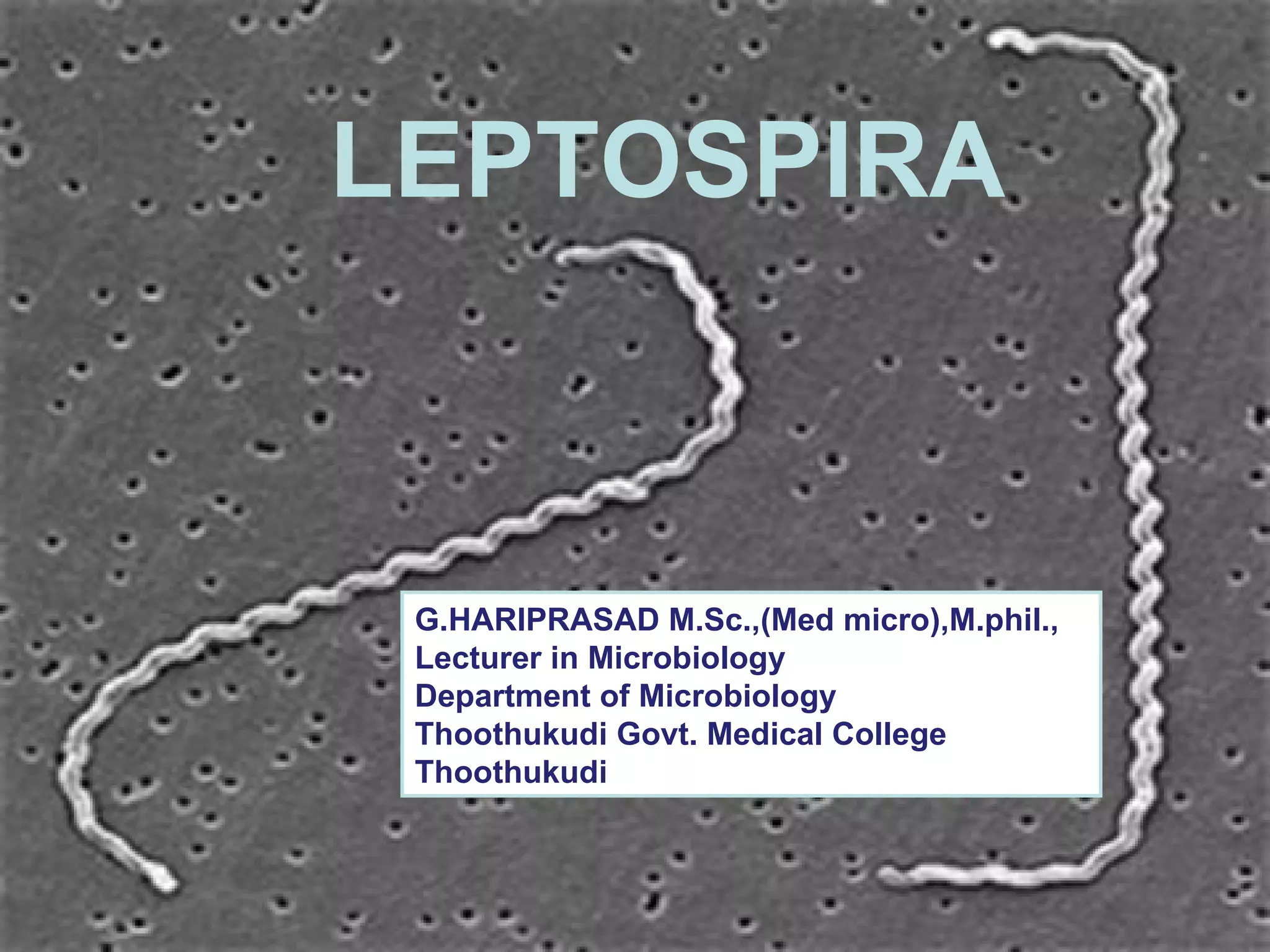
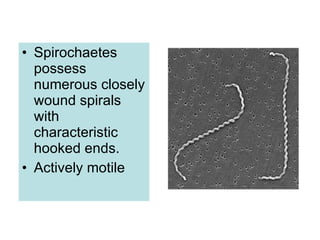
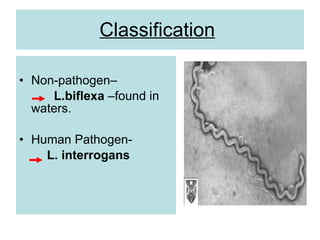
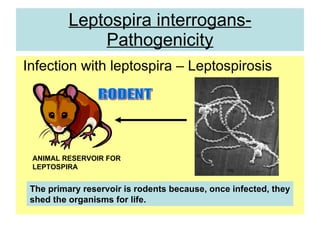
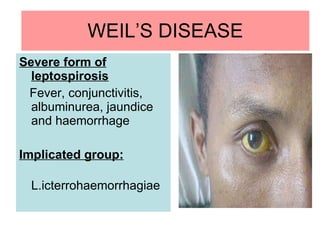
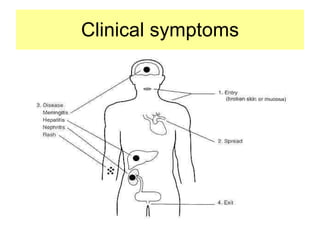
Leptospira is a spirochete bacteria that can cause leptospirosis in humans. There are pathogenic and non-pathogenic strains, with L. interrogans being the primary human pathogen containing 26 serogroups. Infection typically occurs through contact with water contaminated by the urine of infected rodents. Symptoms include fever, jaundice, and hemorrhaging. Laboratory diagnosis involves dark-field microscopy, culture, serological tests, and animal inoculation to identify the infecting serotype. Treatment involves antibiotics like penicillin and tetracycline.