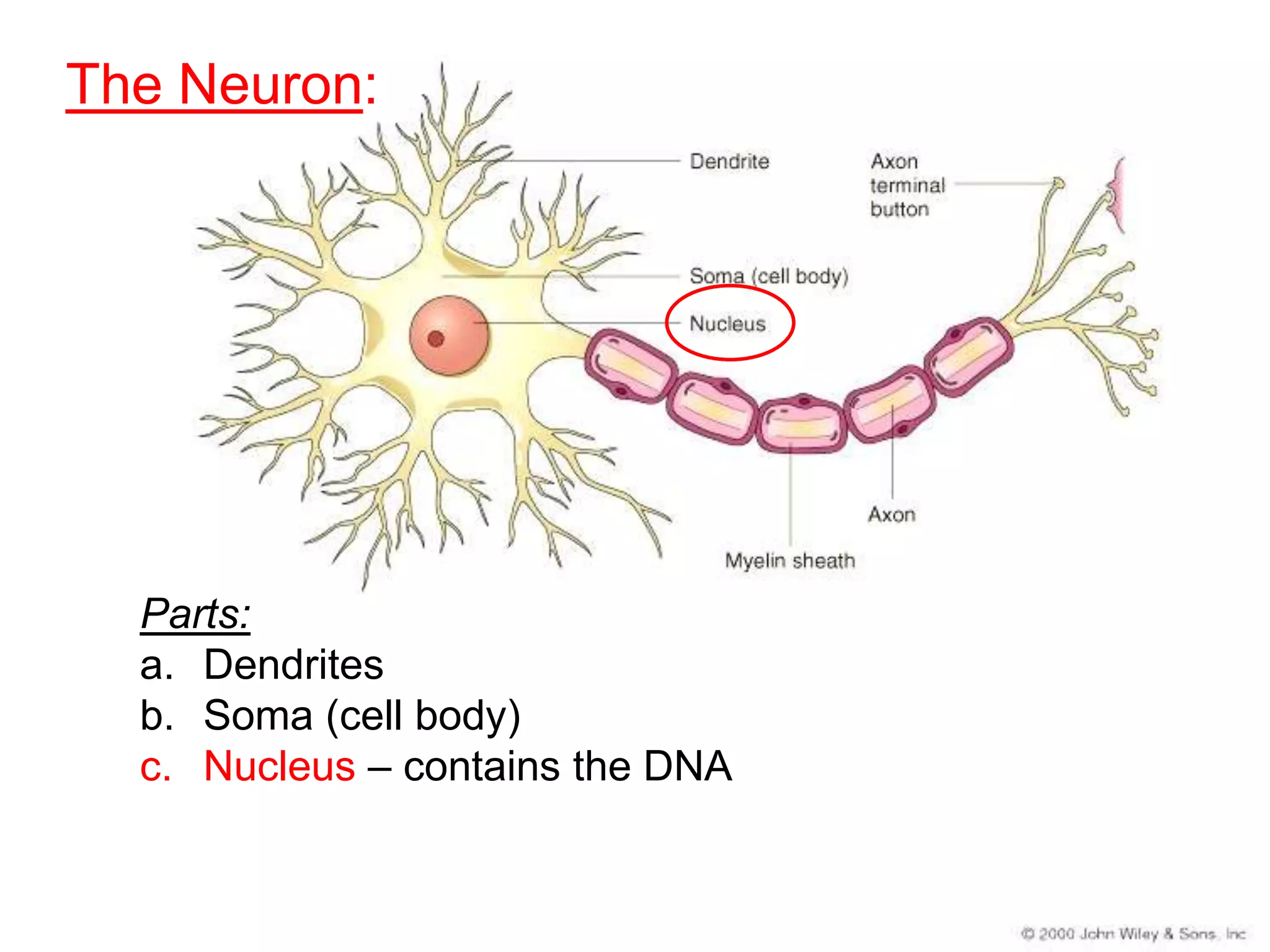
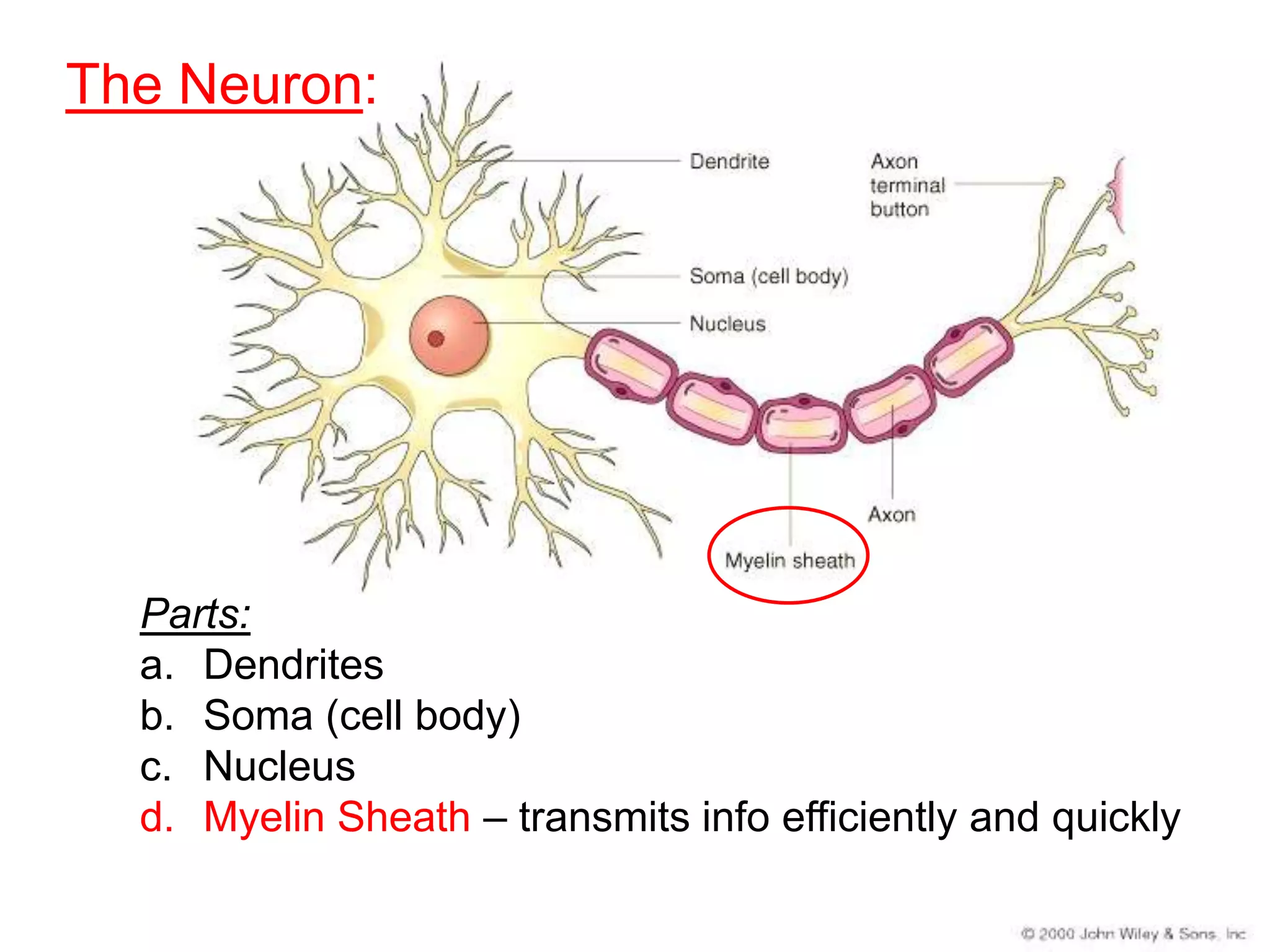
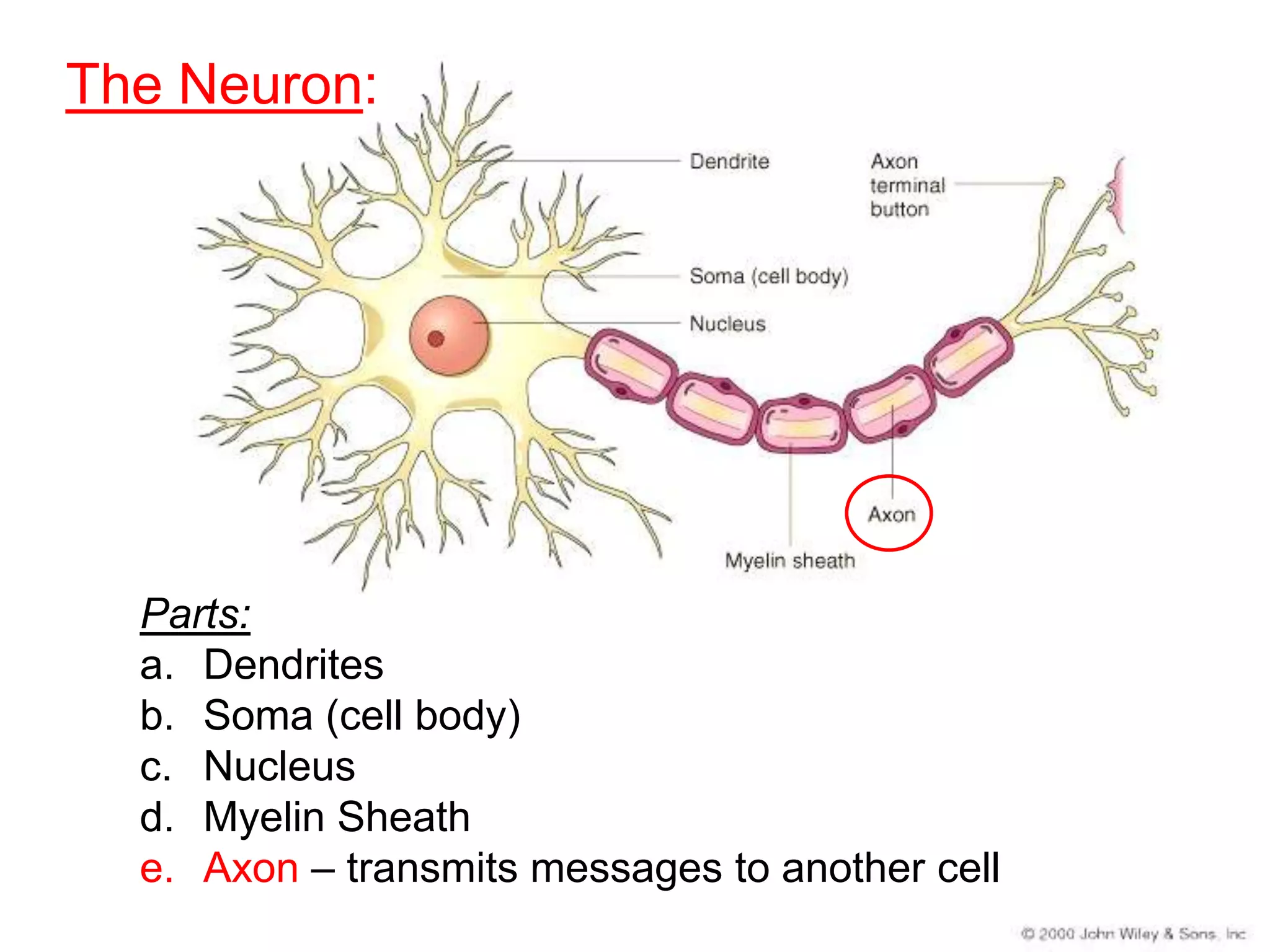
