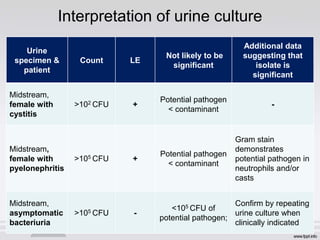
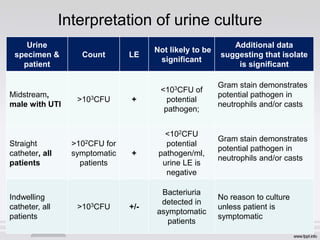
This document discusses significant bacteriuria and how it is defined as ≥105 CFU/ml of bacteria in a urine specimen, or ≥100 CFU/ml for catheterized specimens. It outlines methods for urine examination including microscopy, culture, and chemical tests. Microscopy looks for white blood cells and casts. Culture methods include loop, pour plate, and dip-slide techniques to quantify bacteria. Chemical tests detect nitrites and leukocyte esterase. The interpretation of urine cultures depends on factors like specimen type and patient symptoms. Asymptomatic bacteriuria requires treatment in pregnant women to prevent pyelonephritis.