This document summarizes key information about leprosy (Hansen's disease):
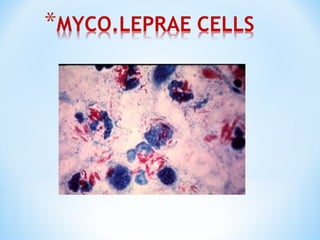
- Leprosy is caused by Mycobacterium leprosy, an acid-fast bacillus first identified in 1873. It primarily affects the skin, nerves, and mucous membranes.
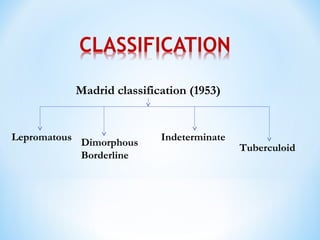
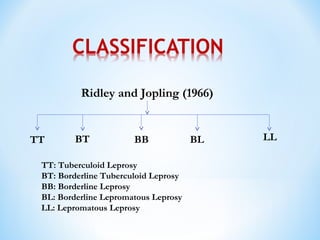
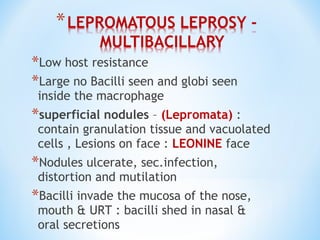
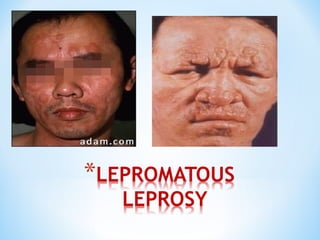
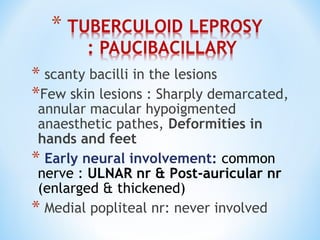
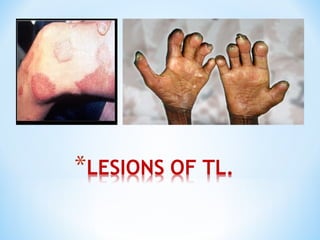
- Clinical presentation ranges from tuberculoid leprosy with few lesions and intact immunity, to lepromatous leprosy with widespread lesions and impaired immunity. The Ridley-Jopling classification further categorizes types of leprosy.
- Diagnosis involves examination of skin and nerve lesions along with bacterial index testing. The Mitsuda reaction skin test assesses host immunity and prognosis.
-