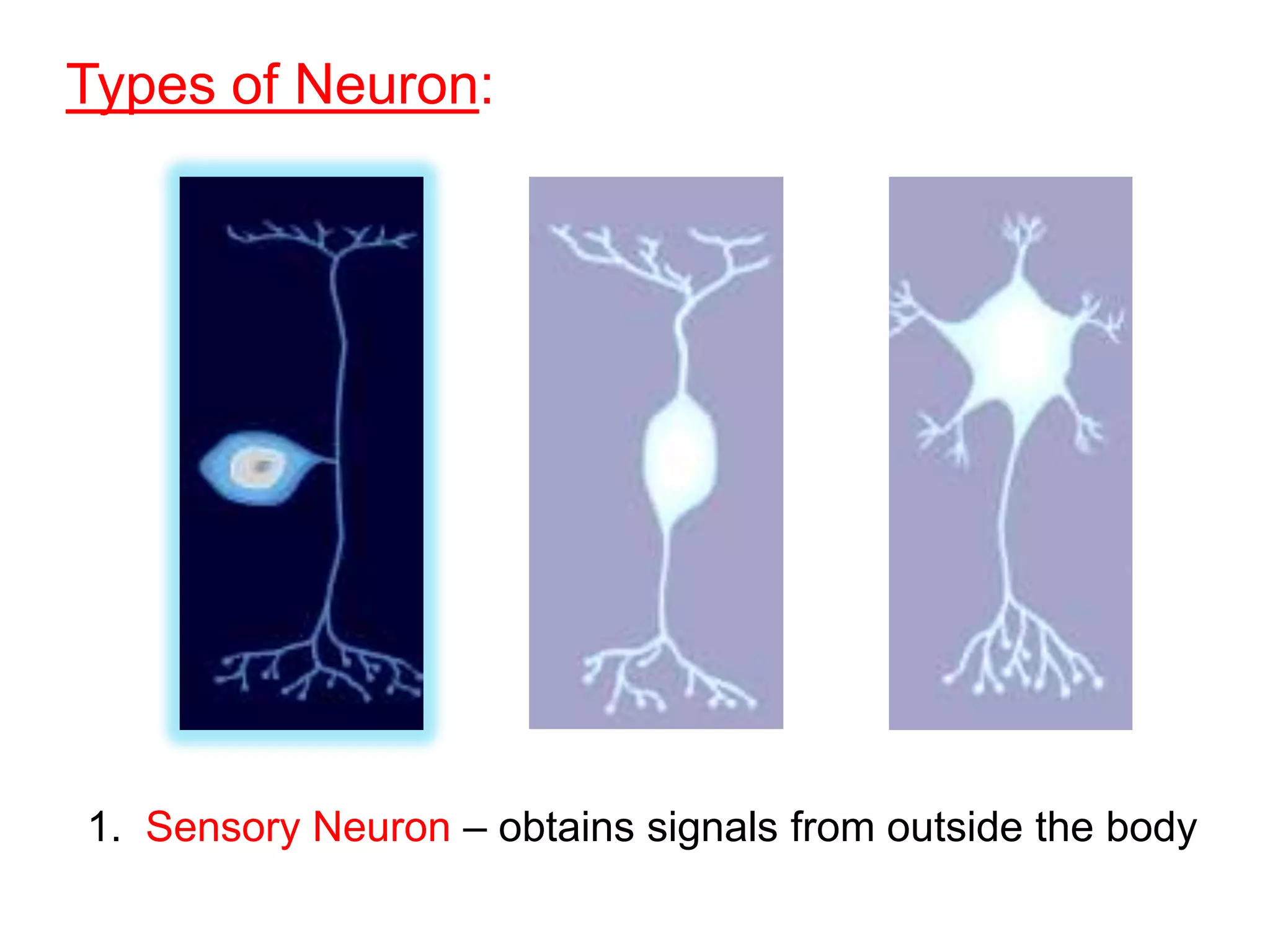
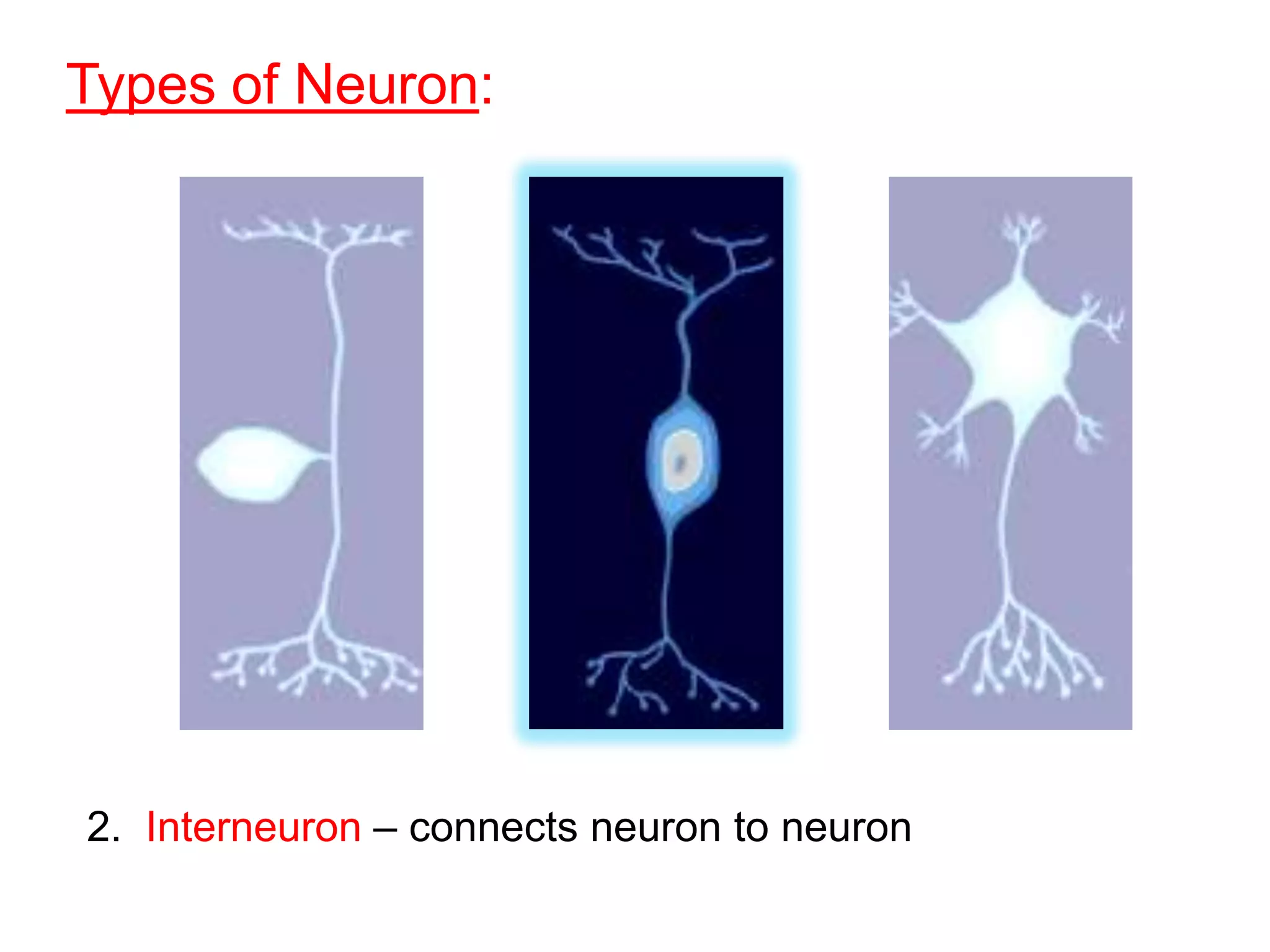
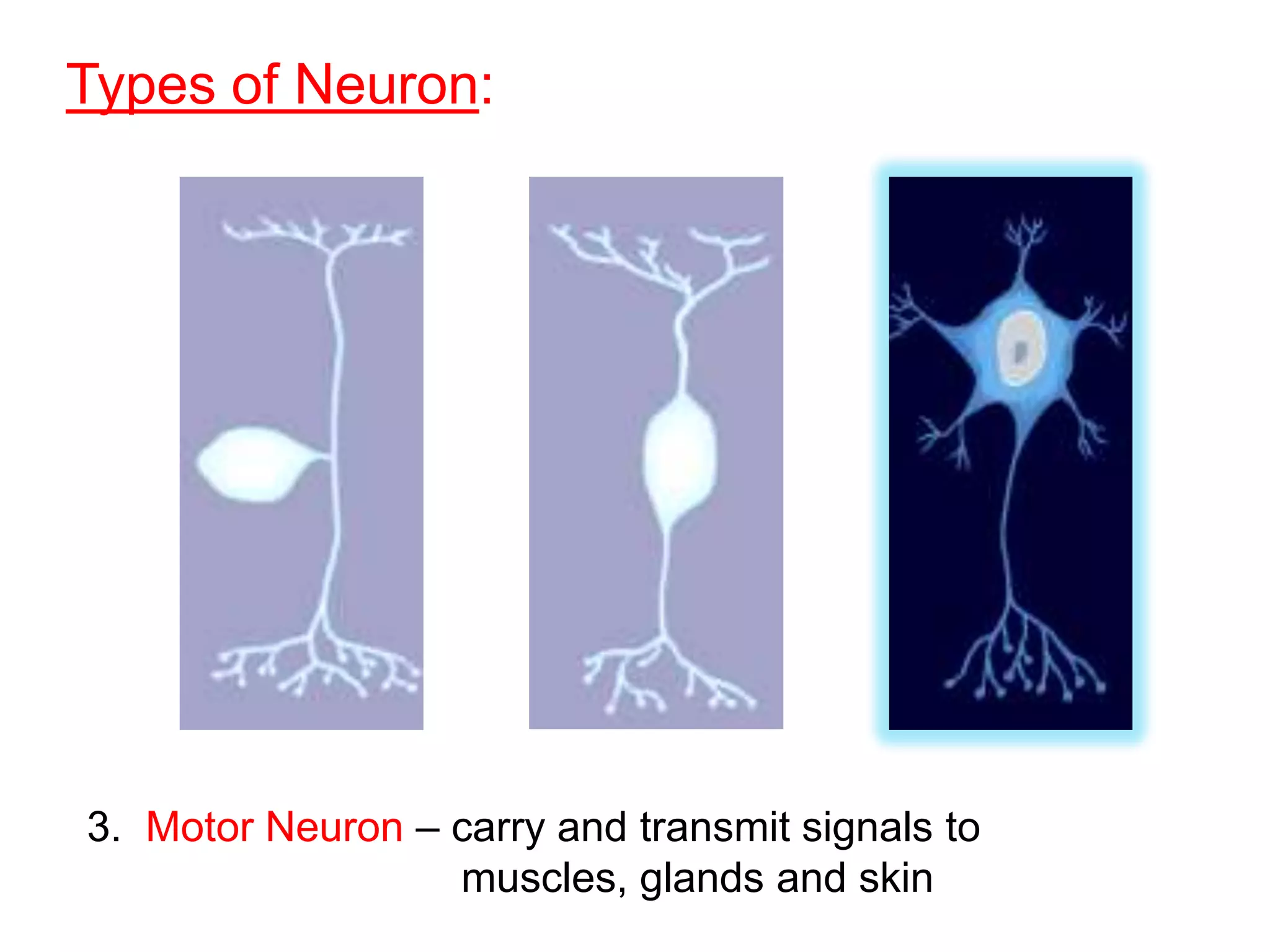
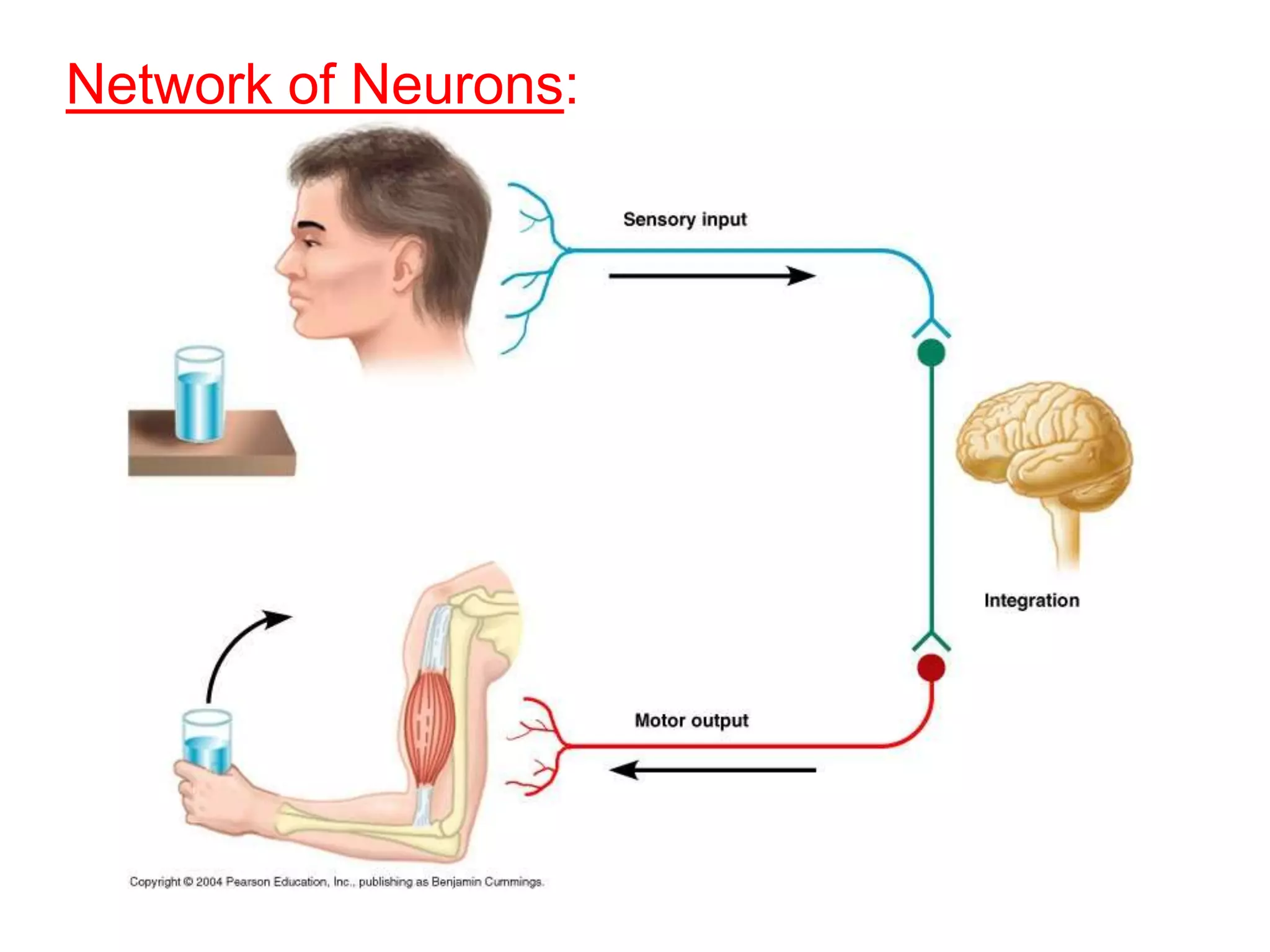
