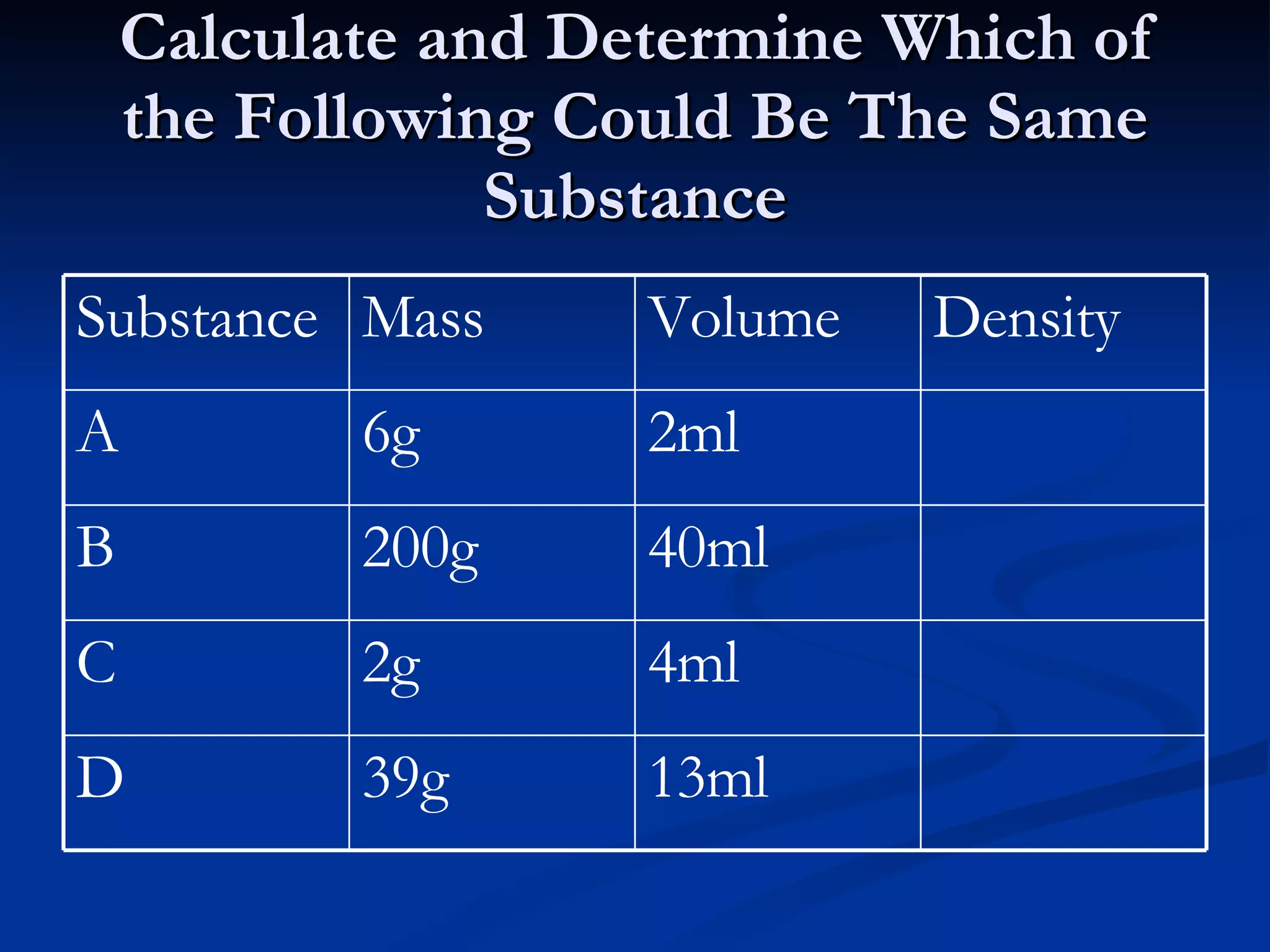
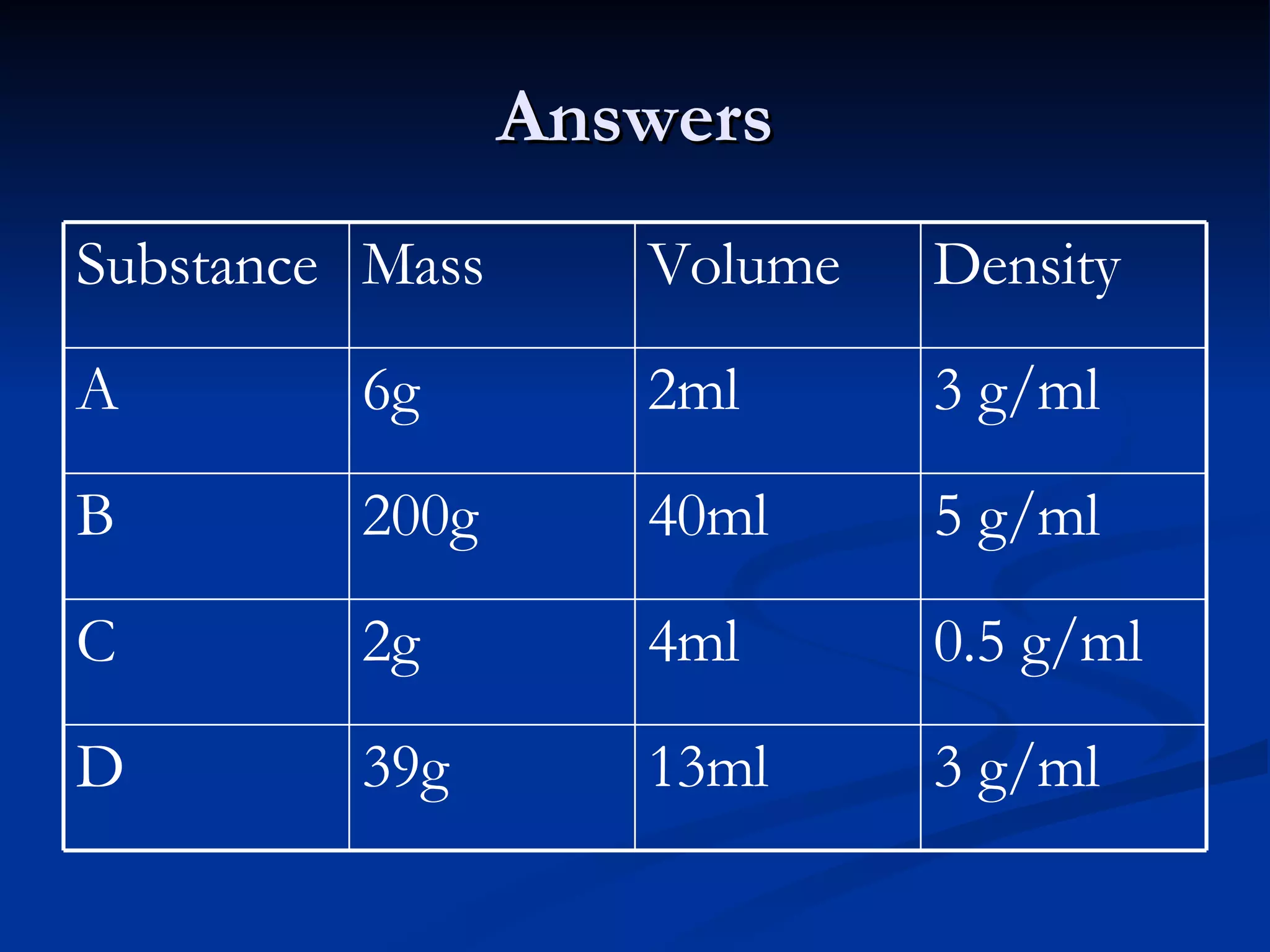
The document discusses how people use water for agriculture, industry, transportation, recreation, and in homes. It provides statistics on the types and amounts of fresh and salt water on Earth. It describes the structure of water molecules and states of water. It discusses concepts such as density, surface tension, capillary action, and water's properties as a solvent.