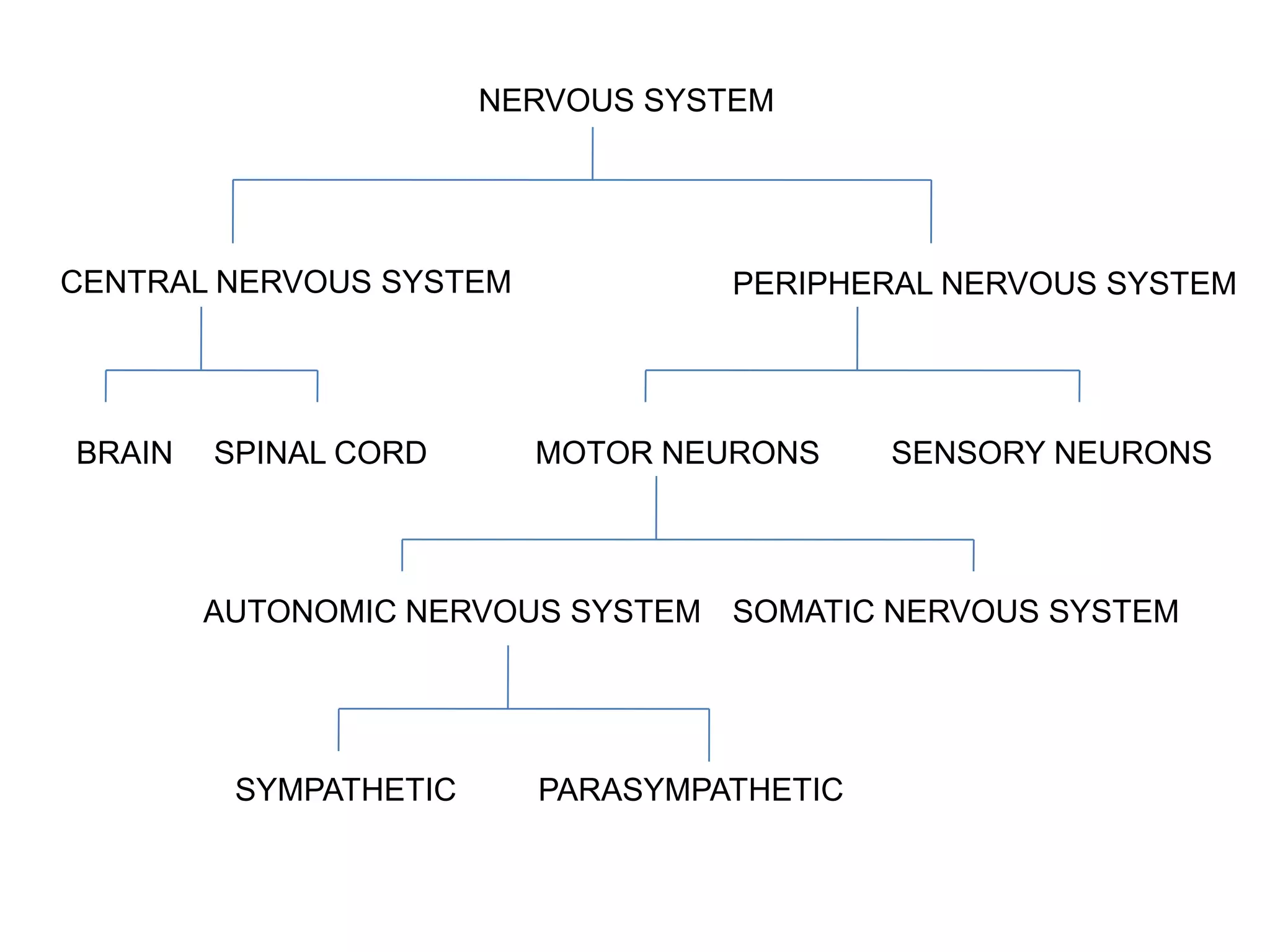
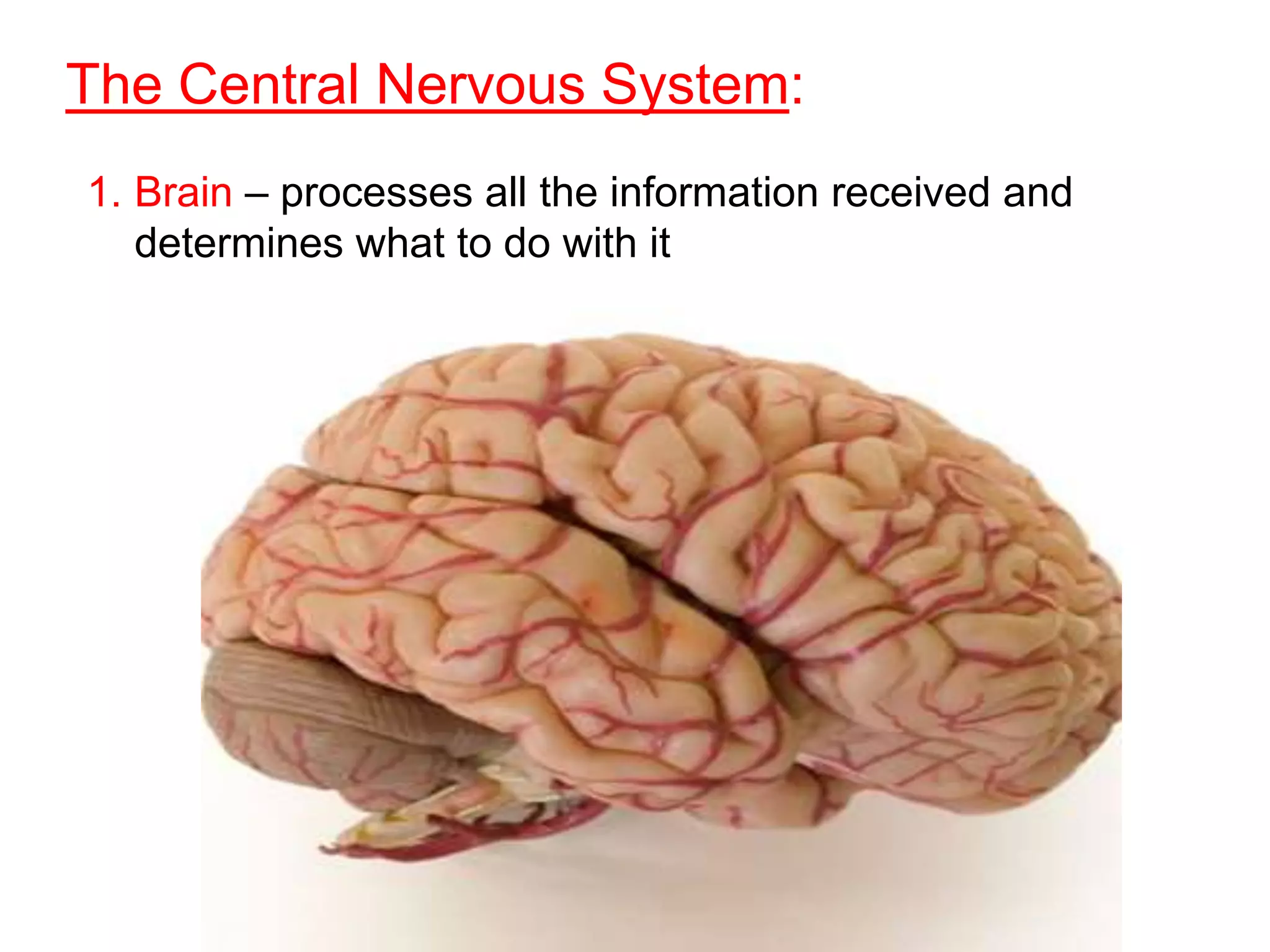
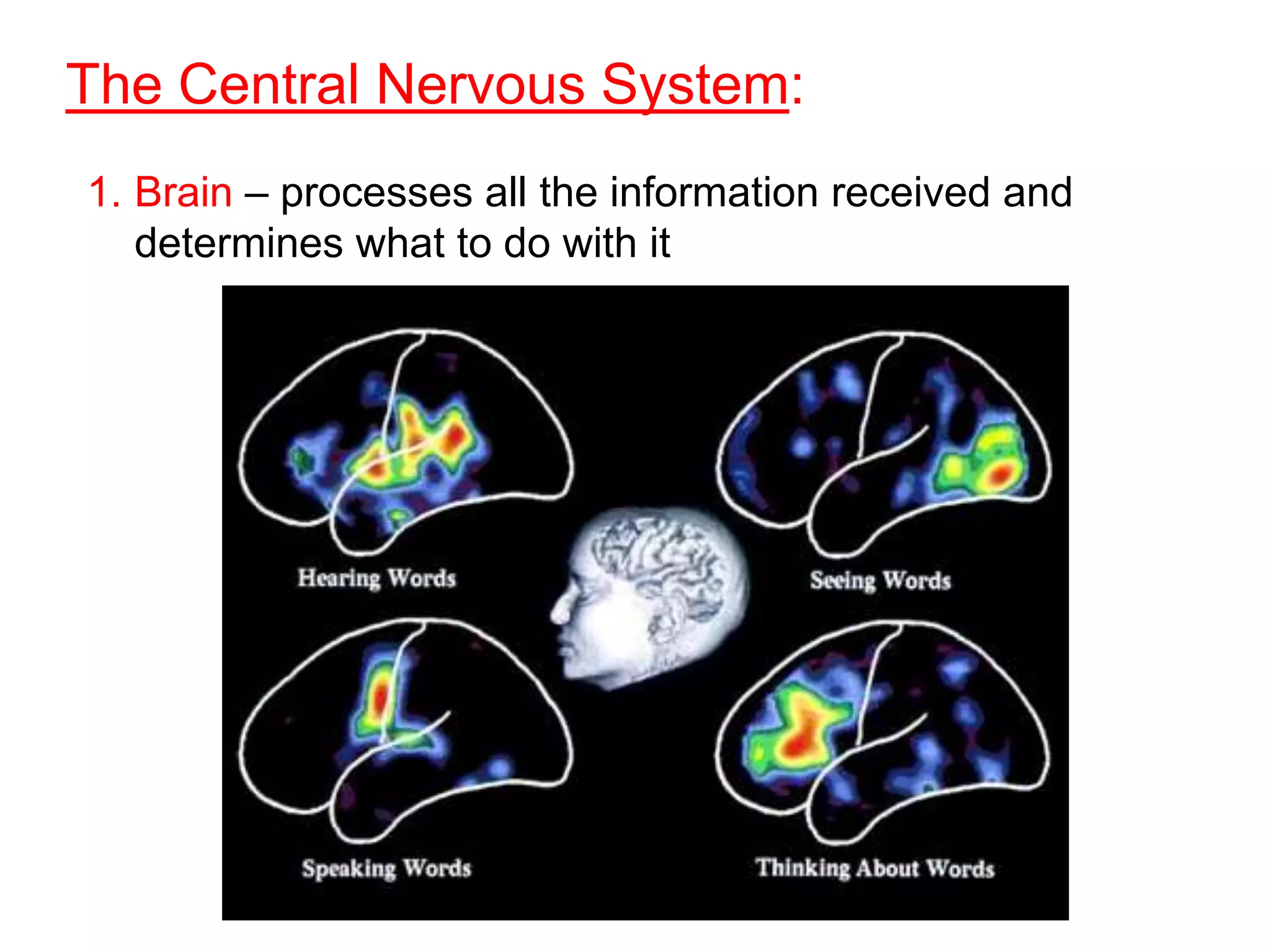
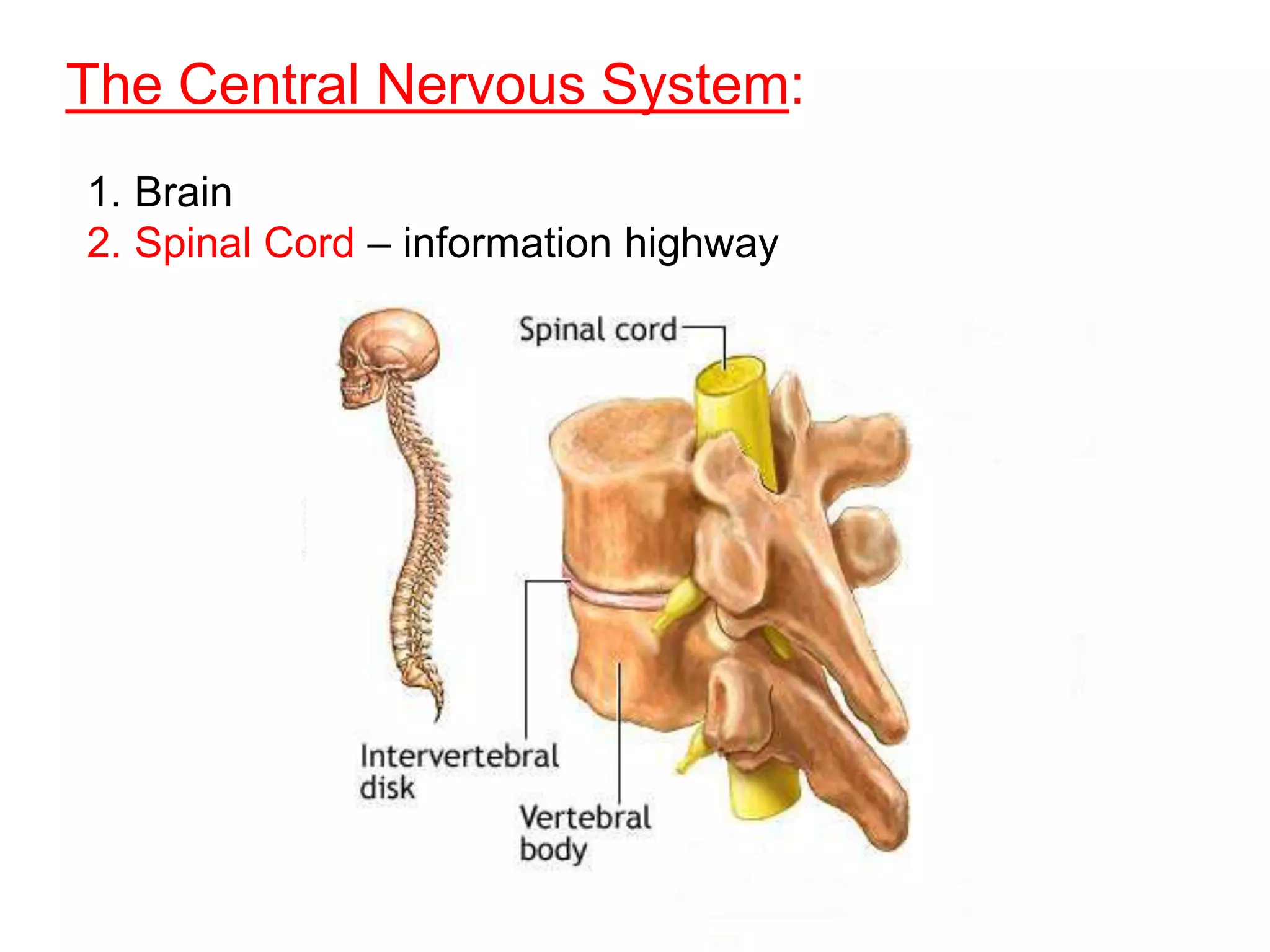
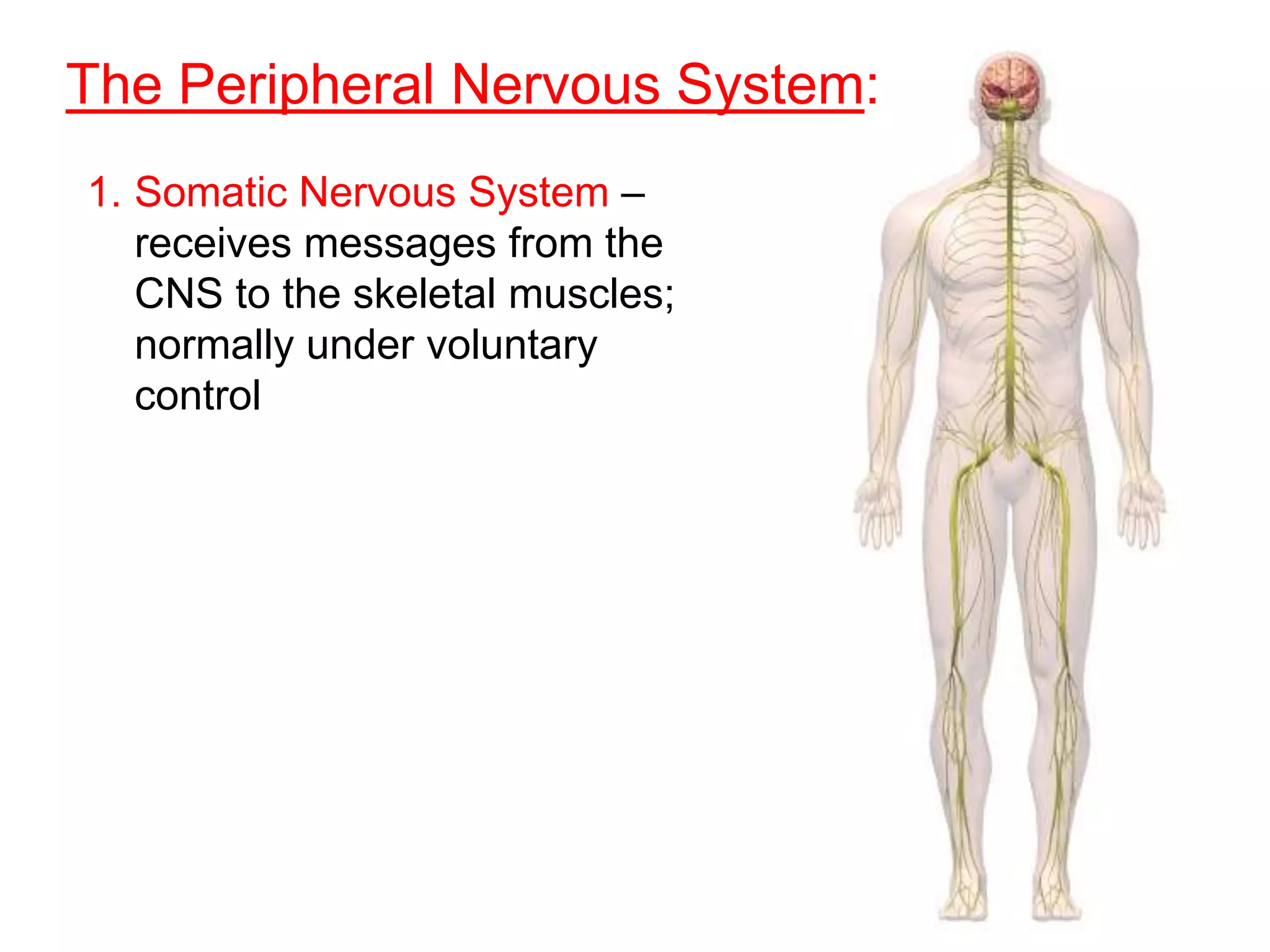
The document describes the structure and function of neurons and the nervous system. It discusses the main parts of a neuron including dendrites, soma, nucleus, myelin sheath and axon. It also describes the three main types of neurons and explains how networks of neurons communicate via the central and peripheral nervous systems. The central nervous system comprises the brain and spinal cord, while the peripheral nervous system includes the somatic and autonomic nervous systems. The document concludes by outlining how different drugs can disrupt signaling in the nervous system.